Abstract
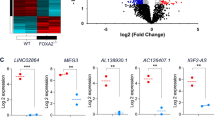
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune disease in which pancreatic beta cells are killed by the infiltrating immune cells as well as the cytokines released by these cells. Many studies indicate that inflammatory mediators have an essential role in this disease. In the present study, we profiled the transcriptome in human islets of langerhans under control conditions or following exposure to the pro-inflammatory cytokines based on the RNA sequencing dataset downloaded from SRA database. After filtered the low-quality ones, the RNA readers was aligned to human genome hg19 by TopHat and then assembled by Cufflinks. The expression value of each transcript was calculated and consequently differentially expressed genes were screened out. Finally, a total of 63 differentially expressed genes were identified including 60 up-regulated and three down-regulated genes. GBP5 and CXCL9 stood out as the top two most up-regulated genes in cytokines treated samples with the log2 fold change of 12.208 and 10.901, respectively. Meanwhile, PTF1A and REG3G were identified as the top two most down-regulated genes with the log2 fold change of −3.759 and −3.606, respectively. Of note, we also found 262 lncRNAs (long non-coding RNA), 177 of which were inferred as novel lncRNAs. Further in-depth follow-up analysis of the transcriptional regulation reported in this study may shed light on the specific function of these lncRNA.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cloonan N, Forrest AR, Kolle G, Gardiner BB, Faulkner GJ, Brown MK, Taylor DF, Steptoe AL, Wani S, Bethel G (2008) Stem cell transcriptome profiling via massive-scale mRNA sequencing. Nat Methods 5:613–619
Mortazavi A, Williams BA, Mccue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B (2008) Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods 5:621–628
Wang Z, Gerstein M, Snyder M (2009) RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet 10:57–63
Grabherr MG, Haas BJ, Yassour M, Levin JZ, Thompson DA, Amit I, Adiconis X, Fan L, Raychowdhury R, Zeng Q (2011) Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat Biotechnol 29:644–652
Guttman M, Garber M, Levin JZ, Donaghey J, Robinson J, Adiconis X, Fan L, Koziol MJ, Gnirke A, Nusbaum C (2010) Ab initio reconstruction of cell type-specific transcriptomes in mouse reveals the conserved multi-exonic structure of lincRNAs. Nat Biotechnol 28:503–510
Cabili MN, Trapnell C, Goff L, Koziol M, Tazon-Vega B, Regev A, Rinn JL (2011) Integrative annotation of human large intergenic noncoding RNAs reveals global properties and specific subclasses. Genes Dev 25:1915–1927
Mitchell Guttman IA, Garber M, French C, Lin MF, Feldser D, Huarte M, Zuk O, Carey BW, Cassady JP, Cabili MN (2009) Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature 458:223–227
Pauli A, Valen E, Lin MF, Garber M, Vastenhouw NL, Levin JZ, Fan L, Sandelin A, Rinn JL, Regev A (2012) Systematic identification of long noncoding RNAs expressed during zebrafish embryogenesis. Genome Res 22:577–591
Kukreja A, Cost G, Marker J, Zhang C, Sun Z, Lin-Su K, Ten S, Sanz M, Exley M, Wilson B (2002) Multiple immuno-regulatory defects in type-1 diabetes. J Clin Investig 109:131–140
Todd JA (2010) Etiology of type 1 diabetes. Immunity 32:457–467
Durinovic-Bello I, Schlosser M, Riedl M, Maisel N, Rosinger S, Kalbacher H, Deeg M, Ziegler M, Elliott J, Roep B (2004) Pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokine production by autoimmune T cells against preproinsulin in HLA-DRB1* 04, DQ8 Type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 47:439–450
Dandona P, Aljada A, Bandyopadhyay A (2004) Inflammation: the link between insulin resistance, obesity and diabetes. Trends Immunol 25:4–7
Epstein FH, Ross R (1999) Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 340:115–126
Hultcrantz M, Hühn MH, Wolf M, Olsson A, Jacobson S, Williams BR, Korsgren O, Flodström-Tullberg M (2007) Interferons induce an antiviral state in human pancreatic islet cells. Virology 367:92–101
Ylipaasto P, Kutlu B, Rasilainen S, Rasschaert J, Salmela K, Teerijoki H, Korsgren O, Lahesmaa R, Hovi T, Eizirik DL (2005) Global profiling of coxsackievirus-and cytokine-induced gene expression in human pancreatic islets. Diabetologia 48:1510–1522
Rasschaert J, Ladrière L, Urbain M, Dogusan Z, Katabua B, Sato S, Akira S, Gysemans C, Mathieu C, Eizirik DL (2005) Toll-like receptor 3 and STAT-1 contribute to double-stranded RNA+ interferon-γ-induced apoptosis in primary pancreatic β-cells. J Biol Chem 280:33984–33991
Liu D, Darville M, Eizirik DL (2001) Double-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) induces β-cell Fas messenger RNA expression and increases cytokine-induced β-cell apoptosis. Endocrinology 142:2593–2599
Foulis A, Farquharson M, Meager A (1987) Immunoreactive α-interferon in insulin-secreting β cells in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Lancet 330:1423–1427
Shimada A, Morimoto J, Kodama K, Suzuki R, Oikawa Y, Funae O, Kasuga A, Saruta T, Narumi S (2001) Elevated serum IP-10 levels observed in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 24:510–515
Nicoletti F, Conget I, Di Mauro M, Di Marco R, Mazzarino M, Bendtzen K, Messina A, Gomis R (2002) Serum concentrations of the interferon-γ-inducible chemokine IP-10/CXCL10 are augmented in both newly diagnosed type I diabetes mellitus patients and subjects at risk of developing the disease. Diabetologia 45:1107–1110
Hanifi-Moghaddam P, Kappler S, Seissler J, Müller-Scholze S, Martin S, Roep B, Strassburger K, Kolb H, Schloot N (2006) Altered chemokine levels in individuals at risk of Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 23:156–163
Wang X, Jia S, Geoffrey R, Alemzadeh R, Ghosh S, Hessner MJ (2008) Identification of a molecular signature in human type 1 diabetes mellitus using serum and functional genomics. J Immunol 180:1929–1937
Martin AP, Rankin S, Pitchford S, Charo IF, Furtado GC, Lira SA (2008) Increased expression of CCL2 in insulin-producing cells of transgenic mice promotes mobilization of myeloid cells from the bone marrow, marked insulitis, and diabetes. Diabetes 57:3025–3033
Christen U, Mcgavern DB, Luster AD, Von Herrath MG, Oldstone MB (2003) Among CXCR3 chemokines, IFN-γ-inducible protein of 10 kDa (CXC chemokine ligand (CXCL) 10) but not monokine induced by IFN-γ (CXCL9) imprints a pattern for the subsequent development of autoimmune disease. J Immunol 171:6838–6845
Eizirik DL, Colli ML, Ortis F (2009) The role of inflammation in insulitis and β-cell loss in type 1 diabetes. Nat Rev Endocrinol 5:219–226
Trapnell C, Pachter L, Salzberg SL (2009) TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 25:1105–1111
Trapnell C, Williams BA, Pertea G, Mortazavi A, Kwan G, Van Baren MJ, Salzberg SL, Wold BJ, Pachter L (2010) Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat Biotechnol 28:511–515
Storey JD, Tibshirani R (2003) Statistical significance for genomewide studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:9440–9445
Wang L, Park HJ, Dasari S, Wang S, Kocher J-P, Li W (2013) CPAT: Coding-Potential Assessment Tool using an alignment-free logistic regression model. Nucleic Acids Res 41:e74
Haas BJ, Zody MC (2010) Advancing RNA-seq analysis. Nat Biotechnol 28:421
Yassour M, Kaplan T, Fraser HB, Levin JZ, Pfiffner J, Adiconis X, Schroth G, Luo S, Khrebtukova I, Gnirke A (2009) Ab initio construction of a eukaryotic transcriptome by massively parallel mRNA sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:3264–3269
Trapnell C, Williams BA, Pertea G, Mortazavi A, Kwan G, Van Baren MJ, Salzberg SL, Wold BJ, Pachter L (2010) Transcript assembly and abundance estimation from RNA-Seq reveals thousands of new transcripts and switching among isoforms. Nat Biotechnol 28:511
Eizirik DL, Sammeth M, Bouckenooghe T, Bottu G, Sisino G, Igoillo-Esteve M, Ortis F, Santin I, Colli ML, Barthson J (2012) The human pancreatic islet transcriptome: expression of candidate genes for type 1 diabetes and the impact of pro-inflammatory cytokines. PLoS Genet 8:e1002552
Rose SD, Swift GH, Peyton MJ, Hammer RE, Macdonald RJ (2001) The role of PTF1-P48 in pancreatic acinar gene expression. J Biol Chem 276:44018–44026
Sellick GS, Barker KT, Stolte-Dijkstra I, Fleischmann C, Coleman RJ, Garrett C, Gloyn AL, Edghill EL, Hattersley AT, Wellauer PK (2004) Mutations in PTF1A cause pancreatic and cerebellar agenesis. Nat Genet 36:1301–1305
Obata J, Yano M, Mimura H, Goto T, Nakayama R, Mibu Y, Oka C, Kawaichi M (2001) p48 subunit of mouse PTF1 binds to RBP-Jκ/CBF-1, the intracellular mediator of Notch signalling, and is expressed in the neural tube of early stage embryos. Genes Cells 6:345–360
Lin JW, Biankin AV, Horb ME, Ghosh B, Prasad NB, Yee NS, Pack MA, Leach SD (2004) Differential requirement for ptf1a in endocrine and exocrine lineages of developing zebrafish pancreas. Dev Biol 274:491–503
Fukuda A, Kawaguchi Y, Furuyama K, Kodama S, Horiguchi M, Kuhara T, Kawaguchi M, Terao M, Doi R, Wright CV (2008) Reduction of Ptf1a gene dosage causes pancreatic hypoplasia and diabetes in mice. Diabetes 57:2421–2431
Christa L, Felin M, Morali O, Simon M-T, Lasserre C, Brechot C, Sève A-P (1994) The human HIP gene, overexpressed in primary liver cancer encodes for a C-type carbohydrate binding protein with lactose binding activity. FEBS Lett 337:114–118
Marselli L, Thorne J, Dahiya S, Sgroi DC, Sharma A, Bonner-Weir S, Marchetti P, Weir GC (2010) Gene expression profiles of Beta-cell enriched tissue obtained by laser capture microdissection from subjects with type 2 diabetes. PLoS One 5:e11499
Terazono K, Uchiyama Y, Ide M, Watanabe T, Yonekura H, Yamamoto H, Okamoto H (1990) Expression of reg protein in rat regenerating islets and its co-localization with insulin in the beta cell secretory granules. Diabetologia 33:250–252
Miyaura C, Chen L, Appel M, Alam T, Inman L, Hughes SD, Milburn JL, Unger RH, Newgard CB (1991) Expression of reg/PSP, a pancreatic exocrine gene: relationship to changes in islet β-cell mass. Mol Endocrinol 5:226–234
Akiyama T, Takasawa S, Nata K, Kobayashi S, Abe M, Shervani NJ, Ikeda T, Nakagawa K, Unno M, Matsuno S (2001) Activation of Reg gene, a gene for insulin-producing β-cell regeneration: poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase binds Reg promoter and regulates the transcription by autopoly (ADP-ribosyl) ation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98:48–53
Kobayashi S, Akiyama T, Nata K, Abe M, Tajima M, Shervani NJ, Unno M, Matsuno S, Sasaki H, Takasawa S (2000) Identification of a receptor for reg (regenerating gene) protein, a pancreatic β-cell regeneration factor. J Biol Chem 275:10723–10726
Okamoto H (1999) The Reg gene family and Reg proteins: with special attention to the regeneration of pancreatic β-cells. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 6:254–262
Yip L, Su L, Sheng D, Chang P, Atkinson M, Czesak M, Albert PR, Collier A-R, Turley SJ, Fathman CG (2009) Deaf1 isoforms control the expression of genes encoding peripheral tissue antigens in the pancreatic lymph nodes during type 1 diabetes. Nat Immunol 10:1026–1033
Pugazhenthi U, Velmurugan K, Tran A, Mahaffey G, Pugazhenthi S (2010) Anti-inflammatory action of exendin-4 in human islets is enhanced by phosphodiesterase inhibitors: potential therapeutic benefits in diabetic patients. Diabetologia 53:2357–2368
Vukkadapu SS, Belli JM, Ishii K, Jegga AG, Hutton JJ, Aronow BJ, Katz JD (2005) Dynamic interaction between T cell-mediated β-cell damage and β-cell repair in the run up to autoimmune diabetes of the NOD mouse. Physiol Genomics 21:201–211
Gerard C, Rollins BJ (2001) Chemokines and disease. Nat Immunol 2:108–115
Jamali Z, Nazari M, Khoramdelazad H, Hakimizadeh E, Mahmoodi M, Karimabad MN, Hassanshahi G, Rezaeian M, Balaei P, Darakhshan S (2013) Expression of CC chemokines CCL2, CCL5, and CCL11 is associated with duration of disease and complications in type-1 diabetes: a study on Iranian diabetic patients. Clin. Lab 11:1
Wellen KE, Hotamisligil GS (2005) Inflammation, stress, and diabetes. J Clin Investig 115:1111–1119
Navarro JF, Milena FJ, Mora C, Leon C, Garcia J (2007) Renal pro-inflammatory cytokine gene expression in diabetic nephropathy: effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and pentoxifylline administration. Am J Nephrol 26:562–570
Boehm U, Klamp T, Groot M, Howard J (1997) Cellular responses to interferon-γ. Annu Rev Immunol 15:749–795
Shenoy AR, Wellington DA, Kumar P, Kassa H, Booth CJ, Cresswell P, Macmicking JD (2012) GBP5 promotes NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and immunity in mammals. Science 336:481–485
Haneklaus M, O’neill LA, Coll RC (2013) Modulatory mechanisms controlling the NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammation: recent developments. Curr Opin Immunol 25(1):40–45
Lehuen A, Diana J, Zaccone P, Cooke A (2010) Immune cell crosstalk in type 1 diabetes. Nat Rev Immunol 10:501–513
Yan B, Wang Z (2012) Long noncoding RNA: its physiological and pathological roles. DNA Cell Biol 31:S-34–S-41
Alvarez ML, Distefano JK (2012) The role of non-coding RNAs in diabetic nephropathy: potential applications as biomarkers for disease development and progression. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 99(1):1–11
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by grants from the Foundation of Heilongjiang Provincial Education Department of China (12531319, 11551238), Foundation of Heilongjiang Provincial Health Department of China (2009-181, 2009-207, 2012-715), Foundation of Heilongjiang Provincial Postdoctor of China (LBH-Z11086). We wish to express our warm thanks to Fenghe (Shanghai) Information Technology Co., Ltd. Their ideas and help gave a valuable added dimension to our research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Bo Li, Chang Long Bi and Ning Lang are co-first authors in this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Bi, C.L., Lang, N. et al. RNA-seq methods for identifying differentially expressed gene in human pancreatic islet cells treated with pro-inflammatory cytokines. Mol Biol Rep 41, 1917–1925 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-013-3016-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-013-3016-2