Abstract
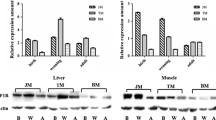
The IGF system plays important roles in growth. Nevertheless, few data have been reported so far on the expression of IGF system members and their relationship with growth in domestic animals, especially pigs. In this study, hepatic transcript level of IGF1, IGF2, IGF binding protein 2 (IGFBP2), IGFBP3 and IGF 1 receptor (IGF1R), plasma protein level of IGF1 and IGFBP3, and eight growth or carcass traits, including chest circumference, body length, body height (BH), body weight, carcass weight, loin muscle area (LMA), back fat thickness and average daily gain, were measured in fast-growing Landrace and slow-growing Lantang pigs at the age of 1, 27, 90, 150 and 180 days. The results showed that liver mRNA level of IGF1, IGF2 and IGF1R, and blood protein level of IGF1 have a similar developmental profile in both Landrace and Lantang pigs. Their levels were higher at the early age than that at other older ages. Hepatic transcript abundances of the two growth inhibitors, IGFBP2 and IGFBP3, were mostly higher in Lantang pigs than that in Landrace pigs, at 5 examined postnatal stages. The IGF system members’ liver mRNA level and/or serum protein level have significant correlation with each other in different age of Landrace or Lantang pigs. Hepatic mRNA level or serum protein level of IGF system members also has significant correlation with investigated traits, especially with BH and LMA, in different age of Lantang or Landrace pigs. Our results revealed the change profiles of porcine IGF system members’ liver transcript level and plasma protein level between different pig breeds and different postnatal developmental ages. Moreover, the correlation analysis results suggest that the IGF system members act coordinately to regulate the growth performance and carcass composition in pigs. The information obtained from the present study is important for elucidation of the regulatory mechanism of IGF system underlying growth, and for genetic improvement in pigs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Denley A, Cosgrove LJ, Booker GW, Wallace JC, Forbes BE (2005) Molecular interactions of the IGF system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 16:421–439. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2005.04.004
Kaplan SA, Cohen P (2007) The somatomedin hypothesis 2007: 50 years later. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:4529–4535. doi:10.1210/jc.2007-0526
Grimberg A, Cohen P (2000) Role of insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins in growth control and carcinogenesis. J Cell Physiol 183:1–9. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(200004)183:1<1:AID-JCP1>3.0.CO;2-J
Khandwala HM, McCutcheon IE, Flyvbjerg A, Friend KE (2000) The effects of insulin-like growth factors on tumorigenesis and neoplastic growth. Endocr Rev 21:215–244
Pollak MN, Schernhammer ES, Hankinson SE (2004) Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer 4:505–518. doi:10.1038/nrc1387
Baker J, Liu JP, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A (1993) Role of insulin-like growth factors in embryonic and postnatal growth. Cell 75:73–82
DeChiara TM, Efstratiadis A, Robertson EJ (1990) A growth-deficiency phenotype in heterozygous mice carrying an insulin-like growth factor II gene disrupted by targeting. Nature 345:78–80. doi:10.1038/345078a0
Liu JP, Baker J, Perkins AS, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A (1993) Mice carrying null mutations of the genes encoding insulin-like growth factor I (Igf-1) and type 1 IGF receptor (Igf1r). Cell 75:59–72
Mathews LS, Hammer RE, Behringer RR, D’Ercole AJ, Bell GI, Brinster RL, Palmiter RD (1988) Growth enhancement of transgenic mice expressing human insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology 123:2827–2833
Tomas FM, Knowles SE, Owens PC, Chandler CS, Francis GL, Read LC, Ballard FJ (1992) Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and especially IGF-I variants are anabolic in dexamethasone-treated rats. Biochem J 282(Pt 1):91–97
Zhao G, Monier-Faugere MC, Langub MC, Geng Z, Nakayama T, Pike JW, Chernausek SD, Rosen CJ, Donahue LR, Malluche HH, Fagin JA, Clemens TL (2000) Targeted overexpression of insulin-like growth factor I to osteoblasts of transgenic mice: increased trabecular bone volume without increased osteoblast proliferation. Endocrinology 141:2674–2682
DeChiara TM, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A (1991) Parental imprinting of the mouse insulin-like growth factor II gene. Cell 64:849–859
Andersson L, Haley CS, Ellegren H, Knott SA, Johansson M, Andersson K, Andersson-Eklund L, Edfors-Lilja I, Fredholm M, Hansson I et al (1994) Genetic mapping of quantitative trait loci for growth and fatness in pigs. Science 263:1771–1774
Nezer C, Moreau L, Brouwers B, Coppieters W, Detilleux J, Hanset R, Karim L, Kvasz A, Leroy P, Georges M (1999) An imprinted QTL with major effect on muscle mass and fat deposition maps to the IGF2 locus in pigs. Nat Genet 21:155–156. doi:10.1038/5935
Van Laere AS, Nguyen M, Braunschweig M, Nezer C, Collette C, Moreau L, Archibald AL, Haley CS, Buys N, Tally M, Andersson G, Georges M, Andersson L (2003) A regulatory mutation in IGF2 causes a major QTL effect on muscle growth in the pig. Nature 425:832–836. doi:10.1038/nature02064
Morison IM, Reeve AE (1998) Insulin-like growth factor 2 and overgrowth: molecular biology and clinical implications. Mol Med Today 4:110–115
Bajpai A, Menon PS (2006) Insulin like growth factors axis and growth disorders. Indian J Pediatr 73:67–71
Liu JL, Yakar S, LeRoith D (2000) Conditional knockout of mouse insulin-like growth factor-1 gene using the Cre/loxP system. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 223:344–351
Pierce AL, Breves JP, Moriyama S, Hirano T, Grau EG (2011) Differential regulation of Igf1 and Igf2 mRNA levels in tilapia hepatocytes: effects of insulin and cortisol on GH sensitivity. J Endocrinol 211:201–210. doi:10.1530/JOE-10-0456
Zhang M, Xuan S, Bouxsein ML, von Stechow D, Akeno N, Faugere MC, Malluche H, Zhao G, Rosen CJ, Efstratiadis A, Clemens TL (2002) Osteoblast-specific knockout of the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) receptor gene reveals an essential role of IGF signaling in bone matrix mineralization. J Biol Chem 277:44005–44012. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208265200
Mohan S, Baylink DJ (2002) IGF-binding proteins are multifunctional and act via IGF-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Endocrinol 175:19–31
Yang SY, Winslet M (2011) The igf system in carcinogenesis and its implication for cancer therapy. Curr Oncol 18:301–302
Baxter RC, Martin JL, Beniac VA (1989) High molecular weight insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex. Purification and properties of the acid-labile subunit from human serum. J Biol Chem 264:11843–11848
Firth SM, Baxter RC (2002) Cellular actions of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Endocr Rev 23:824–854
Modric T, Silha JV, Shi Z, Gui Y, Suwanichkul A, Durham SK, Powell DR, Murphy LJ (2001) Phenotypic manifestations of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 overexpression in transgenic mice. Endocrinology 142:1958–1967
Hoeflich A, Wu M, Mohan S, Foll J, Wanke R, Froehlich T, Arnold GJ, Lahm H, Kolb HJ, Wolf E (1999) Overexpression of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 in transgenic mice reduces postnatal body weight gain. Endocrinology 140:5488–5496
Hoeflich A, Nedbal S, Blum WF, Erhard M, Lahm H, Brem G, Kolb HJ, Wanke R, Wolf E (2001) Growth inhibition in giant growth hormone transgenic mice by overexpression of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2. Endocrinology 142:1889–1898
Wood TL, Rogler LE, Czick ME, Schuller AG, Pintar JE (2000) Selective alterations in organ sizes in mice with a targeted disruption of the insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 gene. Mol Endocrinol 14:1472–1482
Xiong YZ, Deng CY (1999) Principle and method of swine testing. Chinese Agriculture Press, Beijing
Li Z, Cao B, Zhao B, Yang X, Fan MZ, Yang J (2009) Decreased expression of calpain and calpastatin mRNA during development is highly correlated with muscle protein accumulation in neonatal pigs. Comp Biochem Physiol A 152:498–503. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2008.12.004
Li Q, Yin W, Cai M, Liu Y, Hou H, Shen Q, Zhang C, Xiao J, Hu X, Wu Q, Funaki M, Nakaya Y (2010) NO-1886 suppresses diet-induced insulin resistance and cholesterol accumulation through STAT5-dependent upregulation of IGF1 and CYP7A1. J Endocrinol 204:47–56. doi:10.1677/JOE-09-0278
Davis TA, Fiorotto ML (2009) Regulation of muscle growth in neonates. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 12:78–85. doi:10.1097/MCO.0b013e32831cef9f
Davis TA, Suryawan A, Orellana RA, Fiorotto ML, Burrin DG (2010) Amino acids and insulin are regulators of muscle protein synthesis in neonatal pigs. Animal 4:1790–1796. doi:10.1017/S1751731110000984
Davis TA, Fiorotto ML, Burrin DG, Vann RC, Reeds PJ, Nguyen HV, Beckett PR, Bush JA (2002) Acute IGF-I infusion stimulates protein synthesis in skeletal muscle and other tissues of neonatal pigs. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 283:E638–E647. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00081.2002
Reeve JG, Morgan J, Schwander J, Bleehen NM (1993) Role for membrane and secreted insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 in the regulation of insulin-like growth factor action in lung tumors. Cancer Res 53:4680–4685
Hoflich A, Lahm H, Blum W, Kolb H, Wolf E (1998) Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 inhibits proliferation of human embryonic kidney fibroblasts and of IGF-responsive colon carcinoma cell lines. FEBS Lett 434:329–334
Samaras SE, Hammond JM (1995) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 inhibits porcine granulosa cell function in vitro. Am J Physiol 268:E1057–E1064
Conover CA (1992) Potentiation of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) action by IGF-binding protein-3: studies of underlying mechanism. Endocrinology 130:3191–3199
Karas M, Danilenko M, Fishman D, LeRoith D, Levy J, Sharoni Y (1997) Membrane-associated insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 inhibits insulin-like growth factor-I-induced insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling in ishikawa endometrial cancer cells. J Biol Chem 272:16514–16520
Lee CY, Chung CS, Simmen FA (1993) Ontogeny of the porcine insulin-like growth factor system. Mol Cell Endocrinol 93:71–80. doi:10.1016/0303-7207(93)90141-6
Lee CY, Bazer FW, Etherton TD, Simmen FA (1991) Ontogeny of insulin-like growth factors (IGF-I and IGF-II) and IGF-binding proteins in porcine serum during fetal and postnatal development. Endocrinology 128:2336–2344
Hernandez-Sanchez C, Werner H, Roberts CT Jr, Woo EJ, Hum DW, Rosenthal SM, LeRoith D (1997) Differential regulation of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptor gene expression by IGF-I and basic fibroblastic growth factor. J Biol Chem 272:4663–4670
Price WA, Moats-Staats BM, Stiles AD (1995) Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) regulates IGFBP-3 and IGFBP-4 by multiple mechanisms in A549 human adenocarcinoma cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 13:466–476
Mireuta M, Darnel A, Pollak M (2010) IGFBP-2 expression in MCF-7 cells is regulated by the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway through Sp1-induced increase in transcription. Growth Factors 28:243–255. doi:10.3109/08977191003745472
Lee S (2003) Insulin-like growth factor-1 induces skeletal muscle hypertrophy. J Exerc Sci Fit 1:47–53
Duan C, Ren H, Gao S (2010) Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs), IGF receptors, and IGF-binding proteins: roles in skeletal muscle growth and differentiation. Gen Comp Endocrinol 167:344–351. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2010.04.009
Jeon JT, Carlborg O, Tornsten A, Giuffra E, Amarger V, Chardon P, Andersson-Eklund L, Andersson K, Hansson I, Lundstrom K, Andersson L (1999) A paternally expressed QTL affecting skeletal and cardiac muscle mass in pigs maps to the IGF2 locus. Nat Genet 21:157–158. doi:10.1038/5938
Carrodeguas JA, Burgos C, Moreno C, Sanchez AC, Ventanas S, Tarrafeta L, Barcelona JA, Lopez MO, Oria R, Lopez-Buesa P (2005) Incidence in diverse pig populations of an IGF2 mutation with potential influence on meat quality and quantity: an assay based on real time PCR (RT-PCR). Meat Sci 71:577–582. doi:10.1016/j.meatsci.2005.05.002
Van den Maagdenberg K, Stinckens A, Claeys E, Buys N, De Smet S (2008) Effect of the insulin-like growth factor-II and RYR1 genotype in pigs on carcass and meat quality traits. Meat Sci 80:293–303. doi:10.1016/j.meatsci.2007.12.008
Pierzchala M, Pareek CS, Urbanski P, Goluch D, Kamyczek M, Rozycki M, Smoczynski R, Horbanczuk JO, Kuryl J (2012) Study of the differential transcription in liver of growth hormone receptor (GHR), insulin-like growth factors (IGF1, IGF2) and insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF1R) genes at different postnatal developmental ages in pig breeds. Mol Biol Rep 39:3055–3066. doi:10.1007/s11033-011-1068-8
Wang L, Zhang G, Lin F, Jiang B, Dong F, Liu H (2011) Expression of the insulin-like growth factor system in skeletal muscle during embryonic and postnatal development in the first filial generation pigs from Erhualian and Yorkshire reciprocal crosses. Gen Comp Endocrinol 173:56–62. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2011.04.025
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant (Grant number: 30571327) from The National Natural Science Foundation of China, and a grant (Grant number: 2011AA100304) from the 863 Program of China. We thank Dr. Hao Zhang, Chang He and Liang Shuai for their help in preparation of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zicong Li and Zhenfang Wu contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Wu, Z., Ren, G. et al. Expression patterns of insulin-like growth factor system members and their correlations with growth and carcass traits in Landrace and Lantang pigs during postnatal development. Mol Biol Rep 40, 3569–3576 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2430-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2430-1