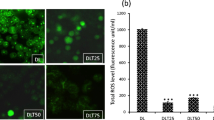
Abstract
Protein Kinase C (PKC) isozymes are key components involved in cell proliferation and their over activation leads to abnormal tumor growth. PKC follows signalling pathway by activation of downstream gene NF-kB and early transcription factor c-Myc. Over activation of NF-kB and c-Myc gene are also linked with unregulated proliferation of cancer cells. Therefore any agent which can inhibit the activation of Protein kinase C, NF-kB and c-Myc may be useful in reducing cancer progression. To investigate this hypothesis we have tested the effect of ellagic acid on these genes in Dalton’s lymphoma bearing (DL). The role of ellagic acid was also tested in regulation of tumor suppressor gene Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1). DL mice were treated with three different doses (40, 60 and 80 mg/kg body weight) of ellagic acid. Ascites cells of mice were used for the experiments. Ellagic acid administration to DL mice decreased oxidative stress by reducing lipid peroxidation. Ellagic acid also down regulates the expression of classical isozymes of PKC i.e. PKCα, PKCβ, and PKCγ as well as activity of total PKC and NF-kB, indicating its antitumor action. The anticarcinogenic action of ellagic acid was also confirmed by up regulation of TGF-β1 and down regulation of c-Myc. Lymphoma prevention by ellagic acid is further supported by decrease in cell proliferation, cell viability, ascites fluid accumulation and increase in life span of DL mice. All these findings suggest that ellagic acid prevents the cancer progression by down regulation of PKC signaling pathway leading to cell proliferation.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Milligan SA, Owens MW, Grisham MB (1998) Differential regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and nuclear factor-kappa B signal transduction pathways by hydrogen peroxide and tumor necrosis factor. Arch Biochem Biophys 352:255–262
Abate C, Patel L, Rauscher FJ, Curran T (1990) Redox regulation of Fos and Jun DNA -binding activity in vitro. Science 249:1157–1161
Jussi K, Vesa A, Juha P (2006) Protein kinase C (PKC) family in cancer progression. Cancer Lett 235:1–10
Black JD (2000) Protein Kinase C mediated regulation of the cell cycle. Front Biosci 5:406–423
Gopalakrishna R, Gundimeda U (2002) Antioxidant regulation of protein kinase C in cancer prevention. J Nutr 132:3819S–3823S
Saijo K, Mecklenbräuker I, Santana A, Leitger M, Schmedt C, Tarakhovsky A (2002) Protein kinase Cβ controls nuclear factor κB activation in B cells through selective regulation of the IκB kinase α. J Exp Med 195:1647–1652
Trushin SA, Pennington KN, Algeciras-Schimnich A, Paya CV (1999) Protein kinase C and calcineurin synergize to activate IkB kinase and NF-kB in T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem 274:22923–22931
Philipp JJ, Ruland J (2007) Aberrant NF-kB signaling in lymphoma: mechanisms, consequences, and therapeutic implications. Blood 109:2700–2707
Anderson MT, Staal FJ, Gitler C, Herzenberg LA, Herzenberg LA (1994) Separation of oxidant-initiated and redox regulated steps in the NF-kB signal transduction pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:11527–11531
Carballo M (1999) Oxidative stress triggers STAT3 tyrosine phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of in human lymphocytes. J Biol Chem 274:17580–17586
Flohe L, Brigelius-Flohé R, Saliou C, Traber MG, Packer L (1997) Redox regulation of NF-kB activation. Free Radic Biol Med 22:1115–1126
Dorai T, Agrawal BB (2004) Role of chemopreventive agents in cancer therapy. Cancer Lett 215:129–140
Singh RP, Dhanalakshmi S, Agarwal R (2002) Phytochemicals as cell cycle modulators. Cell Cycle 1:156–161
Edderkaoui M et al (2008) Ellagic acid induces apoptosis through inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B in pancreatic cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 14(23):3672–3680
Li TM, Chen GW, Su CC, Lin JG, Yeh CC, Cheng KC et al (2005) Ellagic acid indu p53/p21 expression, G1 arrest and apoptosis in human bladder cancer T24 cells. Anticancer Res 25(2A):971–979
Larrosa M, Tomás-Barberán FA, Espín JC (2006) The dietary hydrolysable tannin punicalagin releases ellagic acid that induces apoptosis in human colon adenocarcinoma Caco-2 cells by using the mitochondrial pathway. J Nutr Biochem 17:611–625
Barre B, Perkins ND (2007) A cell cycle regulatory network controlling NF-kB subunit activity and function. EMBO J 26:4841–4855
Adhikary S, Eilers M (2005) Transcriptional regulation and transformation by Myc proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6(8):635–645
Derynck R, Akhurst RJ, Balmain A (2001) TGF-β signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Nat Genet 29:117–129
Sebestyena A, Barna G, Katalin N, Judit J, Sandor P, Eszter K (2005) Smad signal and TGF-β induced apoptosis in human lymphoma cells. Cytokine 30:228–235
Marilyn LG, Long DD, Goodwin SM, Lee C (1997) Transforming growth factor-b1 inhibits membrane association of protein kinase Ca in a human prostate cancer cell line. Endocrinology 138:4657–4664
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Sharma R, Vinayak M (2011) α-Tocopherol attenuates NF-κB activation and proinflammatory cytokine IL-6 secretion in cancer bearing mice. Biosci Rep 31:421–428
Mishra S, Vinayak M (2011) Anti-carcinogenic action of ellagic acid mediated via modulation of oxidative stress regulated genes in Dalton lymphoma bearing mice. Leuk Lymphoma 52(11):2155–2161
Sladowski D, Lebovitz RM, Roeder RD (1993) An improved MTT assay. J Immunol Methods 157:203–207
Dignam JD, Lebovitz RM, Roeder RD (1983) Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res 11:1475–1489
Liu SF, Ye X, Malik AB (1999) Inhibition of NF-kB activation by pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate prevents in vivo expression of proinflammatory genes. Circulation 12:1330–1337
Otamiri T, Sjodah R (1989) Increased lipid peroxidation in malignant tissues of patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer 61:122–125
Ahmed MI, Fayed ST, Hossein H, Tash FM (1999) Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in human cervical carcinoma. Dis Markers 15:283–291
Diplock AT, Rice-Evans AC, Burton RH (1994) Is there a significant role for lipid peroxidation in causation of malignancy and for antioxidants in cancer prevention? Cancer Res 54:19525–19526
Trang-Tiau Wu, Yi Hsien, Yih-Shou H, Jer-Yuh Liu (2008) Reduction of PKCα decreases cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of human malignant hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Biochem 103:9–20
Lønne Gry Kalstad, Cornmark L, Zahirovic IO, Landberg G, Jirström K, Larsson C (2010) PKCα expression is a marker for breast cancer aggressiveness. Mol Cancer 9:76
Graff JR et al (2005) The protein kinase C-β selective inhibitor, enzastaurin (LY317615.HCl), suppresses signaling through the AKT pathway, induces apoptosis, and suppresses growth of human colon cancer and glioblastoma xenografts. Cancer Res 65:7462–7469
Shipp MA, Ross KN, Tamayo P, Weng AP, Kutok JL, Aguiar RC et al (2002) Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma outcome prediction by gene-expression profiling and supervised machine learning. Nat Med 8:68–74
Gokmen-Polar Y, McNulty AM, Hanna KR, Konicek BW, Lynch RL, Bailey SN et al (2001) Elevated protein kinase C β II is an early promotive event in colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 61:1375–1381
Teicher BA, Menon K, Alvarez E, Liu P, Shih C, Faul MM (2001) Antiangiogenic and antitumor effects of a protein kinase C-β inhibitor in human hepatocellular and gastric cancer xenografts. In Vivo 15:185–193
Kamimura K, Hojoand H, Abe M (2004) Characterization of expression of protein kinase C isozymes in human B-cell lymphoma: relationship between its expression and prognosis. Pathol Int 54:224–230
Dorota G, Szeker K, Galfi P, Csordas A, Hofmann J (2010) Protein kinase C in colon cancer cells: expression, Thr514 phosphorylation and sensitivity to butyrate-mediated up regulation as related to the degree of differentiation. Johann Hofmanna Chem Biol Interact 185:25–32
Melanie K, Gudrun P, Kamal KB, Frank DB, Doris M (2007) Apple polyphenols affect protein kinase C activity and the onset of apoptosis in human colon carcinoma Cells. J Agric Food Chem 55:4999–5006
Alvaro V et al (1992) Protein kinase C activity and expression in normal and adenomatous human pituitaries. Int J Cancer 50:724–730
Kusunoki M, Sakanoue Y, Hatada T, Yanagi H, Yamamura T, Utsunomiya J (1992) Protein kinase C activity in human colonic adenoma and colorectal carcinoma. Cancer 69:24–30
Chung CH, Chung Joel S, Parker Kim Ely (2006) Gene expression profiles identify epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and activation of nuclear factor-kB signaling as characteristics of a high-risk head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 66:8210–8218
Hinz M, Lemke P, Anagnostopoulos I, Hacker C, Krappmann D, Mathas S (2002) Nuclear factor kB-dependent gene expression profiling of Hodgkin’s disease tumor cells, pathogenetic significance and link to constitutive signal transducer and activator of transcription activity. J Exp Med 196:605–617
Van Laere SJ, Vander Auwera I, Vanden Eynden GG, Elst HJ, Weyler J, Harris AL et al (2006) Nuclear factor-kappa B signature of inflammatory breast cancer by cDNA microarray validated by quantitative real-time reverse transcription-PCR, immunohistochemistry, and nuclear factor-kappa B DNA binding. Clin Cancer Res 12:3249–3256
Kim SO, Chun KS, Kundu JK, Surh YJ (2004) Inhibitory effects of [6]-gingerol on PMA-induced COX-2 expression and activation of NF-kB and p38 MAPK in mouse skin. Biofactors 21(1–4):27–31
Takada Y, Murakami A, Aggarwal BB (2005) Zerumbone abolishes NF-kappa B and Ik Bα kinase activation leading to suppression of antiapoptotic and metastatic gene expression, up regulation of apoptosis, and down regulation of invasion. Oncogene 24(46):6957–6969
Villalba M, Kasibhatla S, Genestier L, Mahboubi A, Green DR, Altman A (1999) Protein kinase C θ cooperates with calcineurin to induce Fas ligand expression during activation- induced T cell death. J Immunol 163:5813–5819
Zajac-Kaye M (2001) Myc oncogene: a key component in cell cycle regulation and its implication for lung cancer. Lung Cancer 34:S43–S46
Lori M, Donald EM (1997) Protein Kinase C is not necessary for transforming growth factor beta-induced growth-arrest in leukemia cell lines. Leuk Res 21:403–410
Marilyn LG, Yu G, Yu D, Zhu M (2010) PKCα-induced drug resistance in pancreatic cancer cells is associated with transforming growth factor-b1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 29:104
Perlino E, Loverro G, Maiorano E, Giannini T, Cazzolla A, Napoli A et al (1998) Down regulated expression of transforming growth factor βI mRNA in endometrial carcinoma. Br J Cancer 77(8):1260–1266
Acknowledgments
Research was supported by University Grants Commission, India. Sudha Mishra thanks the University Grant Commission, India, for providing a “Research Fellowship in Science for Meritorious Students”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, S., Vinayak, M. Ellagic acid checks lymphoma promotion via regulation of PKC signaling pathway. Mol Biol Rep 40, 1417–1428 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2185-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2185-8