Abstract
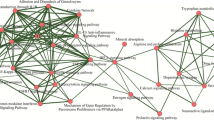
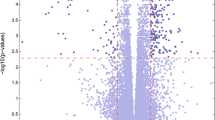
Parkinson disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disease. Most people with PD are idiopathic, with no specific known cause. Recently, several studies have indicated small proportion of PD cases may result from a mutation in some specific genes. However, the involved pathways of these genes and the co-expression patterns of associated pathways still remain unclear. Here, we aimed to systematically investigate PD related pathways by using microarray dataset GSE7621 from the public database library of gene expression omnibus and gene set enrichment analysis on the datasets. Furthermore, candidate transcription factors were also explored by distant regulatory elements software. As a result, 11 up-regulated pathways (such as glycosaminoglycan degradation) and 24 down-regulated pathways (such as ErbB signaling pathway and Long-term depression) were identified as PD related. Most of them were classified into the maps of human diseases, organismal system, and metabolism with no previous reports. Finally, we constructed co-expression networks of related pathways with the significant core genes and transcription factors, such as OCT and HNF3. All of these may be helpful to better understand the molecular mechanisms of human PD in genome wide.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Przedborski S (2005) Pathogenesis of nigral cell death in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 11:S3–S7
Jankovic J (2008) Parkinson’s disease: clinical features and diagnosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79(4):368–376. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2007.131045
Davie CA (2008) A review of Parkinson’s disease. Br Med Bull 86:109–127. doi:10.1093/bmb/ldn013
Lesage S, Brice A (2009) Parkinson’s disease: from monogenic forms to genetic susceptibility factors. Hum Mol Genet 18(R1):R48–R59. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddp012
Nalls MA, Plagnol V, Hernandez DG, Sharma M, Sheerin UM, Saad M, Simon-Sanchez J, Schulte C, Lesage S, Sveinbjornsdottir S, Stefansson K, Martinez M, Hardy J, Heutink P, Brice A, Gasser T, Singleton AB, Wood NW (2011) Imputation of sequence variants for identification of genetic risks for Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Lancet 377(9766):641–649. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62345-8
Samii A, Nutt JG, Ransom BR (2004) Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 363(9423):1783–1793. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16305-8
Feng LR, Maguire-Zeiss KA (2010) Gene therapy in Parkinson’s disease: rationale and current status. CNS Drugs 24(3):177–192. doi:10.2165/11533740-000000000-00000
Obeso JA, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Goetz CG, Marin C, Kordower JH, Rodriguez M, Hirsch EC, Farrer M, Schapira AH, Halliday G (2010) Missing pieces in the Parkinson’s disease puzzle. Nat Med 16(6):653–661. doi:10.1038/nm.2165
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub TR, Lander ES (2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(43):15545
He K, Wang Q, Yang Y, Wang M, Pan Y (2011) A Comparative Study of Mouse Hepatic and Intestinal Gene Expression Profiles under PPARalpha Knockout by Gene Set Enrichment Analysis. PPAR Res 2011:629728. doi:10.1155/2011/629728
Lesnick TG, Papapetropoulos S, Mash DC, Ffrench-Mullen J, Shehadeh L, de Andrade M, Henley JR, Rocca WA, Ahlskog JE, Maraganore DM (2007) A genomic pathway approach to a complex disease: axon guidance and Parkinson disease. PLoS Genet 3(6):e98. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.0030098
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA (2004) affy–analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level. Bioinformatics 20(3):307–315. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btg405
Chiaretti S, Li X, Gentleman R, Vitale A, Vignetti M, Mandelli F, Ritz J, Foa R (2004) Gene expression profile of adult T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia identifies distinct subsets of patients with different response to therapy and survival. Blood 103(7):2771–2778. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-09-3243
Gotea V, Ovcharenko I (2008) DiRE: identifying distant regulatory elements of co-expressed genes. Nucleic Acids Res 36 (Web Server issue):W133-139. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn300
Simunovic F, Yi M, Wang Y, Macey L, Brown LT, Krichevsky AM, Andersen SL, Stephens RM, Benes FM, Sonntag KC (2009) Gene expression profiling of substantia nigra dopamine neurons: further insights into Parkinson’s disease pathology. Brain 132(7):1795–1809
Tun HW, Marlow LA, von Roemeling CA, Cooper SJ, Kreinest P, Wu K, Luxon BA, Sinha M, Anastasiadis PZ, Copland JA (2010) Pathway signature and cellular differentiation in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. PLoS One 5(5):e10696. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0010696
Avraham R, Yarden Y (2011) Feedback regulation of EGFR signalling: decision making by early and delayed loops. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12(2):104–117. doi:10.1038/nrm3048
Cai Z, Zhang H, Liu J, Berezov A, Murali R, Wang Q, Greene MI (2010) Targeting erbB receptors. Semin Cell Dev Biol 21(9):961–966. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2010.09.005
Iwakura Y, Piao YS, Mizuno M, Takei N, Kakita A, Takahashi H, Nawa H (2005) Influences of dopaminergic lesion on epidermal growth factor-ErbB signals in Parkinson’s disease and its model: neurotrophic implication in nigrostriatal neurons. J Neurochem 93(4):974–983. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03073.x
Sancho RM, Law BM, Harvey K (2009) Mutations in the LRRK2 Roc-COR tandem domain link Parkinson’s disease to Wnt signalling pathways. Hum Mol Genet 18(20):3955–3968. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddp337
Domanskyi A, Geissler C, Vinnikov IA, Alter H, Schober A, Vogt MA, Gass P, Parlato R, Schutz G (2011) Pten ablation in adult dopaminergic neurons is neuroprotective in Parkinson’s disease models. FASEB J 25(9):2898–2910. doi:10.1096/fj.11-181958
Santini E, Heiman M, Greengard P, Valjent E, Fisone G (2009) Inhibition of mTOR signaling in Parkinson’s disease prevents L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Sci Signal 2(80):ra36. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2000308
Yang Y, Gehrke S, Haque ME, Imai Y, Kosek J, Yang L, Beal MF, Nishimura I, Wakamatsu K, Ito S, Takahashi R, Lu B (2005) Inactivation of Drosophila DJ-1 leads to impairments of oxidative stress response and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(38):13670–13675. doi:10.1073/pnas.0504610102
Giaime E, Sunyach C, Herrant M, Grosso S, Auberger P, McLean PJ, Checler F, da Costa CA (2006) Caspase-3-derived C-terminal product of synphilin-1 displays antiapoptotic function via modulation of the p53-dependent cell death pathway. J Biol Chem 281(17):11515–11522. doi:10.1074/jbc.M508619200
Levy OA, Malagelada C, Greene LA (2009) Cell death pathways in Parkinson’s disease: proximal triggers, distal effectors, and final steps. Apoptosis 14(4):478–500. doi:10.1007/s10495-008-0309-3
Winslow AR, Rubinsztein DC (2011) The Parkinson disease protein alpha-synuclein inhibits autophagy. Autophagy 7(4):429–431
Gruden MA, Sewell RD, Yanamandra K, Davidova TV, Kucheryanu VG, Bocharov EV, Bocharova OR, Polyschuk VV, Sherstnev VV, Morozova-Roche LA (2011) Immunoprotection against toxic biomarkers is retained during Parkinson’s disease progression. J Neuroimmunol 233(1–2):221–227. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2010.12.001
Benkler M, Agmon-Levin N, Hassin-Baer S, Cohen OS, Ortega-Hernandez OD, Levy A, Moscavitch SD, Szyper-Kravitz M, Damianovich M, Blank M, Chapman J, Shoenfeld Y (2011) Immunology, autoimmunity, and autoantibodies in Parkinson’s disease. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. doi:10.1007/s12016-010-8242-y
Cunningham RL, Giuffrida A, Roberts JL (2009) Androgens induce dopaminergic neurotoxicity via caspase-3-dependent activation of protein kinase Cdelta. Endocrinology 150(12):5539–5548. doi:10.1210/en.2009-0640
Sutherland GT, Matigian NA, Chalk AM, Anderson MJ, Silburn PA, Mackay-Sim A, Wells CA, Mellick GD (2009) A cross-study transcriptional analysis of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 4(3):e4955. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0004955
Jansson B, Jankovic J (1985) Low cancer rates among patients with Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 17(5):505–509. doi:10.1002/ana.410170514
Takegawa K, Mitsumori K, Onodera H, Shimo T, Kitaura K, Yasuhara K, Hirose M, Takahashi M (2000) Studies on the carcinogenicity of potassium iodide in F344 rats. Food Chem Toxicol 38(9):773–781
Hildebrand MS, Sorensen JL, Jensen M, Kimberling WJ, Smith RJ (2008) Autoimmune disease in a DFNA6/14/38 family carrying a novel missense mutation in WFS1. Am J Med Genet A 146A(17):2258–2265. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.32449
Goren B, Kahveci N, Eyigor O, Alkan T, Korfali E, Ozluk K (2005) Effects of intranigral vs intrastriatal fetal mesencephalic neural grafts on motor behavior disorders in a rat Parkinson model. Surg Neurol 64(Suppl 2):S33–S41. doi:10.1016/j.surneu.2005.07.038
Blair E, Redwood C, Ashrafian H, Oliveira M, Broxholme J, Kerr B, Salmon A, Ostman-Smith I, Watkins H (2001) Mutations in the gamma(2) subunit of AMP-activated protein kinase cause familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: evidence for the central role of energy compromise in disease pathogenesis. Hum Mol Genet 10(11):1215–1220
Murphy RT, Mogensen J, McGarry K, Bahl A, Evans A, Osman E, Syrris P, Gorman G, Farrell M, Holton JL, Hanna MG, Hughes S, Elliott PM, Macrae CA, McKenna WJ (2005) Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase disease mimicks hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: natural history. J Am Coll Cardiol 45(6):922–930. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2004.11.053
Lane EL, Soulet D, Vercammen L, Cenci MA, Brundin P (2008) Neuroinflammation in the generation of post-transplantation dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 32(2):220–228. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2008.06.011
Villar-Cheda B, Rodriguez-Pallares J, Valenzuela R, Munoz A, Guerra MJ, Baltatu OC, Labandeira-Garcia JL (2010) Nigral and striatal regulation of angiotensin receptor expression by dopamine and angiotensin in rodents: implications for progression of Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurosci 32(10):1695–1706. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07448.x
Mure H, Hirano S, Tang CC, Isaias IU, Antonini A, Ma Y, Dhawan V, Eidelberg D (2011) Parkinson’s disease tremor-related metabolic network: characterization, progression, and treatment effects. Neuroimage 54(2):1244–1253. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.09.028
Farashahi Yazd E, Rafiee MR, Soleimani M, Tavallaei M, Salmani MK, Mowla SJ (2011) OCT4B1, a novel spliced variant of OCT4, generates a stable truncated protein with a potential role in stress response. Cancer Lett 309(2):170–175. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2011.05.027
Hu J, Qin K, Zhang Y, Gong J, Li N, Lv D, Xiang R, Tan X (2011) Downregulation of transcription factor Oct4 induces an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via enhancement of Ca2+ influx in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 411(4):786–791. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.07.025
Liu D, Zhou P, Zhang L, Wu G, Zheng Y, He F (2011) Differential expression of Oct4 in HPV-positive and HPV-negative cervical cancer cells is not regulated by DNA methyltransferase 3A. Tumour Biol 32(5):941–950. doi:10.1007/s13277-011-0196-z
Deleidi M, Cooper O, Hargus G, Levy A, Isacson O (2011) Oct4-induced reprogramming is required for adult brain neural stem cell differentiation into midbrain dopaminergic neurons. PLoS One 6(5):e19926. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0019926
Wernig M, Zhao JP, Pruszak J, Hedlund E, Fu D, Soldner F, Broccoli V, Constantine-Paton M, Isacson O, Jaenisch R (2008) Neurons derived from reprogrammed fibroblasts functionally integrate into the fetal brain and improve symptoms of rats with Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(15):5856–5861. doi:10.1073/pnas.0801677105
Becker ML, Visser LE, van Schaik RH, Hofman A, Uitterlinden AG, Stricker BH (2011) OCT1 polymorphism is associated with response and survival time in anti-Parkinsonian drug users. Neurogenetics 12(1):79–82. doi:10.1007/s10048-010-0254-5
Li Q, Zhang N, Jia Z, Le X, Dai B, Wei D, Huang S, Tan D, Xie K (2009) Critical role and regulation of transcription factor FoxM1 in human gastric cancer angiogenesis and progression. Cancer Res 69(8):3501–3509. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3045
Raychaudhuri P, Park HJ (2011) FoxM1: a master regulator of tumor metastasis. Cancer Res 71(13):4329–4333. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0640
Strahle U, Blader P, Henrique D, Ingham PW (1993) Axial, a zebrafish gene expressed along the developing body axis, shows altered expression in cyclops mutant embryos. Genes Dev 7(7B):1436–1446
Zhang XM, Lin E, Yang XJ (2000) Sonic hedgehog-mediated ventralization disrupts formation of the midbrain-hindbrain junction in the chick embryo. Dev Neurosci 22(3):207–216
Labosky PA, Kaestner KH (1998) The winged helix transcription factor Hfh2 is expressed in neural crest and spinal cord during mouse development. Mech Dev 76(1–2):185–190
Singleton A, Farrer M, Johnson J, Singleton A, Hague S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Peuralinna T, Dutra A, Nussbaum R (2003) α-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science 302(5646):841
Lücking CB, Dürr A, Bonifati V, Vaughan J, De Michele G, Gasser T, Harhangi BS, Meco G, Denèfle P, Wood NW (2000) Association between early-onset Parkinson’s disease and mutations in the parkin gene. N Engl J Med 342(21):1560–1567
Gandhi S, Muqit M, Stanyer L, Healy D, Abou-Sleiman P, Hargreaves I, Heales S, Ganguly M, Parsons L, Lees A (2006) PINK1 protein in normal human brain and Parkinson’s disease. Brain 129(7):1720–1731
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, B., Xia, C., Lin, Q. et al. Identification of key pathways and transcription factors related to Parkinson disease in genome wide. Mol Biol Rep 39, 10881–10887 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1985-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1985-1