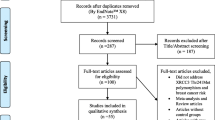
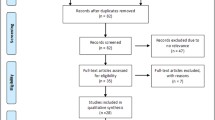
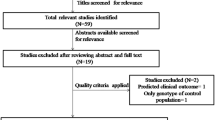
Abstract
The previous published data on the association between X-ray repair cross-complementing group 3 (XRCC3) T241M, A4541G, and A17893G polymorphisms and breast cancer risk remained controversial. Hence, we performed a meta-analysis to investigate the association between breast cancer and XRCC3 T241M (21,910 cases and 23,961 controls), A4541G (9,633 cases and 10,994 controls), and A17893G polymorphisms (10,761 cases and 12,235 controls) in different inheritance models. When all the eligible studies were pooled into the meta-analysis of XRCC3 T241M polymorphism, significantly increased risk of breast cancer was observed in recessive model (odds' ratio [OR] = 1.10, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.04–1.16) and in additive model (OR = 1.10, 95% CI = 1.03–1.16). No significant association was found between A4541G polymorphism and breast cancer risk. When all the eligible studies were pooled into the meta-analysis of XRCC3 A17893G polymorphism, no significant association was found in any genetic model. Additionally, when one study was deleted in the sensitive analysis, the results of XRCC3 A17893G were changed in the additive model (OR = 0.90, 95% CI = 0.82–0.99) and dominant model (OR = 0.94, 95% CI = 0.89–0.99). In summary, this meta-analysis indicates that T241M polymorphism show an increased breast cancer risk and A17893G polymorphism may be associated with decreased breast cancer risk. A study with the larger sample size is needed to further evaluated gene-environment interaction on XRCC3 T241M, A4541G, and A17893G polymorphisms and breast cancer risk.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berns EM, van Staveren IL, Look MP, Smid M, Klijn JG, Foekens JA (1998) Mutations in residues of TP53 that directly contact DNA predict poor outcome in human primary breast cancer. Br J Cancer 77:1130–1136
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2001) Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. Int J Cancer 94:153–156
Wakeford R (2004) The cancer epidemiology of radiation. Oncogene 23:6404–6428
Ronckers CM, Erdman CA, Land CE (2005) Radiation and breast cancer: a review of current evidence. Breast Cancer Res 7:21–32
John EM, Kelsey JL (1993) Radiation and other environmental exposures and breast cancer. Epidemiol Rev 15:157–162
Holmberg E, Holm LE, Lundell M, Mattsson A, Wallgren A, Karlsson P (2001) Excess breast cancer risk and the role of parity, age at first childbirth and exposure to radiation in infancy. Br J Cancer 85:362–366
Brenneman MA, Weiss AE, NickoloV JA, Chen DJ (2000) XRCC3 is required for eYcient repair of chromosome breaks by homologous recombination. Mutat Res 459:89–97
Forget AL, Bennett BT, Knight KL (2004) XRCC3 is recruited to DNA double-strand breaks early and independent of RAD51. J Cell Biochem 93:429–436
Manuguerra M, Saletta F, Karagas MR, Berwick M, Veglia F, Vineis P, Matullo G (2006) XRCC3 and XPD/ERCC2 single nucleotide polymorphisms and the risk of cancer: a HuGE review. Am J Epidemiol 164:297–302
Economopoulos KP, Sergentanis TN (2010) XRCC3 Thr241Met polymorphism and breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 121(2):439–443
Qiu LX, Mao C, Yao L, Yu KD, Zhan P, Chen B, Liu HG, Yuan H, Zhang J, Xue K, Hu XC (2010) XRCC3 5′-UTR and IVS5–14 polymorphisms and breast cancer susceptibility: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 122:489–493
Silva SN, Tomar M, Paulo C, Gomes BC, Azevedo AP, Teixeira V, Pina JE, Rueff J, Gaspar JF (2010) Breast Cancer risk and common single nucleotide polymorphisms in homologous recombination DNA repair pathway genes XRCC2, XRCC3, NBS1 and RAD51. Cancer Epidemiol 34:85–92
Zhang L, Zhang Z, Yan W (2005) Single nucleotide polymorphisms for DNA repair genes in breast cancer patients. Clin Chim Acta 359:150–155
Thyagarajan B, Anderson KE, Folsom AR, Jacobs DR Jr, Lynch CF, Bargaje A, Khaliq W, Gross MD (2006) No association between XRCC1 and XRCC3 gene polymorphisms and breast cancer risk: Iowa Women’s Health Study. Cancer Detect Prev 30:313–321
Han J, Hankinson SE, Ranu H, De Vivo I, Hunter DJ (2004) Polymorphisms in DNA double-strand break repair genes and breast cancer risk in the Nurses’ Health Study. Carcinogenesis 25:189–195
Webb PM, Hopper JL, Newman B, Chen X, Kelemen L, Giles GG, Southey MC, Chenevix-Trench G, Spurdle AB (2005) Double-strand break repair gene polymorphisms and risk of breast or ovarian cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14:319–323
García-Closas M, Egan KM, Newcomb PA, Brinton LA, Titus-Ernstoff L, Chanock S, Welch R, Lissowska J, Peplonska B, Szeszenia-Dabrowska N, Zatonski W, Bardin-Mikolajczak A, Struewing JP (2006) Polymorphisms in DNA double-strand break repair genes and risk of breast cancer: two population-based studies in USA and Poland, and meta-analyses. Hum Genet 119:376–388
Figueiredo JC, Knight JA, Briollais L, Andrulis IL, Ozcelik H (2004) Polymorphisms XRCC1–R399Q and XRCC3–T241M and the risk of breast cancer at the Ontario site of the Breast Cancer Family Registry. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 13:583–591
Jacobsen NR, Nexø BA, Olsen A, Overvad K, Wallin H, Tjønneland A, Vogel U (2003) No association between the DNA repair gene XRCC3 T241M polymorphism and risk of skin cancer and breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 12:584–585
Brooks J, Shore RE, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, Currie D, Afanasyeva Y, Koenig KL, Arslan AA, Toniolo P, Wirgin I (2008) Polymorphisms in RAD51, XRCC2, and XRCC3 are not related to breast cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 17:1016–1019
Millikan RC, Player JS, Decotret AR, Tse CK, Keku T (2005) Polymorphisms in DNA repair genes, medical exposure to ionizing radiation, and breast cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14:2326–2334
Lee SA, Lee KM, Park SK, Choi JY, Kim B, Nam J, Yoo KY, Noh DY, Ahn SH, Kang D (2007) Genetic polymorphism of XRCC3 Thr241Met and breast cancer risk: case–control study in Korean women and meta-analysis of 12 studies. Breast Cancer Res Treat 103:71–76
Loizidou MA, Michael T, Neuhausen SL, Newbold RF, Marcou Y, Kakouri E, Daniel M, Papadopoulos P, Malas S, Kyriacou K, Hadjisavvas A (2008) Genetic polymorphisms in the DNA repair genes XRCC1, XRCC2 and XRCC3 and risk of breast cancer in Cyprus. Breast Cancer Res Treat 112:575–579
Costa S, Pinto D, Pereira D, Rodrigues H, Cameselle-Teijeiro J, Medeiros R, Schmitt F (2007) DNA repair polymorphisms might contribute differentially on familial and sporadic breast cancer susceptibility: a study on a Portuguese population. Breast Cancer Res Treat 103:209–217
Jara L, Dubois K, Gaete D, de Mayo T, Ratkevicius N, Bravo T, Margarit S, Blanco R, Gomez F, Waugh E, Peralta O, Reyes JM, Ibanez G, Gonzalez-Hormazabal P (2010) Variants in DNA double-strand break repair genes and risk of familial breast cancer in a South American population. Breast Cancer Res Treat 122:813–822
Dufloth RM, Costa S, Schmitt F, Zeferino LC (2005) DNA repair gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to familial breast cancer in a group of patients from Campinas, Brazil. Genet Mol Res 4:771–782
Smith TR, Levine EA, Perrier ND, Miller MS, Freimanis RI, Lohman K, Case LD, Xu J, Mohrenweiser HW, Hu JJ (2003) DNA-repair genetic polymorphisms and breast cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 12:1200–1204
Kuschel B, Auranen A, McBride S, Novik KL, Antoniou A, Lipscombe JM, Day NE, Easton DF, Ponder BA, Pharoah PD, Dunning A (2002) Variants in DNA double-strand break repair genes and breast cancer susceptibility. Hum Mol Genet 11:1399–1407
Krupa R, Synowiec E, Pawlowska E, Morawiec Z, Sobczuk A, Zadrozny M, Wozniak K, Blasiak J (2009) Polymorphism of the homologous recombination repair genes RAD51 and XRCC3 in breast cancer. Exp Mol Pathol 87:32–35
Smith TR, Levine EA, Freimanis RI, Akman SA, Allen GO, Hoang KN, Liu-Mares W, Hu JJ (2008) Polygenic model of DNA repair genetic polymorphisms in human breast cancer risk. Carcinogenesis 29:2132–2138
Smith TR, Miller MS, Lohman K, Lange EM, Case LD, Mohrenweiser HW, Hu JJ (2003) Polymorphisms of XRCC1 and XRCC3 genes and susceptibility to breast cancer. Cancer Lett 190:183–190
Sterpone S, Mastellone V, Padua L, Novelli F, Patrono C, Cornetta T, Giammarino D, Donato V, Testa A, Cozzi R (2010) Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in BER and HRR genes, XRCC1 haplotypes and breast cancer risk in Caucasian women. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136:631–636
Sangrajrang S, Schmezer P, Burkholder I, Boffetta P, Brennan P, Woelfelschneider A, Bartsch H, Wiangnon S, Cheisilpa A, Popanda O (2007) The XRCC3 Thr241Met polymorphism and breast cancer risk: a case–control study in a Thai population. Biomarkers 12:523–532
Försti A, Angelini S, Festa F, Sanyal S, Zhang Z, Grzybowska E, Pamula J, Pekala W, Zientek H, Hemminki K, Kumar R (2004) Single nucleotide polymorphisms in breast cancer. Oncol Rep 11:917–922
Pharoah PD, Tyrer J, Dunning AM, Easton DF, Ponder BA (2007) Association between common variation in 120 candidate genes and breast cancer risk. PLoS Genet 3:e42
Breast Cancer Association Consortium (2006) Commonly studied single-nucleotide polymorphisms and breast cancer: results from the Breast Cancer Association Consortium. J Natl Cancer Inst 98:1382–1396
Davey SG, Egger M (1997) Meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. Lancet 350:1182
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analysis. Br Med J 327:557–560
Mantel N, Haenszel W (1959) Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. Natl Cancer Inst 22:719–748
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7:177–188
Begg CB, Mazumdar M (1994) Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 50:1088–1101
Egger M, Smith DG, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Br Med J 315:629–634
Higgins JPT, Green S (2008) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.0.1. The Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xiao-feng He, Wu Wei, and Wei Wang contributed equally to this work and should be considered as co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, XF., Wei, W., Su, J. et al. Association between the XRCC3 polymorphisms and breast cancer risk: meta-analysis based on case–control studies. Mol Biol Rep 39, 5125–5134 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1308-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1308-y