Abstract
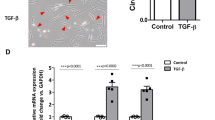
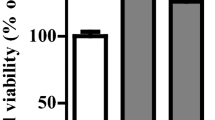
Metastasis of tumor cells is associated with epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), which is a process whereby epithelial cells lose their polarity and acquire new features of mesenchyme. EMT has been reported to be induced by transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), but its mechanism remains elusive. In this study, we performed a study to investigate whether PI3K/Akt and MAPK/Erk1/2 signaling pathways involved in EMT in the human lung cancer A549 cells. The results showed that after treated with TGF-β1 for 48 h, A549 cells displayed more fibroblast-like shape, lost epithelial marker E-cadherin and increased mesenchymal markers Vimentin and Fibronectin. Moreover, TGF-β1-induced EMT after 48 h was accompanied by increased of cell migration and change of Akt and Erk1/2 phosphorylation. In addition, EMT was reversed by PI3K inhibitor LY294002 and MEK1/2 inhibitor U0126, which suggested that A549 cells under stimulation of TGF-β1 undergo a switch into mesenchymal cells and PI3K/Akt and MAPK/Erk1/2 signaling pathways serve to regulate TGF-β1-induced EMT of A549 cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
- FGF:
-
Fibroblast growth factor
- HGF/SF:
-
Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor
- TGF-β1:
-
Transforming growth factor-β1
- TβRI:
-
TGF-β receptors type I
- TβRII:
-
TGF-β receptors type II
References
Voulgari A, Pintzas A (2009) Epithelial–mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis: mechanisms, markers and strategies to overcome drug resistance in the clinic. Biochim Biophys Acta 66:8319–8326
Yang Y, Pan X, Lei W, Wang J, Song J (2006) Transforming growth factor-beta1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and apoptosis via a cell cycle-dependent mechanism. Oncogene 25:7235–7244
Christiansen JJ, Rajasekaran AK (2006) Reassessing epithelial to mesenchymal transition as a prerequisite for carcinoma invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res 66:8319–8326
Cowin P, Rowlands TM, Hatsell SJ (2005) Cadherins and catenins in breast cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17:499–508
Junghans D, Haas IG, Kemler R (2005) Mammalian cadherins and protocadherins: about cell death, synapses and processing. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17:446–452
Thiery JP (2002) Epithelial–mesenchymal transitions in tumor progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2:442–454
Grunert S, Jechlinger M, Beug H (2003) Diverse cellular and molecular mechanisms contribute to epithelial plasticity and metastasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:657–665
Chou TY, Chen WC, Lee AC, Hung SM, Shih NY, Chen MY et al (2009) Clusterin silencing in human lung adenocarcinoma cells induces a mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition through modulating the ERK/Slug pathway. Cell Signal 21:704–711
Fan JM, Ng YY, Hill PA, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Mu W, Atkins RC et al (1999) Transforming growth factor-beta regulates tubular epithelial–myofibroblast transdifferentiation in vitro. Kidney Int 56:1455–1467
Kasai H, Allen JT, Mason RM, Kamimura T, Zhang Z (2005) TGF-beta1 induces human alveolar epithelial to mesenchymal cell transition (EMT). Respir Res 6:56
Ellenrieder V, Hendler SF, Boeck W, Seufferlein T, Menke A, Ruhland C et al (2001) Transforming growth factor-β1 treatment leads to an epithelial–mesenchymal transdifferentiation of pancreatic cancer cells requiring extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 activation. Cancer Res 61:4222–4228
Yang J, Liu Y (2001) Dissection of key events in tubular epithelial tomyofibroblast transition and its implications in renal interstitial fibrosis. Am J Pathol 159:1465–1475
Sarrió D, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Hardisson D, Cano A, Moreno-Bueno G, Palacios J et al (2008) Epithelial–mesenchymal transition in breast cancer relates to the basal-like phenotype. Cancer Res 68:989–997
Miettinen PJ, Ebner R, Lopez AR, Derynck R (1994) TGF-β-induced transdifferentiation of mammary epithelial cells to mesenchymal cells: involvement of type I receptors. J Cell Biol 127:2021–2036
Maeda M, Johnson KR, Wheelock MJ (2005) Cadherin switching: essential for behavioral but not morphological changes during an epithelium-to-mesenchyme transition. J Cell Sci 118:873–887
Shintani Y, Maeda M, Chaika N, Johnson KR, Wheelock MJ (2008) Collagen I promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells via transforming growth factor-beta signaling. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 38:95–104
Sporn MB (1996) The war on cancer. Lancet 347:1377–1381
Larue L, Bellacosa A (2005) Epithelial–mesenchymal transition in development and cancer: role of phosphatidylinositol 3′ kinase/AKT pathways. Oncogene 24:7443–7454
Thiery JP, Sleeman JP (2006) Complex networks orchestrate epithelial–mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:131–142
Mulder KM (2000) Role of Ras and Mapks in TGF-beta signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 11:23–35
Wai PY, Kuo PC (2008) Osteopontin: regulation in tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 27:103–118
Rangaswami H, Kundu GC (2007) Osteopontin stimulates melanoma growth and lung metastasis through NIK/MEKK1-dependent MMP-9 activation pathways. Oncol Rep 18:909–915
Greenlee RT, Hill-Harmon MB, Murray T, Thun M (2001) Cancer statistics, 2001. CA Cancer J Clin 51:15–36
Gupta GP, Massague J (2006) Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell 127:679–695
Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC (2002) Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev Cancer 2:563–572
Gatenby RA, Gillies RJ (2008) A microenvironmental model of carcinogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 8:56–61
Huber MA, Kraut N, Beug H (2005) Molecular requirements for epithelial–mesenchymal transition during tumor progression. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17:548–558
Thiery JP (2003) Epithelial–mesenchymal transitions in development and pathologies. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15:740–746
Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R, Thompson EW (2006) The epithelial–mesenchymal transition: new insights in signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol 172:973–981
Xu J, Lamouille S, Derynck R (2009) TGF-β-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res 19:156–172
Massague J (2000) How cells read TGF-beta signals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 1:169–178
Derynck R, Zhang YE (2003) Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signaling. Nature 425:577–584
Moustakas A, Heldin CH (2005) Non-Smad TGF-β signals. J Cell Sci 118:3573–3584
Derynck R, Akhurst RJ, Balmain A (2001) TGF-beta signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Nat Genet 29:117–129
Janda E, Lehmann K, Killisch I, Jechlinger M, Herzig M, Downward J et al (2002) Ras and TGF[beta] cooperatively regulate epithelial cell plasticity and metastasis: dissection of Ras signaling pathways. J Cell Biol 156:299–313
Gotzmann J, Huber H, Thallinger C, Wolschek M, Jansen B, Schulte-Hermann R et al (2002) Hepatocytes convert to a fibroblastoid phenotype through the cooperation of TGF-beta1 and Ha-Ras: steps towards invasiveness. J Cell Sci 115:1189–1202
Yan W, Fu Y, Tian D, Liao J, Liu M, Wang B (2009) PI3kinase/Akt signaling mediates epithelial–mesenchymal transition in hypoxic hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 382:631–636
Cho HJ, Baek KE, Saika S, Jeong MJ, Yoo J (2007) Snail is required for transforming growth factor-beta-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition by activating PI3 kinase/Akt signal pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 353:337–343
Grände M, Franzen A, Karlsson JO, Ericson LE, Heldin NE, Nilsson M et al (2002) Transforming growth factor-beta and epidermal growth factor synergistically stimulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) through a MEK-dependent mechanism in primary cultured pig thyrocytes. J Cell Sci 115:4227–4236
Uttamsingh S, Bao X, Nguyen KT, Bhanot M, Gong J, Chan JL et al (2008) Synergistic effect between EGF and TGF-beta1 in inducing oncogenic properties of intestinal epithelial cells. Oncogene 27:2626–2634
Xie L, Law BK, Chytil AM, Brown KA, Aakre ME, Moses HL et al (2004) Activation of the Erk pathway is required for TGF-beta1-induced EMT in vitro. Neoplasia 6:603–610
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from National Science Foundation of China (No. 30872553 and 30800631) and Shanghai Science and Technology Committee (No. 10JC1419200).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
X.-F. Chen and H.-J. Zhang contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, XF., Zhang, HJ., Wang, HB. et al. Transforming growth factor-β1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human lung cancer cells via PI3K/Akt and MEK/Erk1/2 signaling pathways. Mol Biol Rep 39, 3549–3556 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1128-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1128-0