Abstract
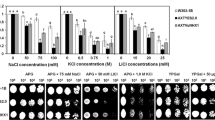
We have cloned a Na+/H+ antiporter gene (GenBank accession no EF440291, PtNHA1) from Puccinellia tenuiflora (so-called alkali grass in Chinese) roots under NaCl salt stress. Its cDNA is 3775 bp and contains a 3414 bp open reading frame. The amino acid sequences of PtNHA1 show high identities with a putative plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter from wheat. PtNHA1 was predicted to contain 11 hypothetical transmembrane domains in the N-terminal part and to localize in the plasma membrane. Genomic DNA gel blot analysis shows that PtNHA1 is a single-copy gene in the alkali grass genome. PtNHA1 is highly expressed in leaves, roots and shoots by RNA gel blot analysis. Furthermore, PtNHA1 gene expression of alkali grass was clearly up-regulated by NaCl salt stress. Overexpression of PtNHA1 in Arabidopsis resulted in enhanced tolerance of transgenic plants to NaCl stress. The ion contents analysis shows that, compared with the wild-type (WT), less Na+ and more K+ were accumulated in transgenic plants under NaCl stress. The results indicate that PtNHA1 play an important role in NaCl salt stress. Additionally, compared with the WT, total activities of ascorbate peroxidase (APX) and catalase (CAT), two key reactive oxygen species (ROS) detoxifying enzymes were high in transgenic plants under salt stress, respectively. The transcript levels of two APX genes (Apx1, s/mApx) and two CAT genes (Cat1, Cat2) in transgenic plants were higher than those in WT. This suggests that overexpression of PtNHA1 results in enhanced ROS-scavenging enzymes of transgenic plants under NaCl salt stress.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maathuis FJM, Amtmann A (1999) K+ nutrition and Na+ toxicity: the basis of cellular K+/Na+ ratios. Ann Bot 84:123–133
Tester M, Davenport R (2003) Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. Ann Bot 91:503–527
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Apse MP, Aharon GS, Sneddon WA, Blumwald E (1999) Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter in Arabidopsis. Science 285:1256–1258
Zhang HX, Hodson J, Williams JP, Blumwald E (2001) Engineering salt tolerant Brassica plants: characterization of yield and seed oil quality in transgenic plants with increased vacuolar sodium accumulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12832–12836
Guan B, Hu YZ, Zeng YL, Wang Y, Zhang FC (2010) Molecular characterization and functional analysis of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene (HcNHX1) from Halostachys caspica. Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11033-010-0307-8
Jha A, Joshi M, Yadav NS, Agarwal PK, Jha B (2010) Cloning and characterization of the Salicornia brachiata Na+/H+ antiporter gene SbNHX1 and its expression by abiotic stress. Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11033-010-0318-5
Blumwald E, Aharon GS, Apse MP (2000) Sodium transport in plant cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1465:140–151
Shi H, Quintero FJ, Pardo JM, Zhu JK (2002) The putative plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS 1 controls long distance Na+ transport in plants. Plant Cell 14:465–477
Shabala L, Cuin TA, Newman I, Shabala S (2005) Salinity-induced ion flux patterns from the excised roots of Arabidopsis sos mutants. Planta 222:1041–1050
Shi H, Ishitani M, Kim C, Zhu JK (2000) The Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance gene SOS 1 encodes a putative Na+/H+ antiporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6896–6901
Qiu QS, Guo Y, Dietrich MA, Schumaker KS, Zhu JK (2002) Regulation of SOS 1 , a plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchanger in Arabidopsis thaliana, by SOS 2 and SOS 3 . Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8436–8441
Shi H, Lee BH, Wu SJ, Zhu JK (2003) Overexpression of a plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter gene improves salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Biotechnol 21:81–85
Katiyar-Agarwal S, Zhu JH, Kim KM, Agarwal M, Fu XM, Huang A, Zhu J-K (2006) The plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 interacts with RCD1 and functions in oxidative stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:18816–18821
Verslues PE, Batelli G, Grillo S, Agius F, Kim Y-S, Zhu J, Agarwal M, Katiyar-Agarwal S, Zhu J-K (2007) Interaction of SOS2 with nucleoside diphosphate kinase 2 and catalases reveals a point of connection between salt stress and H2O2 signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Cell Biol 27:7771–7780
Zhu YJ, Zhang Y, Hu ZZ, Yan SG (2001) Studies on the microscopic structure of Puccinellis tenuiflora roots under different salinity stress. Grassland of China 1:37–40
Peng YH, Zhu YF, Mao YQ, Wang SM, Su WA, Tang ZC (2004) Alkali grass resists salt stress through high [K+] and an endodermis barrier to Na+. J Exp Bot 55:939–949
Wang YC, Chua Y-G, Liu GF, Wang M-H, Jiang J, Hou YJ, Qu GZ, Yang CP (2007) Identification of expressed sequence tags in an alkali grass (Puccinellia tenuiflora) cDNA library. J Plant Physiol 164:78–89
Wang YC, Yang CP, Liu GF, Jiang J (2007) Development of a cDNA microarray to identify gene expression of Puccinellia tenuiflora under saline-alkali stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 45:567–576
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Chen GX, Asada K (1989) Ascorbate peroxidase in tea leaves: occurrence of two isozymes and the differences in their enzymatic and molecular properties. Plant Cell Physiol 30:987–998
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutases. I. Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol 59:309–314
Rao MV, Paliyath G, Ormrod DP (1996) Ultraviolet-B- and ozone induced biochemical changes in antioxidant enzymes of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 110:125–136
Xu HX, Jiang XY, Zhan KH, Cheng XY, Chen XJ, Pardo JM, Cui DQ (2008) Functional characterization of a wheat plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter in yeast. Arch Biochem Biophys 473:8–15
Wang WX, Vinocur B, Altman A (2003) A plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 218:1–14
Zhu JK (2002) Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:247–273
Wu SJ, Lei D, Zhu JK (1996) SOS1, a genetic locus essential for salt tolerance and potassium acquisition. Plant Cell 8:617–627
Niu XM, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM, Pardo JM (1995) Ion homeostasis in NaCl stress environments. Plant Physiol 109:735–742
Pardo JM, Cubero B, Leidi EO, Quintero FJ (2006) Alkali cation exchangers: roles in cellular homeostasis and stress tolerance. J Exp Bot 57:1181–1199
Gao XH, Ren ZH, Zhao YX, Zhang H (2003) Overexpression of SOD2 Increases salt tolerance of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 133:1873–1881
Volkov V, Amtmann A (2006) Thellungiella halophila, a salt-tolerant relative of Arabidopsis thaliana, has specific root ion-channel features supporting K+/Na+ homeostasis under salinity stress. Plant J 48:342–353
Davenport RJ, Munoz-Mayor A, Jha D, Essah PA, Rus A, Tester M (2007) The Na+ transporter AtHKT1;1 controls retrieval of Na+ from the xylem in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 30:497–507
Byrt CS, Platten JD, Spielmeyer W, James RA, Lagudah ES, Dennis ES, Tester M, Munns R (2007) HKT1; 5-like cation transporters linked to Na+ exclusion loci in wheat, Nax2 and Kna1. Plant Physiol 143:1918–1928
Huang S, Spielmeyer W, Lagudah ES, Munns R (2008) Comparative mapping of HKT genes in wheat, barley, and rice, key determinants of Na+ transport, and salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 59:927–937
Qi Z, Spalding EP (2004) Protection of plasma membrane K+ transport by the salt overly sensitive Na+/H+ antiporter during salinity stress. Plant Physiol 136:2548–2555
Qiu QS, Guo Y, Quintero FJ, Pardo JM, Schumaker KS, Zhu JK (2004) Regulation of vacuolar Na+/H+ exchange in Arabidopsis thaliana by the Salt-Overly-Sensitive (SOS) pathway. J Biol Chem 279:207–215
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 55:373–399
Inze D, Montagu MV (1995) Oxidative stress in plants. Curr Opin Biotechnol 6:153–158
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, Van Breusegem F (2004) Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci 9:490–498
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this research was provided by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (DL09EA01) and Youth Science Research Foundation of Harbin City (2005AFQXJ024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Yang, R., Wang, B. et al. Functional characterization of a plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter from alkali grass (Puccinellia tenuiflora). Mol Biol Rep 38, 4813–4822 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0624-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0624-y