Abstract
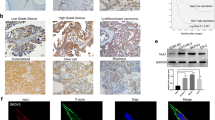
Protein kinases are involved in comprehensive cellular processes and also implicated in many human diseases. SH3-binding domain kinase 1 (SBK1) was first cloned and characterized in rat and the human cDNA was cloned in our lab in 2006, but the expression and function of endogenous protein have not been well studied in human. In this follow up study, we screened a panel of cell lines and tissues, as well as a tumor tissue array for SBK1 expression at both RNA and protein levels. To detect the protein, we generated the first rabbit polyclonal antibody against human SBK1. We show that the SBK1 is expressed in most of the cells and tissues examined, and the protein is highly up-regulated in ovarian serous adenocarcinoma while down-regulated in esophagus squamous cell carcinoma and stomach adenocarcinoma. When over-expressed in an ovarian cancer cells SK-OV-3 by adenovirus infection, SBK1 protected the cells from apoptosis induced by the viral infection, therefore promoting cancer cell survival. Given that a missense mutation K92E in human SBK1 was identified recently from ovarian mucinous carcinoma, together, these results suggest that the wide-spread expression pattern of human SBK1 may predict a broad cellular function, and its dysregulated in certain cancers suggests an involvement of the protein in the pathogenesis of human cancers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lahiry P, Torkamani A, Schork NJ, Hegele RA (2010) Kinase mutations in human disease: interpreting genotype–phenotype relationships. Nat Rev Genet 11:60–74
Stenberg KA, Riikonen PT, Vihinen M (2000) KinMutBase, a database of human disease-causing protein kinase mutations. Nucleic Acids Res 28:369–371
Ortutay C, Valiaho J, Stenberg K, Vihinen M (2005) KinMutBase: a registry of disease-causing mutations in protein kinase domains. Hum Mutat 25:435–442
Knight ZA, Lin H, Shokat KM (2010) Targeting the cancer kinome through polypharmacology. Nat Rev Cancer 10:130–137
Fedorov O, Muller S, Knapp S (2010) The (un)targeted cancer kinome. Nat Chem Biol 6:166–169
Manning G, Whyte DB, Martinez R, Hunter T, Sudarsanam S (2002) The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science 298:1912–1934
Park J, Hu Y, Murthy TV, Vannberg F, Shen B, Rolfs A, Hutti JE, Cantley LC, Labaer J, Harlow E et al (2005) Building a human kinase gene repository: bioinformatics, molecular cloning, and functional validation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:8114–8119
Nara K, Akasako Y, Matsuda Y, Fukazawa Y, Iwashita S, Kataoka M, Nagai Y (2001) Cloning and characterization of a novel serine/threonine protein kinase gene expressed predominantly in developing brain. Eur J Biochem 268:2642–2651
Chung CY, Seo H, Sonntag KC, Brooks A, Lin L, Isacson O (2005) Cell type-specific gene expression of midbrain dopaminergic neurons reveals molecules involved in their vulnerability and protection. Hum Mol Genet 14:1709–1725
Corti S, Locatelli F, Papadimitriou D, Donadoni C, Del Bo R, Crimi M, Bordoni A, Fortunato F, Strazzer S, Menozzi G et al (2006) Transplanted ALDHhiSSClo neural stem cells generate motor neurons and delay disease progression of nmd mice, an animal model of SMARD1. Hum Mol Genet 15:167–187
Wang P, Wang X, Wang F, Wu J (2006) Cloning of human SBK1 cDNA and screening of its interaction proteins. Chin J Biochem Mol Biol 22:313–321
Kent WJ, Sugnet CW, Furey TS et al (2002) The human genome browser at UCSC. Genome Res 12:996–1006
Chou CM, Chen YC, Lee MT, Chen GD, Lu IC, Chen ST, Huang CJ (2006) Expression and characterization of a brain-specific protein kinase BSK146 from zebrafish. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 340:767–775
Wang H, Wang P, Sun X, Luo Y, Wang X, Ma D, Wu J (2007) Cloning and characterization of a novel caspase-10 isoform that activates NF-kappa B activity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1770:1528–1537
Cokol M, Nair R, Rost B (2000) Finding nuclear localization signals. EMBO Rep 1:411–415
Kosugi S, Hasebe M, Tomita M, Yanagawa H (2009) Systematic identification of cell cycle-dependent yeast nucleocytoplasmic shuttling proteins by prediction of composite motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:10171–10176
Sukiennicki TL, Fowell DJ (2006) Distinct molecular program imposed on CD4+ T cell targets by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol 177:6952–6961
Huster D, Purnat TD, Burkhead JL, Ralle M, Fiehn O, Stuckert F, Olson NE, Teupser D, Lutsenko S (2007) High copper selectively alters lipid metabolism and cell cycle machinery in the mouse model of Wilson disease. J Biol Chem 282:8343–8355
LaRosa PC, Riethoven JJ, Chen H, Xia Y, Zhou Y, Chen M, Miner J, Fromm ME (2007) Trans-10, cis-12 conjugated linoleic acid activates the integrated stress response pathway in adipocytes. Physiol Genomics 31:544–553
Magnusson PU, Dimberg A, Mellberg S, Lukinius A, Claesson-Welsh L (2007) FGFR-1 regulates angiogenesis through cytokines interleukin-4 and pleiotrophin. Blood 110:4214–4222
Urashima T, Zhao M, Wagner R, Fajardo G, Farahani S, Quertermous T, Bernstein D (2008) Molecular and physiological characterization of RV remodeling in a murine model of pulmonary stenosis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295:H1351–H1368
Niklaus AL, Pollard JW (2006) Mining the mouse transcriptome of receptive endometrium reveals distinct molecular signatures for the luminal and glandular epithelium. Endocrinology 147:3375–3390
Huang F, Reeves K, Han X, Fairchild C, Platero S, Wong TW, Lee F, Shaw P, Clark E (2007) Identification of candidate molecular markers predicting sensitivity in solid tumors to dasatinib: rationale for patient selection. Cancer Res 67:2226–2238
Gatfield D, Le Martelot G, Vejnar CE, Gerlach D, Schaad O, Fleury-Olela F, Ruskeepaa AL, Oresic M, Esau CC, Zdobnov EM et al (2009) Integration of microRNA miR-122 in hepatic circadian gene expression. Genes Dev 23:1313–1326
Shi S, Yu L, Chiu C, Sun Y, Chen J, Khitrov G, Merkenschlager M, Holzman LB, Zhang W, Mundel P et al (2008) Podocyte-selective deletion of dicer induces proteinuria and glomerulosclerosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:2159–2169
Trynka G, Zhernakova A, Romanos J, Franke L, Hunt KA, Turner G, Bruinenberg M, Heap GA, Platteel M, Ryan AW et al (2009) Coeliac disease-associated risk variants in TNFAIP3 and REL implicate altered NF-kappaB signalling. Gut 58:1078–1083
Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, Macek B, Kumar C, Mortensen P, Mann M (2006) Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks. Cell 127:635–648
Richardson CJ, Gao Q, Mitsopoulous C, Zvelebil M, Pearl LH, Pearl FM (2009) MoKCa database—mutations of kinases in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D824–D831
Greenman C, Stephens P, Smith R, Dalgliesh GL, Hunter C, Bignell G, Davies H, Teague J, Butler A, Stevens C et al (2007) Patterns of somatic mutation in human cancer genomes. Nature 446:153–158
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 30600549).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Guo, J., Wang, F. et al. Human SBK1 is dysregulated in multiple cancers and promotes survival of ovary cancer SK-OV-3 cells. Mol Biol Rep 38, 3551–3559 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0465-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0465-8