Abstract
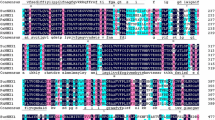
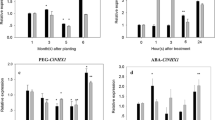
According to sequences of several vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter genes from Xinjiang halophytic plants, a new vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene (HcNHX1) from the halophyte Halostachys caspica was obtained by RACE and RT-PCR using primers corresponding to conserved regions of the coding sequences. The obtained HcNHX1 cDNA was 1,983 bp and contained a 1,656 bp open reading frame encoding a deduced protein of 551 amino acid residues. The deduced amino acid sequence showed high identity with other NHX1 we have cloned previously from halophyte in Xinjiang desert area. The phylogenetic analysis showed that HcNHX1 formed a clade with NHX homologs of Chenopodiaceae. Expression profiles under salt treatment and ABA induction were investigated, and the results revealed that expression of HcNHX1 was induced by NaCl and ABA. To compare the degree of salt tolerance, we over-expressed HcNHX1 in Arabidopsis. Two transgenic lines grew more vigorously than the wild type (WT) under salt stress. The analysis of ion contents indicated that under salt stress, the transgenic plants compartmentalized more Na+ in the leaves compared with wild-type plants. Together, these results suggest that the products of the novel gene HcNHX1 from halophyte Halostachys caspica is a functional tonoplast Na+/H+ antiporter.









Similar content being viewed by others

Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- NHX :
-
Na+/H+ antiporter gene
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- RACE:
-
Rapid amplification of cDNA ends
References
Xu H, Li K, Yang F, Shi Q, Wang X (2009) Overexpression of CsNMAPK in tobacco enhanced seed germination under salt and osmotic stresses. Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9895-6
Flowers TJ, Yeo AR (1995) Viewpoint. Breeding for salinity resistance in crop plants: where next? Aust J Plant Physiol 22:875–884
Agarwal PK, Gupta K, Jha B (2010) Molecular characterization of the Salicornia brachiata SbMAPKK gene and its expression by abiotic stress. Mol Biol Rep 37(2):981–986
Blumwald E, Aharon GS, Apse MP (2000) Sodium transport in plant cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1465:140–151
Glenn EP, Brown JJ, Blumwald E (1999) Salt tolerance and crop potential of halophytes. Crit Rev Plant Sci 18:227–255
Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA, Zhu JK, Bohnert HJ (2000) Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 51:463–499
Gaxiola RA, Rao R, Sherman A, Grisafi P, Alper SL, Fink GR (1999) The Arabidopsis thaliana proton transporters, AtNhx1 and Avp1, can function in cation detoxification in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96:1480–1485
Fukuda A, Nakamura A, Tanaka Y (1999) Molecular cloning and expression of the Na+/H+ exchanger gene in Oryza sativa. Biochim Biophys Acta 1446:149–155
Fukuda-Tanaka S, Inagaki Y, Yamaguchi T, Saito N, Iida S (2000) Colour enhancing protein in blue petals. Nature 407:581
Yamaguchi T, Fukada-Tanaka S, Inagaki Y, Saito N, Yonekura-Sakakibara K, Tanaka Y (2001) Genes encoding the vacuolar Na+/H+ exchanger and flower coloration. Plant Cell Physiol 42:451–461
Ohnishi M, Fukada-Tanaka S, Hoshino A, Takada J, Inagaki Y, Iida S (2005) Characterization of a novel Na+/H+ antiporter gene InNHX2 and comparison of InNHX2 with InNHX1, which is responsible for blue flower coloration by increasing the vacuolar pH in the Japanese morning glory. Plant Cell Physiol 46:259–267
Wang J, Zuo K, Wu W, Song J, Sun X, Lin J (2003) Molecular cloning and characterization of a new Na+/H+ antiporter gene from Brassica napus. DNA Seq 14:351–358
Wu CA, Yang GD, Meng QW, Zheng CC (2004) The cotton GhNHX1 gene encoding a novel putative tonoplast Na+/H+ antiporter plays an important role in salt stress. Plant Cell Physiol 45:600–607
Kagami T, Suzuki M (2005) Molecular and functional analysis of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene of Rosa hybrida. Genes Genet Syst 80:121–128
Zörb C, Noll A, Karl S, Leib K, Yan F, Schubert S (2005) Molecular characterization of Na+/H+ antiporters (ZmNHX) of maize (Zea mays L.) and their expression under salt stress. J Plant Physiol 162:55–66
Chauhan S, Forsthoefel N, Ran Y, Quigley F, Nelson DE, Bohnert HJ (2000) Na+/myo-inositol symporters and Na+/H+ antiport in Mesembryanthemum crystallinum. Plant J 24:511–522
Xia T, Apse MP, Aharon GS, Blumwald E (2002) Identification and characterization of a NaCl-inducible vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter in Beta vulgaris. Physiol Plant 116:206–212
Ma XL, Zhang Q, Shi HZ, Zhu JK, Zhao YX, Ma CL (2004) Molecular cloning and different expression of a vaculor Na+/H+ antiporter gene in Suaeda salsa under salt stress. Biol Plant 48:219–225
Hamada A, Shono M, Xia T, Ohta M, Hayashi Y, Tanaka A et al (2001) Isolation and characterization of a Na+/H+ antiporter gene from the halophyte Atriplex gmelini. Plant Mol Biol 46:35–42
Apse MP, Aharon GS, Sneddon WA, Blumwald E (1999) Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiport in Arabidopsis. Science 285:1256–1258
Gaxiola RA, Li J, Undurraga S, Dang LM, Allen GJ, Alper SL, Fink GR (2001) Drought- and salt-tolerant plants result from overexpression of the AVP1 H+ pump. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98:11444–11449
Zhang HX, Blumwald E (2001) Transgenic salt-tolerant tomato plants accumulate salt in foliage but not in fruit. Nat Biotechnol 19:765–768
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Wang YC, Qu GZ, Li HY, Wu YJ, Wang C, Liu GF, Yang CP (2010) Enhanced salt tolerance of transgenic poplar plants expressing a manganese superoxide dismutase from Tamarix androssowii. Mol Biol Rep 37:1119–1124. doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9884-9
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation: version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1:19–21
Chomczynski PY, Sacci N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidine thiocyanate phenol–chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Deng YB, Jiang YC, Liu J (1998) The xeromorphic and saline morphic structure of leaves and assimilating branches in ten Chenopodiacea species in Xinjiang. Acta Phytoecol Sin 22(2):164–170
Zhu JK (2001) Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plants Sci 6:66–71
Serrano R, Mulet J, Rios G, Marquez J, de Larrinoa I, Leube M, Mendizabal I, Pascual-Ahuir A, Proft M, Ros R, Montesinos C (1999) A glimpse of the mechanism of ion homeostasis during salt stress. J Exp Bot 50:1023–1036
Colmer TD, Epstein E, Dvorak J (1995) Differential solute regulation in leaf blades of various ages in salt-sensitive wheat and a salt-tolerant wheat Lophopyrum elongatum (Host) A. Love amphiploid. Plant Physiol 108:1715–1724
Munns R, Guo J, Passioura JB, Cramer GR (2000) Genetic variation for improving the salt tolerance of durum wheat. Aust J Agric Res 51:69–74
Munns R, James RA (2003) Screening methods for salinity tolerance: a case study with tetraploid wheat. Plant Soil 253:201–218
Saqib M, Akhtar J, Qureshi RH (2005) Na+ exclusion and salt resistance of wheat (Triticum aestivum) in saline-waterlogged conditions are improved by the development of adventitious nodal roots and cortical root aerenchyma. Plant Sci 169:125–130
Sümer A, Zörb C, Yan F, Schubert S (2004) Evidence of sodium toxicity for the vegetative growth of maize (Zea mays L.) during the first phase of salt stress. J Appl Bot 78:135–139
Saqib M, Zörb C, Rengel Z, Schubert S (2005) The expression of the endogenous vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporters in roots and shoots correlates positively with the salt resistance of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Sci 169:959–965
Aleman F, Nieves-Cordones M, Martnez V, Rubio F (2009) Potassium/sodium steady-state homeostasis in Thellungiella halophila and Arabidopsis thaliana under long-term salinity conditions. Plant Sci 176:768–774
Munns R (1993) Physiological processes limiting plant growth in saline soil: some dogmas and hypotheses. Plant Cell Environ 16:15–24
Tester M, Davenport R (2003) Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. Ann Bot 91:503–527
Flowers TJ, Colmer TD (2008) Salinity tolerance in halophytes. New Phytol 179:945–963
Wu T, Tian ZD, Liu J, Xie CH (2009) A novel leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase gene in potato, StLRPK1, is involved in response to diverse stresses. Mol Biol Rep 36:2365–2374. doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9459-9
Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2000) Molecular responses to dehydration and low temperature: differences and cross-talk between two stress signaling pathways. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:217–223
Zhu JK (2001) Cell signaling under salt, water and cold stresses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:401–406
Yokoi S, Quintero FJ, Cubero B, Ruiz MT, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM, Pardo JM (2002) Differential expression and function of Arabidopsis thaliana NHX Na+/H+ antiporters in the salt stress response. Plant J 30:529–539
Wu CX, Gao Xh, Kong XQ, Zhao YX, Zhang H (2009) Molecular cloning and functional analysis of a Na+/H+ antiporter gene ThNHX1 from a halophytic plant Thellungiella halophila. Plant Mol Biol Rep 27:1–12
Fukuda A, Nakamura A, Tagiri A, Tanaka H, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Tanaka Y (2004) Function, intracellular localization and the importance in salt tolerance of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter from rice. Plant Cell Physiol 45:146–159
Li WH, Zhang Q, Kong XQ, Wu CX, Ma XL, Zhang H, Zhao YX (2009) Salt tolerance is conferred in Arabidopsis by overexpression of the vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene SsNHX2, an alternative splicing variant of SsNHX1, from Suaeda salsa. J Plant Biol 52:147–153
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by Xinjiang Key Project of Science and Technology (No. 200731138) and the National Basic Research Supporting Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2009CB126006) to Dr Fuchun Zhang. We would like to thank Mr. Yonghai Liang and Mr. Alimu Abudula for their technical assistance of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.



Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, B., Hu, Y., Zeng, Y. et al. Molecular characterization and functional analysis of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene (HcNHX1) from Halostachys caspica . Mol Biol Rep 38, 1889–1899 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0307-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0307-8