Abstract
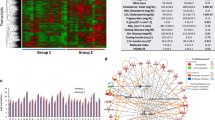
To better understand the molecular basis of dietary obesity, we examined adipose tissue genes differentially expressed in a well-characterized rat model of high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obesity using cDNA microarrays. Male Sprague–Dawley rats were fed either the HFD or the normal diet. Seven weeks later, the weights of obese models (362.92 ± 39.65 g) were significantly higher than those of normal control rats (315.22 ± 42.30 g, P < 0.01) and the wet weights of adipose tissue of rats fed with HFD (9.29 ± 5.14 g) were significantly higher than those of normal control rats (4.09 ± 2.69 g, P < 0.01), which confirmed the successful preparation of obese models. cDNA microarrays containing 9 216 genes/Ests were used to investigate gene expression of adipose tissue. Autoradiographic analysis showed that 532, 154, and 22 genes were differently expressed over 2-, 3-, and 5-fold, respectively. The analysis of gene expression profiles indicated that 276 genes were up-regulated and 432 genes were down-regulated in response to HFD-induced obesity. Different clusters of genes associated with lipid metabolism, extracellular matrix, signal transduction, cytoskeleton, cell apoptosis, etc., such as VLCS-H2, DGAT, ACADVL, PHYH, SCD, ACACA, ACS, MMP-2, MMP-15, CD38, CAMK2D, CACNA1F, CAPZA2, TMOD3, ARPC2, KNS2, TPM1, MAPK8, GADD45B, DAXX, TOK-1, PRKACA, STAT6, were concerned.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization (2000) Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of a WHO consultation. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser 894:1–253
Calle EE, Thun MJ, Petrelli JM et al (1999) Body-mass index and mortality in a prospective cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med 341:1097–1105
Popkin BM, Doak CM (1998) The obesity epidemic is a worldwide phenomenon. Nutr Rev 56:106–114
Tschop M, Heiman ML (2001) Rodent obesity models: an overview. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 109:307–319
Levin BE, Dunn-Meynell AA, McMinn JE et al (2003) A new obesity-prone, glucose-intolerant rat strain (F.DIO). Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 285:R1184–R1191
Farley C, Cook JA, Spar BD et al (2003) Meal pattern analysis of diet-induced obesity in susceptible and resistant rats. Obes Res 11:845–851
Roberts CK, Vaziri ND, Liang KH et al (2001) Reversibility of chronic experimental syndrome X by diet modification. Hypertension 37:1323–1328
Asselbergs FA, Widmer R (2003) Rapid detection of apoptosis through real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction measurement of the small cytoplasmic RNA Y1. Anal Biochem 318:221–229
Arner P (2000) Hunting for human obesity genes? Look in the adipose tissue!. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24:S57–S62
Trayhurn P, Beattie JH (2001) Physiological role of adipose tissue: white adipose tissue as an endocrine and secretory organ. Proc Nutr Soc 60:329–339
Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M et al (1994) Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 372:425–432
Montague CT, Farooqi IS, Whitehead JP et al (1997) Congenital leptin deficiency is associated with severe early onset obesity in humans. Nature 387:903–908
Strobel A, Issad T, Camoin L et al (1998) A leptin missense mutation associated with hypogonadism and morbid obesity. Nat Genet 18:213–215
Farooqi IS, Keogh JM, Kamath S et al (2001) Partial leptin deficiency and human adiposity. Nature 414:34–35
Jia JJ, Tian YB, Cao ZH et al (2010) The polymorphisms of UCP1 genes associated with fat metabolism, obesity and diabetes. Mol Biol Rep 37:1513–1522
Ying S, Liu XM, Sun YM et al (2009) Genetic polymorphism c.1438A > G of the 5-HT(2A) receptor is associated with abdominal obesity in Chinese Northern Han population. Mol Biol Rep 36:91–95
Nadler ST, Stoehr JP, Schueler KL et al (2000) The expression of adipogenic genes is decreased in obesity and diabetes mellitus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:11371–11376
Yu YH, Zhang Y, Oelkers P et al (2002) Posttranscriptional control of the expression and function of acyl-CoA: diacylglycerol acyltransferase-1 in mouse adipocytes. J Biol Chem 277:50876–50884
Antras J, Hilliou F, Redziniak G et al (1989) Decreased biosynthesis of actin and cellular fibronectin during adipose conversion of 3T3–F442A cells. Reorganization of the cytoarchitecture and extracellular matrix fibronectin. Biol Cell 66:247–254
Spiegelman BM, Ginty CA (1983) Fibronectin modulation of cell shape and lipogenic gene expression in 3t3-adipocytes. Cell 35:657–666
Xiao Y, Junfeng H, Tianhong L et al (2006) Cathepsin K in adipocyte differentiation and its potential role in the pathogenesis of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:4520–4527
Dunaif A (1999) Insulin action in the polycystic ovary syndrome. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 28:341–359
Kahn CR (1994) Banting lecture. Insulin action, diabetogenes, and the cause of type II diabetes. Diabetes 43:1066–1084
Llagostera E, Carmona MC, Vicente M et al (2009) High-fat diet induced adiposity and insulin resistance in mice lacking the myotonic dystrophy protein kinase. FEBS Lett 583:2121–2125
Jeong S, Yoon M (2009) Fenofibrate inhibits adipocyte hypertrophy and insulin resistance by activating adipose PPARalpha in high fat diet-induced obese mice. Exp Mol Med 41:397–405
Riant E, Waget A, Cogo H et al (2009) Estrogens protect against high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance and glucose intolerance in mice. Endocrinology 150:2109–2117
Zemel MB (1998) Nutritional and endocrine modulation of intracellular calcium: implications in obesity, insulin resistance and hypertension. Mol Cell Biochem 188:129–136
Gregoire FM, Smas CM, Sul HS (1998) Understanding adipocyte differentiation. Physiol Rev 78:783–809
Kohgo Y, Kato J (1998) Role of apoptosis on morphogenesis and therapy in malignancy. Intern Med 37:182–184
Qian H, Hausman GJ, Compton MM et al (1998) Leptin regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma, tumor necrosis factor, and uncoupling protein-2 expression in adipose tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 246:660–667
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 30973231, 30772364), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (No BK2007230), and the Foundation of Ministry of Education, China (No 20070312001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jie Qiu and Rui Cheng contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, J., Cheng, R., Zhou, Xy. et al. Gene expression profiles of adipose tissue of high-fat diet-induced obese rats by cDNA microarrays. Mol Biol Rep 37, 3691–3695 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0021-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0021-6