Abstract
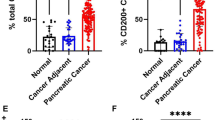
Periostin is over expressed in many epithelial malignant cancers, including lung cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer and colon cancer. It is related with the progression and migration of breast and ovarian cancer cells in vitro. The aim of this study was to investigate the serum level of periostin in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and its relationship with established biological and prognostic factors by enzyme-linked-immunosorbent serologic assay. We also observe the function of periostin on the proliferation and migration of human lung adenocarcinoma cell line (A549) and discuss the mechanism. The mean value for serum periostin (POSTN) was elevated in NSCLC patients (242.84 ± 5.33 pg/ml) compared to the normal healthy volunteers (215.66 ± 11.67 pg/ml) (p = 0.030). The serum level of periostin of NSCLC patients had no connection with gender, age, pathological type, TNM stage, lymph node status, tumor size and invasiveness. We constructed a plasmid named pEGFP-N1/POSTN expressing full-length human periostin. Transfecting the plasmid to A549 cells and periostin was efficiently expressed in transfected A549 cells. Our data showed that periostin could promote the proliferation and migration of A549 cells by inducing vimentin and N-cadherin expression and downregulating E-cadherin expression. These results strongly suggest that periostin is a novel molecular which play an important role during the progression and development of NSCLC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55:74–108. doi:10.3322/canjclin.55.2.74
Takeshita S, Kikuno R, Tezuka K, Amann E (1993) Osteoblast-specific factor 2: cloning of a putative bone adhesion protein with homology with the insect protein fasciclin I. Biochem J 294:271–278
Kruzynska-Frejtag A, Wang J, Maeda M, Rogers R, Krug E, Hoffman S et al (2004) Periostin is expressed within the developing teeth at the sites of epithelial-mesenchymal interaction. Dev Dyn 229:857–868. doi:10.1002/dvdy.10453
Kudo Y, Siriwardena BS, Hatano H, Ogawa I, Takata T (2007) Periostin: novel diagnostic and therapeutic target for cancer. Histol Histopathol 22:1167–1174
Gillan L, Matei D, Fishman DA, Gerbin CS, Karlan BY, Chang DD (2002) Periostin secreted by epithelial ovarian carcinoma is a ligand for αVβ3 and αVβ5 integrins and promotes cell motility. Cancer Res 62:5358–5364
Tai IT, Dai M, Chen LB (2005) Periostin induction in tumor cell line explants and inhibition of in vitro cell growth by anti-periostin antibodies. Carcinogenesis 26:908–915. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgi034
Horiuchi K, Amizuka N, Takeshita S, Takamatsu H, Katsuura M, Ozawa H et al (1999) Identification and characterization of a novel protein, periostin, with restricted expression to periosteum and periodontal ligament and increased expression by transforming growth factor β. J Bone Miner Res 14:1239–1249. doi:10.1359/jbmr.1999.14.7.1239
Ji X, Chen D, Xu C, Harris SE, Mundy GR, Yoneda T (2000) Patterns of gene expression associated with BMP-2-induced osteoblast and adipocyte differentiation of mesenchymal progenitor cell 3T3–F442A. J Bone Miner Metab 18:132–139. doi:10.1007/s007740050103
Lorts A, Schwanekamp JA, Elrod JW, Sargent MA, Molkentin JD (2009) Genetic manipulation of periostin expression in the heart does not affect myocyte content, cell cycle activity, or cardiac repair. Circ Res 104:e1–e7. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.188649
Sasaki BH, Sato Y, Kondo S, Fukai I, Kiriyama M, Yamakawa Y, Fuji Y (2002) Expression of the periostin mRNA Level in neuroblastoma. J Pediatr Surg 37:1293–1297. doi:10.1053/jpsu.2002.34985
Shao R, Bao S, Bai X, Blanchette C, Anderson RM, Dang T et al (2004) Acquired expression of periostin by human breast cancers promotes tumor angiogenesis through up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 expression. Mol Cell Biol 24:3992–4003. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.9.3992-4003.2004
Bao S, Ouyang G, Bai X, Huang Z, Ma C, Liu M (2004) Periostin potently promotes metastatic growth of colon cancer by augmenting cell survival via the Akt/PKB pathway. Cancer Cell 5:329–339. doi:10.1016/S1535-6108(04)00081-9
Chang Y, Lee TC, Li JC, Lai TL, Chua HH, Chen CL et al (2005) Differential expression of osteoblast-specific factor 2 and polymeric immunoglobulin receptor genes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Head Neck 27:873–882. doi:10.1002/hed.20253
Kudo Y, Ogawa I, Kitajima S, Kitagawa M, Kawai H, Gaffney PM, Miyauchi M, Takata T (2006) Periostin promotes invasion and anchorage-independent growth in the metastatic process of head and neck cancer. Cancer Res 66:6928–6935
Baril P, Gangeswaran R, Mahon PC, Caulee K, Kocher HM, Harada T et al (2007) Periostin promotes invasiveness and resistance of pancreatic cancer cells to hypoxia-induced cell death: role of the β4 integrin and the PI3 k pathway. Oncogene 26:2082–2094. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210009
Sasaki H, Auclair D, Fukai I, Kiriyama M, Yamakawa Y, Fuji Y et al (2001) Serum level of the periostin, a homologue of an insect cell adhesion molecule, as a prognostic marker in nonsmall cell lung carcinomas. Cancer 92:843–848. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(20010815)92:4<843::AID-CNCR1391>3.0.CO;2-P
Kang Y, Massague J (2004) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: twist in development and metastasis. Cell 118:277–279. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.07.011
Iwano M, Plieth D, Danoff TM, Xue C, Okada H, Neilson EG (2002) Evidence that fibroblasts derive from epithelium during tissue fibrosis. J Clin Invest 110:341–350. doi:10.1172/JCI15518
Greenburg G, Hay ED (1982) Epithelia suspended in collagen gels can lose polarity and express characteristics of migrating mesenchymal cells. J Cell Biol 95:333–339
Yilmaz M, Christofori G, Lehembre F (2007) Distinct mechanisms of tumor invasion and metastasis. Trends Mol Med 13:535–541. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2007.10.004
Blanco D, Vicent S, Elizegi E, Pino I, Fraga MF, Esteller M, Saffiotti U, Lecanda F, Montuenga LM (2004) Altered expression of adhesion molecules and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in silica-induced rat lung carcinogenesis. Lab Invest 84:999–1012. doi:10.1038/labinvest.3700129
Moch H, Schraml P, Bubendorf L, Mirlacher M, Konnen J, Gasser T, Mihatsch MJ, Kallioniemi OP, Sauter G (1999) High-throughput tissue microarray analysis to evaluate genes uncovered by cDNA microarray screening in renal cell carcinoma. Am J Pathol 154:981–986
Ngan CY, Yamamoto H, Seshimo I, Tsujino T, Man M, Ikeda JI et al (2007) Quantitative evaluation of vimentin expression in tumour stroma of colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 96:986–992. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6603651
Chen JH, Lin HH, Chiang TA, Ho HH, Lee YC, Wang CJ (2008) Gaseous nitrogen oxide promotes human lung cancer cell line A549 migration, invasion, and metastasis via iNOS-mediated MMP-2 production. Toxicol Sci 106:364–375. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfn195
Sasaki H, Yu CY, Dai M, Tam C, Loda M, Auclair D, Chen LB, Elias A (2003) Elevated serum periostin levels in patients with bone metastases from breast but not lung cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 77:245–252. doi:10.1023/A:1021899904332
Soltermann A, Tischler V, Arbogast S, Braun J, Hensch NP, Weder W, Moch H, Kristiansen G (2008) Prognostic significance of epithelial-mesenchymal and mesenchymal-epithelial transition protein expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14:7430–7437. doi:10.1158/1078-0432
Ouyang G, Liu M, Ruan K, Song G, Mao Y, Bao S (2009) Upregulated expression of periostin by hypoxia in non-small-cell lung cancer cells promotes cell survival via the Akt/PKB pathway. Cancer Lett 281:213–219. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2009.02.030
Thiery JP, Sleeman JP (2006) Complex networks orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:131–142. doi:10.1038/nrm1835
Yauch RL, Januario T, Eberhard DA, Cavet G, Zhu W, Fu L et al (2005) Epithelial versus mesenchymal phenotype determines in vitro sensitivity and predicts clinical activity of erlotinib in lung cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 11:8686–8698
Bremnes RM, Veve R, Hirsch FR, Franklin WA (2002) The E-cadherin cell-cell adhesion complex and lung cancer invasion, metastasis, and prognosis. Lung Cancer 36:115–124. doi:10.1016/S0169-5002(01)00471-8
Liu WF, Nelson CM, Pirone DM, Chen CS (2006) E-cadherin engagement stimulates proliferation via Rac1. J Cell Biol 173:431–441. doi:10.1083/jcb.200510087
Shapiro L, Fannon AM, Kwong PD, Thompson A, Lehmann MS, Grubel G et al (1995) Structural basis of cell-cell adhesion by cadherins. Nature 374:327–337. doi:10.1038/374327a0
Gumbiner BM (2000) Regulation of cadherin adhesive activity. J Cell Biol 148:399–404
Hatsell S, Rowlands T, Hiremath M, Cowin P (2003) Beta-catenin and Tcfs in mammary development and cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 8:145–158. doi:10.1023/A:1025944723047
Doherty P, Walsh FS (1996) CAM-FGF receptor interactions: a model for axonal growth. Mol Cell Neurosci 8:99–111. doi:10.1006/mcne.1996.0049
Watabe M, Nagafuchi A, Tsukita S, Takeichi M (1994) Induction of polarized cell-cell association and retardation of growth by activation of the E-cadherin-catenin adhesion system in a dispersed carcinoma line. J Cell Biol 127:247–256
Kandikonda S, Oda D, Niederman R, Sorkin BC (1996) Cadherin-mediated adhesion is required for normal growth regulation of human gingival epithelial cells. Cell Adhes Commun 4:13–24
Croix BS, Sheehan C, Rak JW, Florenes VA, Slingerland JM, Kerbel RS (1998) E-cadherin-dependent growth suppression is mediated by the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(KIP1). J Cell Biol 142:557–571
Cavallaro U, Christofori G (2004) Cell adhesion and signalling by cadherins and Ig-CAMs in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 4:118–132
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by High-Tech Platform for Molecular Diagnosis and Biological Therapy of Critical Illness (XK200507) and Study on Inhibit Action of NSCLC by Exogenous Expression of Let-7 (BK2008326).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, L., Sun, H., Lv, X. et al. Expression of periostin in the serum of NSCLC and its function on proliferation and migration of human lung adenocarcinoma cell line (A549) in vitro. Mol Biol Rep 37, 2285–2293 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9721-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9721-1