Abstract
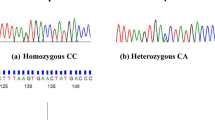
The melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) plays an important role in weight and energy homeostasis and it is associated with lower risk to develop obesity and lower body mass index. The contribution of MC4R mutation to obesity in Vojvodina (Northern Province of Serbia), known as a region with the largest number of overweight people, has not been previously investigated. The objective of this study was to examine the Val103Ile polymorphism of MC4R in a population of Vojvodina and its association with obesity. The study was carried out in a group of 96 persons: 62 obese and 34 normal weight men and women. Anthropometric measurements and cardiovascular risk factors assessment were done. The genotypes were determined by PCR-RFLP. In our on going study, three subjects were heterozygous for Val103Ile mutation (3.12%), and one was homozygous for 103Ile allele (1.04%). Among obese patients no isoleucine allele homozygous was found. The frequencies of the 103Ile allele in a group of obese and normal weight persons were found to be 1.61 and 4.41%, respectively. Val103Ile polymorphism of melanocortin-4 receptor is unlikely to be a major cause of overweight and obesity in Vojvodina, but further studies on larger groups of patients are needed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Must A, Spadano J, Coakley EH et al (1999) The disease burden associated with overweight and obesity. JAMA 282:1523–1529. doi:10.1001/jama.282.16.1523
World Health Organization Geneva, Switzerland (1998) Report no. WHO/NUT/NCD/98-1. Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. p 276
Micić D, Jorga J, Stokić E, et al (2004) National guide for the doctors in primary health care. Republic experts for the developing and implementation of the guides in clinical practice, Belgrade, Serbia. pp 1–22 (in Serbian)
Gantz I, Miwa H, Konda Y et al (1993) Molecular cloning, expression, and gene localisation of a fourth melanocortin receptor. J Biol Chem 268:15174–15179
Stutzmann F, Vatin V, Cauchi S, Morandi A, Jouret B, Landt O, Tounian P, Levy-Marchal C, Buzzetti R, Pinelli L, Balkau B, Horber F, Bougne`res P, Froguell P, Meyre D (2007) Non-synonymous polymorphisms in melanocortin-4 receptor protect against obesity: the two facets of a Janus obesity gene. Hum Mol Genet 16(15):1837–1844. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddm132
Hinney A, Bettecken T, Tarnow P et al (2006) Prevalence, spectrum, and functional characterization of melanocortin-4 receptor gene mutations in a representative population-based sample and obese adults from Germany. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91(5):1761–1769. doi:10.1210/jc.2005-2056
Tao YX (2005) Molecular mechanisms of the neural melanocortin receptor dysfunction in severe early onset obesity. Mol Cell Endocrinol 239(1–2):1–14. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2005.04.012
Farooqi IS (2006) The severely obese patient—a genetic work-up. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 2(3):172–177. doi:10.1038/ncpendmet0137
Ochoa MC, Azcona C, Biebermann H et al (2007) A novel mutation Thr162Arg of the melanocortin 4 receptor gene in a Spanish children and adolescent population. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 66(5):652–658. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2007.02788.x
Gotoda T, Scott J, Aitman TJ (1997) Molecular screening of the human melanocortin 4 receptor gene: identification of a missense variant showing no assotiation with obesity, plasma glucose or insulin. Diabetologia 40:976–979. doi:10.1007/s001250050777
Farooqi IS, Keogh JM, Yeo GS et al (2003) Clinical spectrum of obesity and mutations in the melanocortin 4 receptor gene. N Engl J Med 348:1085–1095. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa022050
Zakel UA, Wudy SA, Heinzel-Gutenbrunner M et al (2005) Prevalence of melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R) mutations and polymorphisms in consecutively ascertained obese children and adolescents from a pediatric health care utilization population. Klin Padiatr 217(4):244–249. doi:10.1055/s-2005-836589
Rutanen J, Pihlajamaki J, Karhapaa P et al (2004) The Val103Ile polymorphism of melanocortin-4 receptor regulates energy expenditure and weight gain. Obes Res 12:1060–1066. doi:10.1038/oby.2004.133
Geller F, Reichwald K, Dempfle A et al (2004) Melanocortin-4 receptor gene variant I103 is negatively associated with obesity. Am J Hum Genet 74:572–581. doi:10.1086/382490
Heid IM, Vollmert C, Hinney A et al (2005) Association of the 103I MC4R allele with decreased body mass in 7937 participants of two population based surveys. J Med Genet 42:e21. doi:10.1136/jmg.2004.027011
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS (1972) Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma without use of preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 18:499–502
Sambrook JF, Russel DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory Press, USA
StatSoft, Inc. (2008) Statistica (data analysis software system), version 8.0. www.statsoft.com
Rosmond R, Chagnon M, Bouchard C et al (2001) A missense mutation in the human melanocortin-4 receptor gene in relation to abdominal obesity and salivary cholesterol. Diabetologica 44:1335–1338. doi:10.1007/s001250100649
Rong R, Tao YX, Cheung BMY et al (2006) Identification and functional characterization of three novel human melanocortin-4 receptor gene variants in an obese Chinese population. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 65:198–205. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2006.02573.x
Marti A, Corbalán MS, Forga L et al (2003) A novel nonsense mutation in the melanocortin-4 receptor associated with obesity in a Spanish population. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 27(3):385–388. doi:10.1038/sj.ijo.0802244
Young EH, Wareham NJ, Farooqi S et al (2007) The V103I polymorphism of the MC4R gene and obesity: population based studies and meta-analysis of 29, 563 individuals. Int J Obes 31:1437–1441. doi:10.1038/sj.ijo.0803609
Heid IM, Vollmert C, Kronenberg F et al (2008) Association of the MC4R V103I polymorphism with the metabolic syndrome: the kora study. Obesity (Silver Spring) 16:369–376. doi:10.1038/oby.2007.21
Brönner G, Sattler AM, Hinney A et al (2006) The 103I variant of the melanocortin 4 receptor is associated with low serum triglyceride levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91(2):535–538. doi:10.1210/jc.2005-0919
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stokić, E., Djan, M., Vapa, L. et al. Polymorphism Val103Ile of the melanocortin-4 receptor gene in the Serbian population. Mol Biol Rep 37, 33–37 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9500-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9500-z