Abstract
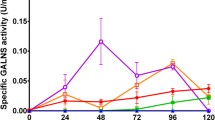
Morquio A is an autosomal recessive disease caused by the deficiency of N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase (GALNS), leading to the lysosomal accumulation of keratan-sulfate and chondroitin-6-sulfate. We evaluated in HEK293 cells the effect of the cytomegalovirus immediate early enhancer/promoter (CMV) or the elongation factor 1α (EF1α) promoters, and the coexpression with the sulfatase modifying factor 1 (SUMF1) on GALNS activity. Four days postransfection GALNS activity in transfected cells with CMV-pIRES-GALNS reached a plateau, whereas in cells transfected with EF1α-pIRES-GALNS continued to increase until day 8. Co-transfection with pCXN-SUMF1 showed an increment up to 2.6-fold in GALNS activity. Finally, computational analysis of transcription factor binding-sites and CpG islands showed that EF1α promoter has long CpG islands and high-density binding-sites for Sp1 compared to CMV. These results show the advantage of the SUMF1 coexpression on GALNS activity and indicate a considerable effect on the expression stability using EF1α promoter compared to CMV.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neufeld E, Muenzer J (2001) The mucopolysaccharidosis. In: Scriver C, Beaudet A, Sly W et al (eds) The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited diseases, vol III. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 3421–3452
Montaño AM, Tomatsu S, Gottesman G et al (2007) International Morquio A registry: clinical manifestation and natural course of Morquio A disease. J Inherit Metab Dis 30:165–174
Ashworth JL, Biswas S, Wraith E et al (2006) Mucopolysaccharidoses and the eye. Surv Ophthalmol 51:1–17
Vellodi A, Young EP, Cooper A et al (1997) Bone marrow transplantation for mucopolysaccharidosis type I: experience of two British centres. Arch Dis Child 76:92–99
Tomatsu S, Montaño A, Ohashi A et al (2007) Enzyme replacement therapy in a murine model of Morquio A syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 17:815–824
Tomatsu S, Fukuda M, Masue K et al (1991) Morquio disease: isolation, characterization and expression of full-length cDNA for human N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 181:677–683
Bielicki J, Fuller M, Guo X et al (1995) Expression, purification and characterization of recombinant human N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulphatase. Biochem J 311:333–339
Tomatsu S, Montaño A, Gutiérrez M et al (2007) Characterization and pharmacokinetic study of recombinant human N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase. Mol Genet Metab 91:69–78
Cosma M, Pepe P, Annunziata I et al (2003) The multiple sulfatase deficiency gene encodes an essential and limiting factor for the activity of sulfatases. Cell 113:445–456
Landgrebe J, Dierks T, Schamidt B et al (2003) The human SUMF1 gene required for posttranslational sulfatase modification, defines a new gene family which is conserved from pro- to eukaryotes. Gene 316:47–56
Tomatsu S, Montaño A, Nishioka T et al (2005) Mutation and polymorphism spectrum of the GALNS gene in mucopolysaccharidosis IVA (Morquio A). Hum Mutat 26:500–512
Fraldi A, Biffi A, Lombarda A et al (2007) SUMF1 enhances sulfatase activities in vivo in five sulfatase deficiencies. Biochem J 403:305–312
Fraldi A, Hemsley H, Crawley A et al (2007) Functional correction of CNS lesions in MPS-IIIA mouse model by intracerebral AAV-mediated delivery of sulfamidase and SUMF1 genes. Hum Mol Genet 16:2693–2702
Takakusaki T, Hisayasu S, Hirai Y et al (2005) Coexpression of formylglycine-generating enzyme is essential for synthesis and secretion of functional arylsulfatase A in a mouse model of metachromatic leukodystrophy. Hum Gene Ther 16:929–936
Cheng S, Smith A (2003) Gene therapy progress and prospects: gene therapy of lysosomal storage disorders. Gene Ther 10:1275–1281
Ellinwood M, Vite C, Haskins M (2004) Gene therapy for lysosomal storage diseases: the lessons and promise of animal models. J Gene Med 6:481–506
Hodges BL, Cheng SH (2006) Cell and gene-based therapies for the lysosomal storage diseases. Curr Gene Ther 6:227–241
Ponder KP, Melniczek JR, Xu L et al (2002) Therapeutic neonatal hepatic gene therapy in mucopolysaccharidosis VII dogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:13102–13107
Sferra T, Backstrom K, Wang C et al (2004) Widespread correction of lysosomal storage following intrahepatic injection of a recombinant adeno-associated virus in the adult MPS VII mouse. Mol Ther 10:478–491
Traas AM, Wang P, Ma X et al (2007) Correction of clinical manifestations of canine mucopolysaccharidosis I with neonatal retroviral vector gene therapy. Mol Ther 15:1423–1431
Papadakis E, Nicklin S, Baker A et al (2004) Promoters and control elements: designing expression cassettes for gene therapy. Curr Gene Ther 4:89–113
Collas P (1998) Modulation of plasmid DNA methylation and expression in zebrafish embryons. Nucleic Acids Res 26:4454–4461
Toniatti C, Bujard H, Cortese R et al (2004) Gene therapy progress and prospects: transcription regulatory systems. Gene Ther 11:649–657
Hyun-Jeong H, Eun-Sook P, Seongman K et al (2004) Long-term enzymatic and phenotypic correction in the phenylcetonuria mouse model by adeno-associated virus vector-mediated gene transfer. Pediatr Res 56:278–284
Jung S, Han I, Limave A et al (2001) Adeno-associated viral vector-mediated gene transfer results in long-term enzymatic and functional correction in multiple organs of Fabry mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:2676–2681
Liu Y, Xu L, Henning A et al (2005) Liver-directed neonatal gene therapy prevents cardiac, bone, ear, and eye disease in mucopolysaccharidosis I mice. Mol Ther 11:35–47
Mount J, Herzog R, Tillson M (2002) Sustained phenotypic correction of hemophilia B dogs with a factor IX null mutation by liver-direct gene therapy. Blood 99:2670–2675
Nakai H, Herzog R, Hagstrom J et al (1998) Adeno-associated viral vector-mediated gene transfer of human blood coagulation factor IX into mouse liver. Blood 91:4600–4607
Smale S (2001) Core promoters: active contributors to combinatorial gene regulation. Genes Dev 15:2503–2508
Mcleod D, Chariton J, Mullins J et al (1994) Sp1 sites in the mouse aprt gene promoter are required to prevent methylation of the CpG island. Genes Dev 8:2282–2292
Butler J, Kodonaga J (2002) The RNA polymerase II core promoter: a key component in the regulation of gene expression. Genes Dev 16:2583–2592
Brandeis M, Frank D, Keshet I et al (1994) Sp1 elements protect a CpG island from de novo methylation. Nature 371:435–438
Barrera L (2003) Desarrollo de un modelo de vectores usando virus adenoasociados libre de adenovirus para corregir la deficiencia enzimática en las mucopolisacaridosis. In: Leimpn S (ed) Congreso de Errores innatos del Metabolismo y Pesquisa Neonatal, Abstracts, Iguazú, Argentina, p 32
Aubin R, Weinfeild M, Paterson M (1991) Preparation of recombinant plasmid DNA for DNA-mediated gene transfer. In: Murray EJ (ed) Methods in molecular biology: gene transfer and expression protocols, vol 7, 1st edn. The Humana Press, Clifton, pp 3–13
Okoyama H, Chen C (1991) Calcium phosphate mediated gene transfer into established cell lines. In: Murray EJ (ed) Methods in molecular biology: gene transfer and expression protocols, vol 7, 1st edn. The Humana Press, Clifton, pp 15–20
vanDiggelen O, Zhao H, Kleijer W et al (1993) A fluorometric enzyme assay for the diagnosis of Morquio type A. Clin Chem Acta 187:131–140
Matys V, Kel-Margoulis O, Fricke E et al (2006) TRANSFAC and its module TRANSCompel: transcriptional gene regulation in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D108–D110
Nakashima Y, Tomatsu S, Hori T et al (1994) Mucopolysaccharidosis IV A: molecular cloning of the human N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase gene (GALNS) and analysis of the 5′-flanking region. Genomics 20:99–104
Wang J, Xie J, Lu H et al (2007) Existence of transient functional double-stranded DNA intermediates during recombinant AAV transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:13104–13109
Timpe J, Bevington J, Casper J et al (2005) Mechanisms of adeno-associated virus genome encapsidation. Curr Gene Ther 5:273–284
Brooks A, Harkins R, Wang P et al (2004) Transcriptional silencing is associated with extensive methylation of the CMV promoter following adenoviral gene delivery to muscle. J Gene Med 6:395–404
Kim I, Józkowicz A, Piedra P (2001) Lifetime correction of genetic deficiency in mice with a single injection of helper-dependent adenoviral vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:13282–13287
Roeser D, Preusser-Kunze A, Scgmidt B et al (2006) A general binding mechanism for all human sulfatases by the formylglycine-generating enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:81–86
Tomatsu S, Gutierrez M, Nishioka T et al (2005) Development of MPS IVA mouse (Galnstm(hC79S.mC76S)slu) tolerant to human N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase. Hum Mol Genet 14:3321–3335
Tomatsu S, Montano A, Lopez P et al (2006) Determinant factors of spectrum of missense variants in mucopolysaccharidosis IVA gene. Mol Genet Metab 89:139–149
Ogawa R, Kagiya G, Kodaki T et al (2007) Construction of strong mammalian promoters by random cis-acting element elongation. Biotechniques 42:628–632
Sandelin A, Carninci P, Lenhard B et al (2007) Mammalian RNA polymerase II core promoters: insights from genome-wide studies. Nat Rev Genet 8:424–436
Alon U (2007) Network motifs: theory and experimental approaches. Nat Rev Genet 8:450–461
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Pontificia Universidad Javeriana’s Genomic Initiative (ID 000950). CJAD received a scholarship from Instituto Colombiano para el Desarrollo de la Ciencia y la Tecnología—COLCIENCIAS. We would like to thank Johanna Luna and Rocio Cuaspa for their assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Carlos J. Alméciga-Díaz and Maria A. Rueda-Paramo contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alméciga-Díaz, C.J., Rueda-Paramo, M.A., Espejo, A.J. et al. Effect of elongation factor 1α promoter and SUMF1 over in vitro expression of N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase. Mol Biol Rep 36, 1863–1870 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-008-9392-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-008-9392-3