Abstract
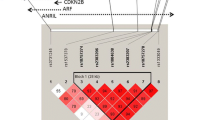
Background Two single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs, rs10757278 and rs2383207) on chromosome 9p21 have been proved to be associated with myocardial infarction. We investigated whether these two genetic markers are determinants of early-onset coronary artery disease. Methods and results A total of 444 consecutive patients were studied including 212 cases with coronary stenosis ≥50% or previous myocardial infarction and 232 controls without documented coronary artery disease. Ligase detection reaction was performed to detect two SNPs. After adjustment of clinical parameters, significant associations were identified for the rs2383207 and rs10757278 SNPs, with A/G and G/G genetypes at rs10757278 and G/G genetype carriers at rs2383207 having a higher risk of early-onset coronary artery disease than carriers of A/A genotype (odds ratio [OR] 2.207, 95% CI: 1.069–4.394, P = 0.028; OR 3.051, 95% CI: 1.086–8.567, P = 0.004; OR 2.964, 95% CI: 1.063–8.265, P = 0.038, respectively). There were no associations between rs10757278 and rs2383207 genotypes and the severity of coronary artery disease (both P > 0.05). Conclusions The rs10757278 and rs2383207 variants are determinants for early-onset coronary artery disease. These markers may help the identification of patients at increased risk for early-onset coronary artery disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAD:
-
Coronary artery disease
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- MI:
-
Myocardial infarction
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
References
McPherson R, Pertsemlidis A, Kavaslar N et al (2007) A common allele on chromosome 9 associated with coronary heart disease. Science 316:1488–1491
Helgadottir A, Thorleifsson G, Manolescu A et al (2007) A common variant on chromosome 9p21 affects the risk of myocardial infarction. Science 316:1491–1493
Shen GQ, Li L, Rao S et al (2008) Four SNPs on chromosome 9p21 in a South Korean population implicate a genetic locus that confers high cross-race risk for development of coronary artery disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28:360–365. Epub 2007 Nov 29
Jia EZ, Wang J, Yang ZJ et al (2007) Association of the mutation for the human carboxypetidase E gene exon 4 with the severity of coronary artery atherosclerosis. Mol Biol Rep 2007 Dec 16. Epub ahead of print
Zeng WW, Zhou B, Liu HR et al (2007) Identification of the tree shrew ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) and its expression in tissues: cDNA sequence and expression of tree shrew ABCA1. Mol Biol Rep 2007 Dec 16. Epub ahead of print
Bazrgar M, Karimi M, Fathzadeh M et al (2007) Apolipoprotein E polymorphism in Southern Iran: E4 allele in the lowest reported amounts. Mol Biol Rep 2007 Jun 27. Epub ahead of print
Shah SH (2007) Gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to coronary artery disease. Pediatr Blood Cancer 48:738–741
Christensen K, Murray JC (2007) What genome-wide association studies can do for medicine. N Engl J Med 356:1094–1097
Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium (2007) Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature 447:661–678
Broeckel U, Hengstenberg C, Mayer B et al (2002) A comprehensive linkage analysis for myocardial infarction and its related risk factors. Nat Genet 30:210–214
Fischer M, Broeckel U, Holmer S et al (2005) Distinct heritable patterns of angiographic coronary artery disease in families with myocardial infarction. Circulation 111:855–862
Wichmann HE, Gieger C, Illig T (2005) KORA-gen—resource for population genetics, controls and a broad spectrum of disease phenotypes. Gesundheitswesen 67(Suppl 1):S26–S30
Samani NJ, Erdmann J, Hall AS et al (2007) Genomewide association analysis of coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 357:443–453
Favis R, Day JP, Gerry NP (2000) Universal DNA array detection of small insertions and deletions in BRCA1 and BRCA2. Nat Biotechnol 18:561–564
Xiao Z, Xiao J, Jiang Y et al (2006) A novel method based on ligase detection reaction for low abundant YIDD mutants detection in hepatitis B virus. Hepatol Res 34:150–155
Lowe SW, Sherr CJ (2003) Tumor suppression by Ink4a-Arf: progress and puzzles. Curr Opin Genet Dev 13:77–83
Hannon GJ, Beach D (1994) p15INK4B is a potential effector of TGF-beta-induced cell cycle arrest. Nature 371:257–261
Kalinina N, Agrotis A, Antropova Y et al (2004) Smad expression in human atherosclerotic lesions: evidence for impaired TGF-beta/Smad signaling in smooth muscle cells of fibrofatty lesions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24:1391–1396
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by Nanjing Scientific Development Grant for 2006 (2006ZD016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhong Chen and Qi Qian contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Qian, Q., Ma, G. et al. A common variant on chromosome 9p21 affects the risk of early-onset coronary artery disease. Mol Biol Rep 36, 889–893 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-008-9259-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-008-9259-7