Abstract
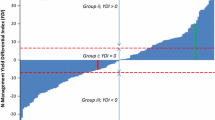
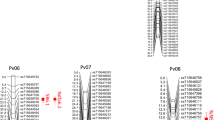
Common bean is an important staple crop in Eastern Africa and Latin America. Low soil fertility is a major limitation to agronomic productivity. Symbiotic nitrogen fixation (SNF) is an important property of legumes, leading to high protein levels and high nutritional value. Nitrogen (N) metabolism and yield traits were evaluated in the common bean population DOR 364 × BAT 477 in field experiments under moderate and low phosphorus (P) soil conditions resembling environments found on farmers’ fields. Low P availability in soil severely limits seed yield, and trait correlations with yield reveal that high biomass as well as early maturity and efficient seed filling are important for good performance in low P stress, resembling drought resistance. Investigation of SNF and soil N uptake under low P stress showed reduced seed nitrogen levels and major variation in soil-derived N. In low P conditions, no significant reduction of %N derived from the atmosphere (%Ndfa) was observed; however, %Ndfa was correlated with yield, indicating that under stress SNF becomes an important asset. Significant genetic variation was observed for yield, yield components, and SNF ability suggesting that traits can be improved by breeding. Quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for %Ndfa and seed N concentration were discovered on chromosomes Pv07 and Pv02; independent yield QTLs were identified on the same chromosomes. Two QTL hotspots that affect several traits including yield components were found on Pv02 and Pv06; the latter represents a constitutive QTL hotspot independent from the environment. QTLs may be used for marker design and molecular breeding.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 100SdW:
-
100 seed weight
- SdCN:
-
Carbon to nitrogen ratio in seed
- DF:
-
Days to flowering
- DPM:
-
Days to physiological maturity
- TNdfs:
-
Nitrogen derived from soil per hectare
- TNdfa:
-
Nitrogen derived from the atmosphere per hectare
- %Ndfa:
-
Percentage of nitrogen derived from the atmosphere
- FVFM:
-
Photosynthetic efficiency on younger fully expanded leaf
- LP:
-
Low phosphorus
- MP:
-
Moderate phosphorus
- PBH:
-
Pod Biomass at harvest
- PHI:
-
Pod harvest index
- PNA:
-
Pod number per area
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait locus
- RIL:
-
Recombinant inbred line
- SdC:
-
Seed carbon content in per cent
- SdN:
-
Seed nitrogen content in per cent
- SdN_ha:
-
Seed nitrogen per hectare
- SdNA:
-
Seed number per area
- ShBH:
-
Shoot biomass at harvest
- SCMR:
-
SPAD chlorophyll meter reading in younger fully expanded leaf
- SBH:
-
Stem biomass at harvest
- SCOND:
-
Stomatal conductance on younger fully expanded leaf
- Yd:
-
Yield per hectare
References
Andrews M, Lea PJ (2013) Our nitrogen “footprint”: the need for increased crop nitrogen use efficiency. Ann Appl Biol 163:165–169. doi:10.1111/aab.12052
Araújo SS, Beebe S, Crespi M et al (2015) Abiotic stress responses in legumes: strategies used to cope with environmental challenges. Crit Rev Plant Sci 34:237–280. doi:10.1080/07352689.2014.898450
Asfaw A, Blair MW (2012) Quantitative trait loci for rooting pattern traits of common beans grown under drought stress versus non-stress conditions. Mol Breed 30:681–695. doi:10.1007/s11032-011-9654-y
Asfaw A, Blair MW, Struik PC (2012) Multienvironment quantitative trait loci analysis for photosynthate acquisition, accumulation, and remobilization traits in common bean under drought stress. G3 (Bethesda) 2:579–595. doi:10.1534/g3.112.002303
Assefa T, Beebe SE, Rao IM et al (2013) Pod harvest index as a selection criterion to improve drought resistance in white pea bean. Field Crop Res 148:24–33. doi:10.1016/j.fcr.2013.04.008
Batjes N (1997) A world data set of derived properties by FAO-UNESCO soil unit for global modelling
Batjes NH (2011) Global distribution of soil phosphorus retention potential. Wageningen, Plant Research International (PRI), Wageningen UR and ISRIC Worl Soil Information. Report 6, 42
Beebe S (2012) Common bean breeding in the tropics. In: Janick J (ed) Plant breeding reviews. pp 357–427
Beebe SE, Rojas-Pierce M, Yan X et al (2006) Quantitative trait loci for root architecture traits correlated with phosphorus acquisition in common bean. Crop Sci 46:413–423. doi:10.2135/cropsci2005.0226
Beebe SE, Rao IM, Cajiao C, Grajales M (2008) Selection for drought resistance in common bean also improves yield in phosphorus limited and favorable environments. Crop Sci 48:582–592. doi:10.2135/cropsci2007.07.0404
Beebe SE, Rao IM, Blair MW, Acosta-Gallegos JA (2013) Phenotyping common beans for adaptation to drought. Front Physiol 4:1–20. doi:10.3389/fphys.2013.00035
Blair MW, Galeano CH, Tovar E et al (2012) Development of a Mesoamerican intra-genepool genetic map for quantitative trait loci detection in a drought tolerant × susceptible common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) cross. Mol Breed 29:71–88. doi:10.1007/s11032-010-9527-9
Bliss FA (1993) Breeding common bean for improved biological nitrogen fixation. Plant Soil 152:71–79
Bourion V, Laguerre G, Depret G et al (2007) Genetic variability in nodulation and root growth affects nitrogen fixation and accumulation in pea. Ann Bot 100:589–598. doi:10.1093/aob/mcm147
Broughton WJ, Hern G, Blair M et al (2003) Beans (Phaseolus spp.)—model food legumes. Plant Soil 55:55–128
Chavarro MC, Blair MW (2010) QTL analysis and effect of the fin locus on tropical adaptation in an inter-gene pool common bean population. Trop Plant Biol 3:204–218. doi:10.1007/s12042-010-9058-x
CIAT (1988) Simbiosis Leguminosa-Rizobio; manual de métodos de evaluacón, selección y manejo agronómico. Seccion Microbiologia de suelos, programa de pastos tropicales y programa de fríjol. Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical (CIAT), Cali, Colombia
Cichy KA, Blair MW, Galeano CH et al (2009a) QTL analysis of root architecture traits and low phosphorus tolerance in an Andean bean population. Crop Sci 49:59–68
Cichy KA, Snapp SS, Blair MW (2009b) Plant growth habit, root architecture traits and tolerance to low soil phosphorus in an Andean bean population. Euphytica 165:257–268. doi:10.1007/s10681-008-9778-2
Ferguson B, Lin M-H, Gresshoff PM (2013) Regulation of legume nodulation by acidic growth conditions. Plant Signal Behav 8:e23426. doi:10.4161/psb.23426
Galeano CH, Fernandez AC, Franco-Herrera N et al (2011) Saturation of an intra-gene pool linkage map: towards a unified consensus linkage map for fine mapping and synteny analysis in common bean. PLoS One 6:e28135
Hall AE, Richard A, Condon AG et al (1994) Carbon isotopo discriminations and plant breeding. In: Plant breeding reviews. Ju. Wiley, Janick, pp 81–113
Hungria M, Vargas MAT (2000) Environmental factors affecting N2 fixation in grain legumes in the tropics, with an emphasis on Brazil. Field Crop Res 65:151–164. doi:10.1016/S0378-4290(99)00084-2
Jiang C, Gao X, Liao L et al (2007) Phosphate starvation root architecture and anthocyanin accumulation responses are modulated by the gibberellin-DELLA signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 145:1460–1470. doi:10.1104/pp.107.103788
Kamfwa K, Cichy KA, Kelly JD (2015) Genome-wide association analysis of symbiotic nitrogen fixation in common bean. Theor Appl Genet. doi:10.1007/s00122-015-2562-5
Leidi EO, Rodriguez-Navarro DN (2000) Nitrogen and phosphorus availability limit N fixation in bean. New Phytol 147:337–346
Li B, Li Y, Wu H et al (2016) Root exudates drive interspecific facilitation by enhancing nodulation and N 2 fixation. PNAS 113:6496–6501. doi:10.1073/pnas.1523580113
Lynch JP, Beebe SE (1995) Adaptations of beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) to low-phosphorus availability. Hortscience 30:1165–1171
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants, 2nd Ed. Academic Press Inc., London, UK
Miguel MA, Widrig A, Vieira RF et al (2013) Basal root whorl number: a modulator of phosphorus acquisition in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Ann Bot 112:973–982. doi:10.1093/aob/mct164
Miklas PN, Porch TG (2010) Guidelines for common bean QTL nomenclature. Annu Rep Bean Improv Coop 53:202–204
Mourice SK, Tryphone GM (2012) Evaluation of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) genotypes for adaptation to low phosphorus. International Scholarly Research Network Agronomy ID309614:1–9. doi: 10.5402/2012/309614
Olivera M, Tejera N, Iribarne C (2004) Growth, nitrogen fixation and ammonium assimilation in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris): effect of phosphorus. Physiol Plant 121:498–505. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.2004.00355.x
Polanía J, Rao M, Beebe S, Garcia R (2009) Root development and distribution under drought stress in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in a soil tube system. Agronomia Colombiana 27:25–32
Polania J, Poschenrieder C, Beebe S, Rao IM (2016a) Effective use of water and increased dry matter partitioned to grain contribute to yield of common bean improved for drought resistance. Front Plant Sci. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.00927
Polania J, Poschenrieder C, Beebe S, Rao IM (2016b) Estimation of phenotypic variability in symbiotic nitrogen fixation ability of common bean under drought stress using 15N natural abundance in grain. Eur J Agron 79:66–73. doi:10.1016/j.eja.2016.05.014
Ramaekers L, Remans R, Rao IM et al (2010) Strategies for improving phosphorus acquisition efficiency of crop plants. Field Crop Res 117:169–176
Ramaekers L, Galeano CH, Garzón N et al (2013) Identifying quantitative trait loci for symbiotic nitrogen fixation capacity and related traits in common bean. Mol Breed 31:163–180. doi:10.1007/s11032-012-9780-1
Ramírez M, Flores-Pacheco G, Reyes JL et al (2013) Two common bean genotypes with contrasting response to phosphorus deficiency show variations in the microRNA 399-mediated PvPHO2 regulation within the PvPHR1 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci 14:8328–8344. doi:10.3390/ijms14048328
Rao IM (2014) Advances in improving adaptation of common bean and Brachiaria forage grasses to abiotic stresses in the tropics. In: Pessarakl M (ed) Handbook of plant and crop physiology, Third Edit. CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group, Boca Raton, FL., pp 847–889
Rao IM, Miles JW, Beebe SE, Horst WJ (2016) Root adaptations to soils with low fertility and aluminium toxicity. Ann Bot. doi:10.1093/aob/mcw073
Remans R, Beebe S, Blair M et al (2007) Physiological and genetic analysis of root responsiveness to auxin-producing plant growth-promoting bacteria in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) Plant Soil 302:149–161
Rotaru V, Sinclair TR (2009) Interactive influence of phosphorus and iron on nitrogen fixation by soybean. Environ Exp Bot 66:94–99
SAS-Institute (2011) SAS Institute Inc. 2011. SAS® 9.3 System Options: Reference, Second Edition
Shearer G, Kohl DH (1986) N2-fixation in field settings: estimations based on natural 15N abundance. Aust J Plant Physiol 13:699–756. doi:10.1071/PP9860699c
Silva DA, Fátima Esteves AJ, Messias U et al (2014) Efficiency in the use of phosphorus by common bean genotypes. Sci Agric 71:232–239
Singh A (2015) Nitrogen and phosphorus resorption efficiency in some leguminous and non-leguminous tropical tree species planted on coal mine spoil in a tropical dry environment. Ambit J Educ Res Rev 1:1–7
Sponchiado BN, White JW, Castillo JA, Jones PG (1989) Root growth of four common bean cultivars in relation to drought tolerance in environments with contrasting soil types. Exp Agric 25:249–257
Tsvetkova GE, Georgiev GI (2007) Changes in phosphate fractions extracted from different organs of phosphorus starved nitrogen fixing pea plants. J Plant Nutr 30:2129–2140. doi:10.1080/01904160701700616
Unkovich MJ, Pate JS, Sanford P, Armstrong EL (1994) Potential precision of the delta-N-15 natural-abundance method in-field estimates of nitrogen-fixation by crop and pasture legumes in south-west Australia. Aust J Agric Res 45:119–132
Vadez V, Lasso JH, Beck DP, Drevon JJ (1999) Variability of N2-fixation in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L .) under P deficiency is related to P use efficiency N2-fixation tolerance to P deficiency. Euphytica 199079:231–242. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2012.03.013
Voorrips R (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng Z-B (2012) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC.( http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm)
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the CGIAR Research Program on Grain Legumes. We would like to thank all donors who supported this work through their contributions to the CGIAR Fund. We acknowledge the contributions made by E. Tovar, G. Borrero, and M. Rivera and the Bean Breeding team of the Bean Program of the International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT). We also thank M. Otero and J. Molina for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Diaz LM: Writing of the manuscript, analysis of genetic data, and statistical analysis of phenotypic data
Ricaurte J: Field evaluation and statistical analysis of phenotypic data
Cajiao C: Trial design and field evaluation
Galeano C: Idea conception and preliminary analysis of linkage and QTL
Rao I: leadership of physiological evaluations, discussion, and improvements of the manuscript
Beebe S: Idea conception, leadership of field trial activities, discussion, and improvements of the manuscript
Raatz B: leadership of genetic analysis and writing of the manuscript
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Key Message
Low phosphorus stress in Phaseolus vulgaris reduces yield and seed nitrogen, but has no strong effect on percentage of nitrogen derived from the atmosphere. QTLs were identified for SNF and yield components.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Fig. 1
(DOCX 104 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
(DOCX 43 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
(DOCX 19 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
(XLSX 17 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diaz, L.M., Ricaurte, J., Cajiao, C. et al. Phenotypic evaluation and QTL analysis of yield and symbiotic nitrogen fixation in a common bean population grown with two levels of phosphorus supply. Mol Breeding 37, 76 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-017-0673-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-017-0673-1