Abstract
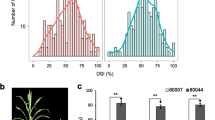
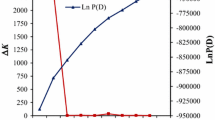
Maize rough dwarf disease (MRDD) is a worldwide viral disease and causes significant yield losses in maize (Zea mays L.) production. In this study, we mapped and characterized quantitative trait loci (QTL) conferring resistance to MRDD using 89 F8 recombinant inbred lines derived from a cross between X178 (resistant parent) and B73 (susceptible). The population was evaluated for MRDD resistance in Baoding, Hebei Province, China (a hot spot of MRDD incidence) under natural infection in 2008 and 2009 and artificial inoculation in 2010. Genotypic variances for disease severity index (DSI) were highly significant in the population. Heritability estimates for DSI evaluation were 0.472 and 0.467 in 2008 and 2009, respectively. The linkage map was constructed using 514 gene-derived single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and 72 simple sequence repeat markers, spanning a genetic distance of 1,059.72 cM with an average interval of 1.8 cM between adjacent markers. Multiple-QTL model mapping detected a major QTL for MRDD resistance on chromosome 8, explaining 24.6–37.3% of the phenotypic variation across three environments. In 2010, an additional QTL was detected on chromosome 10, explaining 15.8% of the phenotypic variation. The major QTL on chromosome 8 and the SNP markers (SNP31, SNP548, and SNP284) co-located with the QTL peak have potential for further functional genomic analysis and use in molecular marker-assisted selection for MRDD resistance in maize.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asins M (2002) Present and future of quantitative trait locus analysis in plant breeding. Plant Breed 121:281–291
Bar-tsur A, Saadi H, Antignus Y (1988) Resistance of corn genotypes to maize rough dwarfs virus [in Israel]. Maydica 33:189–200
Beavis WD (1998) QTL analyses: power, precision, and accuracy. In: Paterson AH (ed) Molecular dissection of complex traits. CRC Press, New York, pp 145–162
Chen YK (2006) Germplasm evaluation and quantitative trait loci identification of resistance to maize rough dwarf virus in maize. Dissertation, Xinjiang Agricultural University
Ching A, Caldwell KS, Jung M, Dolan M, Smith OSH, Tingey S, Morgante M, Rafalski AJ (2002) SNP frequency, haplotype structure and linkage disequilibrium in elite maize inbred lines. BMC Genet 3:19
Cho RJ, Mindrinos M, Richards DR, Sapolsky RJ, Anderson M, Drenkard E, Dewdney J, Reuber TL, Stammers M, Federspiel N (1999) Genome-wide mapping with biallelic markers in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Genet 23:203–207
Collard BCY, Jahufer MZZ, Brouwer J, Pang ECK (2005) An introduction to markers, quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping and marker-assisted selection for crop improvement: the basic concepts. Euphytica 142:169–196
Darvasi A, Weinreb A, Minke V, Weller J, Soller M (1993) Detecting marker-QTL linkage and estimating QTL gene effect and map location using a saturated genetic map. Genetics 134:943
De Leon C (2004) Maize diseases: a guide for field identification. Cimmyt, E1 Batan
Di DP, Miao H, Lu Y, Tian L (2005) Study on the method of inoculation and identification for the resistance of maize to maize rough dwarf virus. J Agric Univ Hebei 28:76–78
Diévart A, Clark SE (2004) LRR-containing receptors regulating plant development and defense. Development 131:251
Dovas C, Eythymiou K, Katis N (2004) First report of Maize rough dwarf virus (MRDV) on maize crops in Greece. Plant Pathol 53:238
Duble C, Melchinger A, Kuntze L, Stork A, Lubberstedt T (2000) Molecular mapping and gene action of Scm1 and Scm2, two major QTL contributing to SCMV resistance in maize. Plant Breed 119:299–303
Fay D, Bender A (2006) Genetic mapping and manipulation: chapter 4-SNPs: introduction and two-point mapping. The C. elegans Research Community, WormBook. http://www.wormbook.org/chapters/www_SNPsintrotwopointmap/SNPsintrotwopointmap.html#ftn.d0e8. Accessed 17 Feb 2006
Francia E, Tacconi G, Crosatti C, Barabaschi D, Bulgarelli D, Dall’Aglio E, Vale G (2005) Marker assisted selection in crop plants. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 82:317–342
George M, Prasanna B, Rathore R, Setty T, Kasim F, Azrai M, Vasal S, Balla O, Hautea D, Canama A (2003) Identification of QTLs conferring resistance to downy mildews of maize in Asia. Theor Appl Genet 107:544–551
Guo QT, Li Z, Dong Z (1995a) The observation and analysis of varietal resistance of maize rough dwarf virus disease. Plant Prot 1:21–23
Guo QT, Li Z, Dong Z (1995b) The relationship between maize rough dwarf disease occurrence and resistance of varieties. J Shanxi Agric Sci 23:40–44
Haley CS, Andersson L (1997) Linkage mapping of quantitative trait loci in plants and animals. In: Dear PH (ed) Genome mapping—a practical approach. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 49–71
Hallauer AR, Miranda J (1988) Quantitative genetics in maize breeding. Iowa State University, Ames
Harpaz I (1959) Needle transmission of a new maize virus. Nature 184:77–78. doi:10.1038/184077a0
Hittalmani S, Shashidhar H, Bagali PG, Huang N, Sidhu J, Singh V, Khush G (2002) Molecular mapping of quantitative trait loci for plant growth, yield and yield related traits across three diverse locations in a doubled haploid rice population. Euphytica 125:207–214
Huang X, Feng Q, Qian Q, Zhao Q, Wang L, Wang A, Guan J, Fan D, Weng Q, Huang T (2009) High-throughput genotyping by whole-genome resequencing. Genome Res 19:1068
Ji ZF, Wang A, Li J, Dong X, Chen Z (1998) The relationships between maize rough dwarf disease occurrence and varieties and sowing date. Plant Prot 24:27–29
Li B (2009) Fine mapping of the locus on chromosome 7 conferring resistance to maize (Zea mays L.) rough dwarf disease. Dissertation, Shandong University
Li CB, Song JC, Jiang LJ, Yang CY, Wang QB, Wang SY (2002) Identification of RAPD markers linked to MRDV resistance genes and their applications to marker-assisted selection. Acta Agron Sin 28:564–568
Liu ZZ, Chi SM (1996) Resistance of corn genotypes to maize rough dwarf virus. Maize Sci 4:68–70
Liu XH, Tan ZB, Rong TZ (2009) Molecular mapping of a major QTL conferring resistance to SCMV based on immortal RIL population in maize. Euphytica 167:229–235
Lu YG, Di D, Miao H, Tian L (2001) Identification and analysis on resistance of introduced foreign and domestic maize inbreds to MRDV. J Agric Univ Hebei 5:22–25
Ma X, Cui D, Liu H, Liu X, Ning L, Chen H (2010) Development of STS-PCR markers for maize rough dwarf virus resistant genes. J Maize Scie 18:61–64, 67
Marques C, Araujo J, Ferreira J, Whetten R, O’malley D, Liu BH, Sederoff R (1998) AFLP genetic maps of Eucalyptus globulus and E. tereticornis. Theor Appl Genet 96:727–737
Melchinger A (1990) Use of molecular markers in breeding for oligogenic disease resistance. Plant Breed 104:1–19
Miao HQ, Chen X (1997) Occurrence and damage of maize rough dwarf virus in Hebei province. Plant Prot 23:17–18
Michelmore R (1995) Molecular approaches to manipulation of disease resistance genes. Annu Rev Phytopathol 33:393–427
Mohan M, Nair S, Bhagwat A, Krishna T, Yano M, Bhatia C, Sasaki T (1997) Genome mapping, molecular markers and marker-assisted selection in crop plants. Mol Breed 3:87–103
Muchero W, Ehlers JD, Close TJ, Roberts PA (2011) Genic SNP markers and legume synteny reveal candidate genes underlying QTL for Macrophomina phaseolina resistance and maturity in cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.]. BMC Genomics 12:8
Picoult-Newberg L, Ideker TE, Pohl MG, Taylor SL, Donaldson MA, Nickerson DA, Boyce-Jacino M (1999) Mining SNPs from EST databases. Genome Res 9:167
Rafalski A (2002) Applications of single nucleotide polymorphisms in crop genetics. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:94–100
Ribaut JM, Betrán J (1999) Single large-scale marker-assisted selection (SLS-MAS). Mol Breed 5:531–541
Robertson-Hoyt LA, Jines MP, Balint-Kurti PJ, Kleinschmidt CE, White DG, Payne GA, Maragos CM, Molnár TL, Holland JB (2006) QTL mapping for fusarium ear rot and fumonisin contamination resistance in two maize populations. Crop Sci 46:1734–1743
Röder MS, Korzun V, Wendehake K, Plaschke J, Tixier MH, Leroy P, Ganal MW (1998) A microsatellite map of wheat. Genetics 149:2007–2023
Saghai-Maroof M, Soliman K, Jorgensen RA, Allard R (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:8014–8018
Salmeron JM, Oldroyd GED, Rommens CMT, Scofield SR, Kim HS, Lavelle DT, Dahlbeck D, Staskawicz BJ (1996) Tomato Prf is a member of the leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes and lies embedded within the Pto kinase gene cluster. Cell 86:123–133
SAS I (1999) SAS/STAT user’s guide, version 8. SAS Institute Inc, Cary
Sessa G, D’Ascenzo M, Martin GB (2000) Thr38 and Ser198 are Pto autophosphorylation sites required for the AvrPto–Pto-mediated hypersensitive response. EMBO J 19:2257–2269
Shang YF, Zhao J, Du S, LU X, Wang S, Sun H, Yang C (2001) Identification and investigation on resistance to virus diseases of both maize commercial varieties and germplasm at seedling stage. Shandong Agric Sci 4:3–5
Shi LY, Li XH, Xie CX, Hao ZF, Weng JF, Zhang SH, Pan GT (2011) Development of SCARs from AFLP markers linked to resistance to maize rough dwarf virus (MRDV) using bulked segregant analysis in maize. Sci Agric Sinica 44:1763–1774
Shiu SH, Bleecker AB (2003) Expansion of the receptor-like kinase/Pelle gene family and receptor-like proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 132:530
Singh R, Tan SG, Panandam JM, Rahman RA, Ooi LCL, Low ETL, Sharma M, Jansen J, Cheah SC (2009) Mapping quantitative trait loci(QTLs) for fatty acid composition in an interspecific cross of oil palm. BMC Plant Biol 9:114
Tanksley SD (1993) Mapping polygenes. Annu Rev Genet 27:205–233
Torii KU (2000) Receptor kinase activation and signal transduction in plants: an emerging picture. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:361–367
Van Ooijen J (2004) MapQTL(R) 5, software for the mapping of quantitative trait loci in experimental populations. Kyazma BV, Wageningen
Van Ooijen J, Voorrips R (2001) JoinMap(R) 3.0, software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen, pp 1–51
Wang F (2007) Mapping QTL for maize rough dwarf virus. Dissertation, Shandong University
Wang AL, Chen Z, Shao X, Wei G (1998) A preliminary survey on resistance to maize rough dwarf disease of maize inbred lines. Maize Sci 6:65–66
Wang AL, Zhao D, Chen Z, Wang J, Shao X, Wei G (2000) Genetic analysis for maize rough dwarf virus resistance and for recurrent selection. J Maize Sci 8:80–82
Xu M, Melchinger A, Xia X, Lübberstedt T (1999) High-resolution mapping of loci conferring resistance to sugarcane mosaic virus in maize using RFLP, SSR, and AFLP markers. Mol Gen Genet 261:574–581
Young N (1996) QTL mapping and quantitative disease resistance in plants. Annu Rev Phytopathol 34:479–501
Yu H, Xie W, Wang J, Xing Y, Xu C, Li X, Xiao J, Zhang Q (2011) Gains in QTL detection using an ultra-high density SNP map based on population sequencing relative to traditional RFLP/SSR markers. PloS One 6:e17595. doi:17510.11371/journal.pone.0017595
Zhang YS (2005) Construction of genetic map and analysis of transgenic maize via pollen-tube pathway. Dissertation, Shandong University
Zhang S, Li X, Wang Z, George M, Jeffers D, Wang F, Liu X, Li M, Yuan L (2003) QTL mapping for resistance to SCMV in Chinese maize germplasm. Maydica 48:307–312
Zhang W, Chao S, Manthey F, Chicaiza O, Brevis J, Echenique V, Dubcovsky J (2008) QTL analysis of pasta quality using a composite microsatellite and SNP map of durum wheat. Theor Appl Genet 117:1361–1377
Zhou J, Loh YT, Bressan RA, Martin GB (1995) The tomato gene Pti1 encodes a serine/threonine kinase that is phosphorylated by Pto and is involved in the hypersensitive response. Cell 83:925–935
Zhou J, Tang X, Martin GB (1997) The Pto kinase conferring resistance to tomato bacterial speck disease interacts with proteins that bind a cis-element of pathogenesis-related genes. EMBO J 16:3207–3218
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Professor Miao Hongqin and other group members from the Institute of Plant Protection, Hebei Academy of Agricultural and Forestry Sciences, China, for MRDD resistance evaluation. This work was jointly supported by the International Cooperation Project for Science and Technology (2007DFA3-1010), National Natural Science Foundation of China (30771350), and National Hi-Tech Research Program (2006AA100103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Ly., Hao, Zf., Weng, Jf. et al. Identification of a major quantitative trait locus for resistance to maize rough dwarf virus in a Chinese maize inbred line X178 using a linkage map based on 514 gene-derived single nucleotide polymorphisms. Mol Breeding 30, 615–625 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-011-9652-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-011-9652-0