Abstract
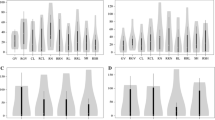
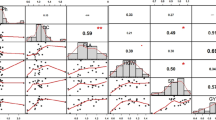
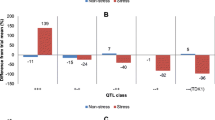
Rice is one of the most important food crops in the world. Abiotic stresses directly or indirectly affect the physiological status of rice and negatively alter its overall metabolism. Drought in rain-fed, lowland ecosystems is particularly harmful to growth and yield. As with many other food crops, drought tolerance in rice is a polygenic trait in which many genes localized in various quantitative trait loci (QTL) have additive effects on resistance to desiccation. For these reasons, breeding drought-tolerant rice is complex, time-consuming, and cost-intensive. Marker-assisted breeding (MAB) is a more efficient approach but requires comprehensive molecular linkage maps. Increased trehalose accumulation in various tissues correlates with exposure of the plant to drought. Elevated trehalose levels probably play roles in osmo-protection and the stabilization of various essential functions. Here, we document trehalose accumulation, the activity of the enzyme trehalase, and plant growth in three Mexican rice genotypes: two drought-tolerant accessions (Temporalero A95 and Sabanero A95) and one drought-sensitive variety (Morelos A98). Our data show that similar trehalose contents were found in roots of all three accessions under irrigated conditions, but that drought enhanced the synthesis of trehalose only in drought-tolerant varieties. Changes in the levels of non-structural sugars accompanied the accumulation of trehalose. Increased trehalase activities and photosynthetic capacities in drought-tolerant varieties was observed under stress conditions, which was accompanied by lower stomatal resistance and better water-holding capacity. We conclude that DNA markers built around trehalose metabolism can be used during MAB to study drought tolerance in rice and other crops.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anselmino O, Gilg E (1913) Über das Vorkmmen von Trehalose in Selaginella lepidophylla. Ber Deut Pharm Ges 23:326–330
Avonce N, Mendoza-Vargas A, Morett E, Iturriaga G (2006) Insights on the evolution of trehalose biosynthesis. BMC Evol Biol 6:109
Birch GG (1963) Trehalose. Adv Carbohydr Chem 18:201–225
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brodmann D, Schuller A, Ludwing-Müller J, Aeschbacher RA, Wiemken A, Boller T, Wingler A (2002) Induction of trehalase in Arabidopsis plants infected with the trehalose-producing pathogen Plasmodiophorra brassicae. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15:693–700
Cook MG, Evans LT (1983) Some physiological aspects of the domestication and improvement of rice (Oryza spp.). Field Crops Res 6:219–238
Drennan PM, Smith P, Goldsworthy D, van Staden J (1993) The ocurrence of Trehalose in the leaves of the desiccation-tolerant angiosperm Myrothamnus febellifolius. J Plant Physiol 142:493–496
Eastmond PJ, van Dijken AJ, Spielman M, Kerr A, Tissier AF, Dickinson HG, Jones JD, Smeekens SC, Graham IA (2002) Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase, which catalyses the first step in trehalose synthesis, is essential for Arabidopsis embryo maturation. Plant J 29:225–235
Ekanayake IJ, Garrity DP, Masajo TM, O′Toole JC (1985) Root pulling resistance in rice: inheritance and association with drought tolerance. Euphytica 34:905–913
El-Bashinti T, Hamamci H, Öktem HA, Yücel M (2005) Biochemical analysis of trehalose and its metabolizing enzymes in wheat under abiotic stress conditions. Plant Sci 169:47–54
Elbein AD (1974) The metabolism of alpha, alpha-trehalose. Adv Carbohydr Chem 30:227–256
García AB, de Almeida EJ, Iyer S, Gerats T, van Montagu M, Caplan AB (1997) Effects of osmoprotectants upon NaCl stress in rice. Plant Physiol 115:159–169
Garg AK, Kim J-K, Owens ThG, Ranwala AP, Choi YD, Kochian LV, Wu RJ (2002) Trehalose accumulation in rice plants confers high tolerance levels to different abiotic stresses. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 99(25):15898–15903
Ge LF, Chao DY, Shi M, Zhu MZ, Gao JP, Lin HX (2008) Overexpression of the trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase gene OsTPP1 confers stress tolerance in rice and results in the activation of stress responsive genes. Planta 228:191–201
Goddijn O, van Dun K (1999) Trehalose metabolism in plants. Trends Plant Sci 4(8):315–319
Goff SA et al (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp japonica). Science 226(5565):92–100
Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA, Zhu JK, Bohner HJ (2000) Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Mol Biol 51:463–499
Jang I-Ch, Oh S-J, Seo J-S, Choi W-B, Song SI, Kim ChH, Kim YSh, Seo HS, Choi YD, Nahm BH, Kim J-K (2003) Expression of a bifunctional fusion of the Escherichia coli genes for trehalose-6-phosphate synthase and trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase in transgenis rice plants increases trehalose accumulation and abiotic stress tolerance without stunting growth. Plant Physiol 131:516–524
Kamoshita A, Chandra babu R, Manikanda Boopathi N, Fukai S (2008) Phenotypic and genotypic analysis of drought-resistance traits for development of rice cultivars adapted to rainfed enviroments. Field Crops Res 109:1–23
Kolbe A, Tiesen A, Schluepmann H, Paul M, Ulrich S, Geigenberg P (2005) Trehalose-6-phosphate regulates starch synthesis via posttranslational redox activation of a ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:11118–11123
Li ZK, Xu JL (2007) Breeding for drought and salt tolerant rice (Oryza sativa L): progress and perspectives. In: Jenks MA, Hasegawa PM, Jain SM (eds) Advances in molecular-breeding toward drought and salt tolerant crops. Springer, Berlin, pp 531–536
Lilley JM, Fukai S (1994) Effects of timing and severity of water deficit on four diverse rice cultivars. III. Phenological development, crop growth and grain yield. Field Crops Res 37:225–234
Lu H, Liu Z, Wu N, Berné S, Saito Y, Liu B (2002) Rice domestication and climatic change: phytolith evidence from East China. Boreas 31:378–385
Ludlow MM, Muchow RC (1990) A critical evaluation of traits for improving crop yields in water-limited environments. Adv Agron 43:107–153
Müller J, Boller T, Wiemken A (1995) Trehalose and trehalase in plants: recent developments. Plant Sci 112:1–9
Müller J, Aeschbacher RA, Wingler A, Boller T, Wiemken A (2001) Trehalose and trehalase in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 125:1086–1093
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid grow and bioassays with tobacco tissues cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Ohno Y (1976) Varietal differences of photosynthetic efficiency and dry matter production in Indica rice. Trop Agric 53:115–123
Paul M, Pellny T, Goddijn O (2001) Enhancing photosynthesis with sugar signals. Trends Plant Sci 6:197–200
Pellny TK, Ghannoum O, Conroy JP, Schluepmann H, Smeekens S, Andralojc J, Krause KP, Goddijn O, Paul MJ (2004) Genetic modification of photosynthesis with E. coli genes for trehalose synthesis. Plant Biotechnol J 2:71–82
Pilon-Smits EAH, Terry N, Sears T, Kim H, Zayed A, Hwang S, van Dun K, Verwoerd ThC, Krutwagen RWHH, Goddijn OJM (1998) Trehalose-producing transgenic tobacco plants show improved growth performance under drought stress. J Plant Physiol 152:525–532
Rosa M, Hilal M, Ganzález JA, Prado FE (2004) Changes in soluble carbohydrates and related enzymes induced by low temperature during early development stages of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) seedlings. J Plant Physiol 161:683–689
Rosa M, Prado C, Podazza G, Interdonato R, González JA, Hilal M, Prado FE (2010) Soluble sugars-Metabolism, sensing and abiotic stress. A complex network in life of plants. Plant Signal Behav 4:388–393
Satoh-Nagasawa N, Nagasawa N, Malcomber S, Sakai H, Jackson D (2006) A trehalose metabolic enzyme controls inflorescence architecture in maize. Nature 441:227–230
Strom AR, Kaasen I (1993) Trehalose metabolism in Escherichia coli: stress protection and stress regulation of gene expression. Mol Microbiol 8:205–210
Thevelein JM, Hohmann S (1995) Trehalose synthase: guard to the gate of glycolysis in yeast? Trends Biochem Sci 20:3–10
van Dijken AJ, Schluepmann H, Smeekens SC (2004) Arabidopsis trehalose-6-phosphate synthase 1 is essential for normal vegetative growth and transition to flowering. Plant Physiol 135:969–977
Wade LJ, McLaren CG, Quintana L, Hampichitvitaya D, Rajatasereekul S, Sarawgi AK, Kumar A, Ahmed HU, Sarwoto, Singh AK (1999) Genotype by environment interactions in diverse rainfed lowland rice environment. Field Crops Res 64:35–50
Zhang J, Zheng HG, Ali ML, Triphathy JN, Aarti A, Pathan MS, Sarial AK, Robin S, Nguyen TT, Babu RC (1999) Molecular dissection of drought tolerance in rice: from physio-morphological traits to field performance. In: O’Toole JC, Ito O, Hardy B (eds) Genetic improvement of rice for water-limited environments. International Rice Research Institute, pp 331–343
Zhao XQ, Xu Jl, Zhao M, Lafitte R, Zhu LH, Fu BY, Gao YM, Li ZK (2008) QTL′s affecting morph-physiological traits related to drought tolerance detected in overlapping introgression lines of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Sci 174:618–625
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the INIFAP (Instituto Nacional de Investigaciones Forestales, Agrícolas y Pecuarias) Unidad Zacatepec for providing the rice seeds used in this work and the Centro de Investigación y de Estudios Avanzados del IPN, Unidad Irapuato, for the facilities to run the experiments. Thanks to Ing. Agr. Fernanda Esparza for help in the art work. We are grateful to W.J. Broughton for his help with the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deyanira, QM., Estrada-Luna, A.A., Altamirano-Hernández, J. et al. Use of trehalose metabolism as a biochemical marker in rice breeding. Mol Breeding 30, 469–477 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-011-9636-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-011-9636-0