Abstract
Agar-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles (Fe3O4@agar) were prepared simply through in situ co-precipitation of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions via NH4OH in an aqueous solution of Agar. Coating of Ag+ ions on the surface of the latter followed by mild reduction of Ag+ with NaBH4 gives Fe3O4@Agar-Ag NPs. The magnetic Fe3O4@Agar-Ag nanocatalyst was characterized thoroughly by FT‐IR, XRD, SEM, TEM, VSM, EDX, TGA, and ICP analyses. Its catalytic activity was assessed in the synthesis of 12-aryl-8,9,10,12-tetrahydrobenzo[a]xanthene-11-one, 14-aryl-14H-dibenzo[a,j]xanthenes, and 1,8-dioxo-octahydroxanthene derivatives through a one-pot condensation of dimedone, 2-naphthol, and aryl aldehydes in EtOH. This novel method represents lots of advantages compared to the previous researches, such as avoiding the toxic catalysts, easy method for isolation of the products, satisfying yields, totally clean conditions, and simplicity of the methodology. This catalytic system is attributed to an eco-friendly process, high catalytic activity, and facility of recovery using an external magnet.
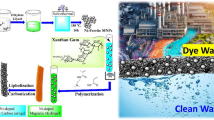
Graphical abstract

A novel and magnetically recyclable catalyst known as Fe3O4@Agar-Ag NPs as a heterogeneous catalyst were synthesized by a simple method. Using this facile, efficient, and eco-friendly Nanocomposite, for the different models of xanthene reaction was represented.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maleki A, Aghaei M, Ghamari N (2016) Facile synthesis of tetrahydrobenzoxanthenones via a one-pot three-component reaction using an eco-friendly and magnetized biopolymer chitosan-based heterogeneous nanocatalyst. Appl Organomet Chem 30:939–942. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.3524
Tabatabaeian K, Khorshidi A, Mamaghani M et al (2011) One-pot synthesis of tetrahydrobenzo[a]xanthen-11-one derivatives catalyzed by ruthenium chloride hydrate as a homogeneous catalyst. Can J Chem 89:623–627. https://doi.org/10.1139/v11-042
Shirini F, Khaligh NG (2012) Succinimide-N-sulfonic acid: an efficient catalyst for the synthesis of xanthene derivatives under solvent-free conditions. Dye Pigment 95:789–794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2012.06.022
Kumar A, Rout L, Achary LSK et al (2017) Greener route for synthesis of aryl and alkyl-14H-dibenzo [a.j] xanthenes using graphene oxide-copper ferrite nanocomposite as a recyclable heterogeneous catalyst. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42975
Rahimi J, Maleki A (2020) Preparation of a trihydrazinotriazine-functionalized core-shell nanocatalyst as an extremely efficient catalyst for the synthesis of benzoxanthenes. Mater Today Chem 18:100362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2020.100362
Bacci JP, Kearney AM, Van Vranken DL (2005) Efficient two-step synthesis of 9-aryl-6-hydroxy-3H-xanthen-3-one fluorophores. J Org Chem 70:9051–9053. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo051243i
Naidu KRM, Krishna BS, Kumar MA et al (2012) Design, synthesis and antiviral potential of 14-aryl/heteroaryl-14H- dibenzo[a, j]xanthenes using an efficient polymer-supported catalyst. Molecules 17:7543–7555. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17067543
Dos Santos WH, Da Silva-Filho LC (2016) Facile and efficient synthesis of xanthenedione derivatives promoted by niobium pentachloride. Chem Pap 70:1658–1664. https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2016-0098
El-Brashy AM, El-Sayed Metwally M, El-Sepai FA (2004) Spectrophotometric determination of some fluoroquinolone antibacterials by binary complex formation with xanthene dyes. Farmaco 59:809–817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.farmac.2004.07.001
Knight CG, Stephens T (1989) Xanthene-dye-labelled phosphatidylethanolamines as probes of interfacial pH. Stud Phospholipid Vesicles Biochem J 258:683–689. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj2580683
Rewcastle GW, Atwell GJ, Zhuang L et al (1991) Potential antitumor agents. 61. structure-activity relationships for in vivo colon 38 activity among disubstituted 9-Oxo-9H-xanthene-4-acetic Acids. J Med Chem 34:217–222. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm00105a034
Jung H-A, Su B-N, Keller WJ et al (2006) Antioxidant xanthones from the pericarp of garcinia mangostana (Mangosteen). J Agric Food Chem 54:2077–2082. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf052649z
Makino M, Fujimoto Y (1999) Flavanones from Baeckea frutescens. Phytochemistry 50:273–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(98)00534-2
Hiranrat A, Mahabusarakam W (2008) New acylphloroglucinols from the leaves of Rhodomyrtus tomentosa. Tetrahedron 64:11193–11197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2008.09.054
E-journal CE, Hassankhani A, Mosaddegh E et al (2012) H4SiW12O40 catalyzed one-pot synthesis of 12-aryl-8,9,10,12-tetrahydrobenzo[a]xanthen-11-ones under solvent free conditions. 9:786–790
Reza Tayebee BM (2017) diazepine - tetrazole and benzodiazepine - 2 - carboxamide derivatives with the aid of MCM - 48 / H 5 PW 10 V 2 O 40. J Chem Sci 125:335–344
Kantevari S, Bantu R, Nagarapu L (2007) HClO4-SiO2 and PPA-SiO2 catalyzed efficient one-pot Knoevenagel condensation, Michael addition and cyclo-dehydration of dimedone and aldehydes in acetonitrile, aqueous and solvent free conditions: scope and limitations. J Mol Catal A Chem 269:53–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2006.12.039
Saadat A, Zare A, Jamadi F, Abdolalipour-Saretoli M (2018) Highly efficient synthesis of 1-Thioamidoalkyl-2-naphthols and 14-Aryl-14H-dibenzo[a, j]xanthenes using a novel ionic liquid: Catalyst preparation, characterization and performing the reactions. Bull Chem React Eng & Catal 13:204–212. https://doi.org/10.9767/bcrec.13.2.1280.204-212
Sheikh S, Nasseri MA, Chahkandi M et al (2020) Functionalized magnetic PAMAM dendrimer as an efficient nanocatalyst for a new synthetic strategy of xanthene pigments. Hazard Mater 400: 122985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122985
Venu Madhav J, Thirupathi Reddy Y, Narsimha Reddy P et al (2009) Cellulose sulfuric acid: an efficient biodegradable and recyclable solid acid catalyst for the one-pot synthesis of aryl-14H-dibenzo[a.j]xanthenes under solvent-free conditions. J Mol Catal A Chem 304:85–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2009.01.028
Rezayati S, Erfani Z, Hajinasiri R (2015) Phospho sulfonic acid as efficient heterogeneous Brønsted acidic catalyst for one-pot synthesis of 14H-dibenzo[a, j]xanthenes and 1,8-dioxo-octahydro-xanthenes. Chem Pap 69:536–543. https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0058
Maleki A (2012) Fe 3O 4/SiO 2 nanoparticles: an efficient and magnetically recoverable nanocatalyst for the one-pot multicomponent synthesis of diazepines. Tetrahedron 68:7827–7833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2012.07.034
Maleki A (2013) One-pot multicomponent synthesis of diazepine derivatives using terminal alkynes in the presence of silica-supported superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Tetrahedron Lett 54:2055–2059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2013.01.123
Maleki A (2014) One-pot three-component synthesis of pyrido[2′,1′:2,3]imidazo[4,5-c]isoquinolines using Fe3O4@SiO2-OSO3H as an efficient heterogeneous nanocatalyst. RSC Adv 4:64169–64173. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra10856f
Maleki A (2018) Green oxidation protocol: selective conversions of alcohols and alkenes to aldehydes, ketones and epoxides by using a new multiwall carbon nanotube-based hybrid nanocatalyst via ultrasound irradiation. Ultrason Sonochem 40:460–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.07.020
Esmaeili MS, Varzi Z, Taheri-Ledari R, Maleki A (2021) Preparation and study of the catalytic application in the synthesis of xanthenedione pharmaceuticals of a hybrid nano-system based on copper, zinc and iron nanoparticles. Res Chem Intermed 47:973–996. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-020-04311-8
Trang VT, Tam LT, Van Quy N et al (2017) Functional iron oxide-silver hetero-nanocomposites: controlled synthesis and antibacterial activity. J Electron Mater 46:3381–3389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-017-5314-2
Mousavi Mashhadi SA, Kassaee MZ, Eidi E (2019) Magnetically recyclable nano copper/chitosan in O-arylation of phenols with aryl halides. Appl Organomet Chem 33:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.5042
Ghavami M, Koohi M, Kassaee MZ (2013) Selective nanocatalyst for an efficient Ugi reaction: magnetically recoverable Cu(acac)2/NH2-T/SiO2atFe3O4 nanoparticles. J Chem Sci 125:1347–1357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-013-0506-7
Abdolmohammadi S, Hossaini Z (2019) Fe3O4 MNPs as a green catalyst for syntheses of functionalized [1,3]-oxazole and 1H-pyrrolo-[1,3]-oxazole derivatives and evaluation of their antioxidant activity. Mol Divers 23:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-019-09916-9
Chen Y, Zhang Z, Jiang W et al (2019) RuIII@CMC/Fe3O4 hybrid: an efficient, magnetic, retrievable, self-organized nanocatalyst for green synthesis of pyranopyrazole and polyhydroquinoline derivatives. Mol Divers 23:421–442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-018-9887-3
Ezzatzadeh E (2021) Chemoselective oxidation of sulfi des to sulfoxides using a novel Zn-DABCO functionalized Fe3O4 MNPs as highly effective nanomagnetic catalyst. Asian J Nanosci Mater 4:125–136. https://doi.org/10.26655/AJNANOMAT.2021.2.3
Ezzatzadeh E, Hossaini Z (2020) 2D ZnO/Fe3O4 nanocomposites as a novel catalyst-promoted green synthesis of novel quinazoline phosphonate derivatives. Appl Organomet Chem 34:e5596. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.5596
Rezayati S, Ramazani A, Sajjadifar S et al (2021) Design of a schiff base complex of copper coated on epoxy-modified core-shell MNPs as an environmentally friendly and novel catalyst for the one-pot synthesis of various chromene-annulated heterocycles. ACS Omega 6:25608–25622. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c03672
Wang M, Han J, Shi H (2020) Synthesis and inhibition performance of a Fe3O4/Chitosan-supported inhibitor. J Vinyl Addit Technol 26:304–308. https://doi.org/10.1002/vnl.21744
Nian D, Shi P, Sun J et al (2019) Application of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone–ferrosoferric oxide nanoparticles in targeted imaging of breast tumors. J Int Med Res 47:1749–1757. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060519834457
Sadjadi S, Kahangi FG, Dorraj M, Heravi MM (2020) Ag nanoparticles stabilized on cyclodextrin polymer decorated with multi-nitrogen atom containing polymer: an efficient catalyst for the synthesis of xanthenes. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020241
Maleki A, Panahzadeh M, Eivazzadeh-keihan R (2019) Agar: a natural and environmentally-friendly support composed of copper oxide nanoparticles for the green synthesis of 1,2,3–triazoles. Green Chem Lett Rev 12:395–406. https://doi.org/10.1080/17518253.2019.1679263
Bahrami S, Hassanzadeh-Afruzi F, Maleki A (2020) Synthesis and characterization of a novel and green rod-like magnetic ZnS/CuFe2O4/agar organometallic hybrid catalyst for the synthesis of biologically-active 2-amino-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile derivatives. Appl Organomet Chem 34:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.5949
Eivazzadeh-Keihan R, Moghim Aliabadi HA, Radinekiyan F et al (2021) Investigation of the biological activity, mechanical properties and wound healing application of a novel scaffold based on lignin-agarose hydrogel and silk fibroin embedded zinc chromite nanoparticles. RSC Adv 11:17914–17923. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra01300a
Xiao Q, Liu C, Ni H et al (2019) β-Agarase immobilized on tannic acid-modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles for efficient preparation of bioactive neoagaro-oligosaccharide. Food Chem 272:586–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.08.017
Armisén R, Gaiatas F (2009) Agar. In: Phillips GO, Williams PA (eds) Handbook of hydrocolloids. Woodhead Publishing Limited, pp 82–107. https://doi.org/10.1533/9781845695873.82.
Hsieh SL, Huang BY, Hsieh SL et al (2010) Green fabrication of agar-conjugated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Nanotechnology. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/21/44/445601
Hoseinzade K, Mousavi-Mashhadi SA, Shiri A (2021) Copper immobilization on Fe3O4@Agar: an efficient superparamagnetic nanocatalyst for green ullmann-type cross-coupling reaction of primary and secondary amines with aryl iodide derivatives. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 31:4648–4658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02106-x
Sonei S, Gholizadeh M, Taghavi F (2020) Cu(II) anchored on modified magnetic nanoparticles: as a green and efficient recyclable nano catalyst for one pot synthesis of 12-Aryl-8,9,10,12tetrahydrobenzo[a]xanthene-11-oneʺ. Polycycl Aromat Compd 40:1127–1142. https://doi.org/10.1080/10406638.2018.1531431
Skumiel A, Kaczmarek K, Flak D et al (2020) The influence of magnetic nanoparticle concentration with dextran polymers in agar gel on heating efficiency in magnetic hyperthermia. J Mol Liq. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.112734
Dung TT, Danh TM, Hoa LTM et al (2009) Structural and magnetic properties of starch-coated magnetite nanoparticles. J Exp Nanosci 4:259–267. https://doi.org/10.1080/17458080802570609
Gecim B, Winer WO (1987) Thermal conductivity of lubricants at high pressures. J Tribol 109:566–567. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3261507
Burdușel AC, Gherasim O, Grumezescu AM et al (2018) Biomedical applications of silver nanoparticles: an up-to-date overview. Nanomaterials 8:1–24. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8090681
Keyhaniyan M, Shiri A, Eshghi H, Khojastehnezhad A (2018) Novel design of recyclable copper(II) complex supported on magnetic nanoparticles as active catalyst for Beckmann rearrangement in poly(ethylene glycol). Appl Organomet Chem 32:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4344
Ghadamyari Z, Shiri A, Khojastehnezhad A, Seyedi SM (2019) Zirconium (IV) porphyrin graphene oxide: a new and efficient catalyst for the synthesis of 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-ones. Appl Organomet Chem 33:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.5091
Keyhaniyan M, Shiri A, Eshghi H, Khojastehnezhad A (2018) Synthesis, characterization and first application of covalently immobilized nickel-porphyrin on graphene oxide for Suzuki cross-coupling reaction. New J Chem 42:19433–19441. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nj04157a
Ghadamyari Z, Khojastehnezhad A, Seyedi SM, Shiri A (2019) Co(II)-porphyrin immobilized on graphene oxide: an efficient catalyst for the beckmann rearrangement. ChemistrySelect 4:10920–10927. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201902811
Rafiee E, Ataei A, Nadri S et al (2014) Combination of palladium and oleic acid coated-magnetite particles: characterization and using in Heck coupling reaction with magnetic recyclability. Inorganica Chim Acta 409:302–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2013.09.042
Mousavi M, Bakavoli M, Shiri A, Eshghi H (2018) Pure water-induced dehalogenation of 2,4-Di- tert-amino-6-substituted-5-halogenopyrimidines. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:5852–5857. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b04127
Mousavi-mashhadi SA, Shiri A (2021) On-water and efficient ullmann-type O-arylation cross coupling reaction of phenols and aryl tosylates in the presence of Fe3O4@Starch-Au as Nanocatalyst. Chemistry Select 6:3941–3951. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202004327
Esfahani HRM, Foroughifar N, Mobinikhaledi A, Moghanian H (2013) Ammonium oxalate as an efficient catalyst for one-pot synthesis of tetrahydrobenzo [a]xanthen-11-one derivatives under solvent-free conditions. Synth React Inorg Met Nano-Metal Chem 43:752–755. https://doi.org/10.1080/15533174.2012.754767
Bi Fatemeh Mirjalili B, Bamoniri A, Zamani L (2012) Nano-TiCl4/SiO2: an efficient and reusable catalyst for the synthesis of tetrahydrobenzo[a]xanthenes-11-ones. Lett Org Chem 9:338–343. https://doi.org/10.2174/157017812801264700
Zare Fekri L, Darya-Laal AR (2020) NiFe2O4@SiO2@amino glucose magnetic nanoparticle as a green, effective and magnetically separable catalyst for the synthesis of xanthene-ones under solvent-free condition. Polycycl Aromat Compd 40:1539–1556. https://doi.org/10.1080/10406638.2018.1559207
Taghavi F, Gholizadeh M, Saljooghi AS, Ramezani M (2016) Metal free synthesis of tetrahydrobenzo[: A] xanthenes using orange peel as a natural and low cost efficient heterogeneous catalyst. RSC Adv 6:87082–87087. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra17607k
Mane P, Shinde B, Mundada P et al (2020) Sodium acetate/MWI: a green protocol for the synthesis of tetrahydrobenzo[α]xanthen-11-ones with biological screening. Res Chem Intermed 46:231–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-019-03945-7
Rajitha B, Sunil Kumar B, Thirupathi Reddy Y et al (2005) Sulfamic acid: a novel and efficient catalyst for the synthesis of aryl-14H-dibenzo[a.j]xanthenes under conventional heating and microwave irradiation. Tetrahedron Lett 46:8691–8693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2005.10.057
Thirumalai D, Gajalakshmi S (2020) An efficient heterogeneous iron oxide nanoparticle catalyst for the synthesis of 9-substituted xanthene-1,8-dione. Res Chem Intermed 46:2657–2668. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-020-04112-z
Hasaninejad A, Shekouhy M, Miar M, Firoozi S (2016) Sulfonated polyethylene glycol (PEG-SO3H) as eco-friendly and potent water soluble solid acid for facile and green synthesis of 1,8-Dioxo-Octahydroxanthene and 1,8-Dioxo-Decahydroacridine derivatives. Synth React Inorg Met Nano-Metal Chem 46:151–157. https://doi.org/10.1080/15533174.2014.900799
Chaudhary GR, Bansal P, Kaur N, Mehta SK (2014) Recyclable CuO nanoparticles as heterogeneous catalysts for the synthesis of xanthenes under solvent free conditions. RSC Adv 4:49462–49470. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra07620f
Zhou J, Liu D, Wu F et al (2019) Synthesis of SCMNPs@imine/SO3H magnetic nanocatalyst by chlorosulfonic acid as sulfonating agents and their application for the preparation of 12-aryl-8,9,10,12-tetrahydrobenzo[a]xanthen-11-one and 1,8-dioxooctahydroxanthene derivatives. Mater Res Exp. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab5c90
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Research Council of Ferdowsi University of Mashhad (3/52357).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoseinzade, K., Mousavi-Mashhadi, S.A. & Shiri, A. An efficient and green one-pot synthesis of tetrahydrobenzo[a]xanthenes, 1,8-dioxo-octahydroxanthenes and dibenzo[a,j]xanthenes by Fe3O4@Agar-Ag as nanocatalyst. Mol Divers 26, 2745–2759 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-021-10368-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-021-10368-3