Abstract
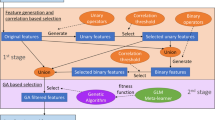
It is important to identify which proteins can interact with nucleic acids for the purpose of protein annotation, since interactions between nucleic acids and proteins involve in numerous cellular processes such as replication, transcription, splicing, and DNA repair. This research tries to identify proteins that can interact with DNA, RNA, and rRNA, respectively. mRMR (Minimum redundancy and maximum relevance), with its elegant mathematical formulation, has been applied widely in processing biological data and feature analysis since its introduction in 2005. mRMR plus incremental feature selection (IFS) is known to be very efficient in feature selection and analysis, and able to improve both effectiveness and efficiency of a prediction model. IFS is applied to decide how many features should be selected from feature list provided by mRMR. In the end, the selected features of mRMR and IFS are further refined by a conventional feature selection method—forward feature wrapper (FFW), by reordering the features. Each protein is coded by 132 features including amino acid compositions and physicochemical properties. After the feature selection, k-Nearest Neighbor algorithm, the adopted prediction model, is trained and tested. As a result, the optimized prediction accuracies for the DNA, RNA, and rRNA are 82.0, 83.4, and 92.3%, respectively. Furthermore, the most important features that contribute to the prediction are identified and analyzed biologically. The predictor, developed for this research, is available for public access at http://chemdata.shu.edu.cn/protein_na_mrmr/.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vigneault F, Guerin SL (2005) Regulation of gene expression: probing DNA–protein interactions in vivo and in vitro. Expert Rev Proteomics 2: 705–718
Hegarat N, Francois JC, Praseuth D (2008) Modem tools for identification of nucleic acid-binding proteins. Biochimie 90: 1265–1272
Li W, Lin K, Feng K, Cai Y (2008) Prediction of protein structural classes using hybrid properties. Mol Divers 12: 171–179
Cai YD, Qian Z, Lu L, Feng KY, Meng X, Niu B, Zhao GD, Lu WC (2008) Prediction of compounds’ biological function (metabolic pathways) based on functional group composition. Mol Divers 12: 131–137
Cai YD, Lu L (2008) Predicting N-terminal acetylation based on feature selection method. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 372: 862–865
Lu L, Shi XH, Li SJ, Xie ZQ, Feng YL, Lu WC, Li YX, Li H, Cai YD (2009) Protein sumoylation sites prediction based on two-stage feature selection. Mol Divers. doi:10.1007/s11030-009-9149-5
Niu B, Jin Y, Lu L, Fen K, Gu L, He Z, Lu W, Li Y, Cai Y (2009) Prediction of interaction between small molecule and enzyme using AdaBoost. Mol Divers 13: 313–320
Niu B, Jin YH, Feng KY, Lu WC, Cai YD, Li GZ (2008) Using AdaBoost for the prediction of subcellular location of prokaryotic and eukaryotic proteins. Mol Divers 12: 41–45
Jin YH, Niu B, Feng KY, Lu WC, Cai YD, Li GZ (2008) Predicting subcellular localization with AdaBoost learner. Protein Pept Lett 15: 286–289
Lu L, Qian Z, Shi X, Li H, Cai YD, Li Y (2009) A knowledge-based method to predict the cooperative relationship between transcription factors. Mol Divers. doi:10.1007/s11030-009-9177-1
Henikoff S, Greene EA, Pietrokovski S, Bork P, Attwood TK, Hood L (1997) Gene families: the taxonomy of protein paralogs and chimeras. Science 278: 609–614
Marcotte EM, Pellegrini M, Ng HL, Rice DW, Yeates TO, Eisenberg D (1999) Detecting protein function and protein–protein interactions from genome sequences. Science 285: 751–753
Yu XJ, Cao JP, Cai YD, Shi TL, Li YX (2006) Predicting rRNA-, RNA-, and DNA-binding proteins from primary structure with support vector machines. J Theor Biol 240: 175–184
Cai YD, Lin SL (2003) Support vector machines for predicting rRNA-, RNA-, and DNA-binding proteins from amino acid sequence. BBA-Proteins Proteomics 1648: 127–133
Ahmad S, Sarai A (2004) Moment-based prediction of DNA-binding proteins. J Mol Biol 341: 65–71
Shanahan HP, Garcia MA, Jones S, Thornton JM (2004) Identifying DNA-binding proteins using structural motifs and the electrostatic potential. Nucleic Acids Res 32: 4732–4741
Jones S, Barker JA, Nobeli I, Thornton JM (2003) Using structural motif templates to identify proteins with DNA binding function. Nucleic Acids Res 31: 2811–2823
Szilagyi A, Skolnick J (2006) Efficient prediction of nucleic acid binding function from low-resolution protein structures. J Mol Biol 358: 922–933
Stawiski EW, Gregoret LM, Mandel-Gutfreund Y (2003) Annotating nucleic acid-binding function based on protein structure. J Mol Biol 326: 1065–1079
Peng HC, Long FH, Ding C (2005) Feature selection based on mutual information: Criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach 27: 1226–1238
Cai YD, He JF, Li XL, Lu L, Yang XY, Feng KY, Lu WC, Kong XY (2009) A novel computational approach to predict transcription factor DNA binding preference. J Proteome Res 8: 999–1003
Xu XC, Yu D, Fang W, Cheng YS, Qian ZL, Lu WC, Cai YD, Feng KY (2008) Prediction of peptidase category based on functional domain composition. J Proteome Res 7: 4521–4524
Liu L, Cai YD, Lu WC, Feng KY, Peng CR, Niu B (2009) Prediction of protein–protein interactions based on PseAA composition and hybrid feature selection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 380: 318–322
Friedman J, Baskett F, Shustek LJ (1975) An algorithm for finding nearest neighbors. IEEE Trans Comput 24: 1000–1006
Cover TM, Hart PE (1967) Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans Inf Theory IT-13: 21–27
Li WZ, Jaroszewski L, Godzik A (2001) Clustering of highly homologous sequences to reduce the size of large protein databases. Bioinformatics 17: 282–283
Wang GL, Dunbrack RL (2003) PISCES: a protein sequence culling server. Bioinformatics 19: 1589–1591
Chothia C, Finkelstein AV (1990) The classification and origins of protein folding patterns. Annu Rev Biochem 59: 1007–1039
Frishman D, Argos P (1997) Seventy-five percent accuracy in protein secondary structure prediction. Proteins 27: 329–335
Mucchielli-Giorgi MH, Hazout S, Tuffery P (1999) PredAcc: prediction of solvent accessibility. Bioinformatics 15: 176–177
JenJacobson L (1997) Protein-DNA recognition complexes: conservation of structure and binding energy in the transition state. Biopolymers 44: 153–180
Shazman S, Mandel-Gutfreund Y (2008) Classifying RNA- binding proteins based on electrostatic properties. Plos Comput Biol 4. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000146
Sanchez-Diaz P, Penalva LOF (2006) Post-transcription meets post-genomic: the saga of RNA binding proteins in a new era. RNA Biol 3: 101–109
Graveley BR (2004) A protein interaction domain contacts RNA in the prespliceosome. Mol Cell 13: 302–304
Woodson SA, Leontis NB (1998) Structure and dynamics of ribosomal RNA. Curr Opin Struct Biol 8: 294–300
Moine H, Cachia C, Westhof E, Ehresmann B, Ehresmann C (1997) The RNA binding site of S8 ribosomal protein of Escherichia coli: Selex and hydroxyl radical probing studies. RNA 3: 255–268
Powers T, Noller HF (1995) Hydroxyl radical footprinting of ribosomal-proteins on 16s ribosomal-RNA. RNA 1: 194–209
Stern S, Powers T, Changchien LM, Noller HF (1989) RNA–protein interactions in 30s ribosomal-subunits—folding and function of 16s ribosomal-RNA. Science 244: 783–790
Bleichert F, Grannemant S, Osheim YN, Beyer AL, Baserga SJ (2006) The PINc domain protein Utp24, a putative nuclease, is required for the early cleavage steps in 18S rRNA maturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 9464–9469
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
YouLang Yuan, XiaoHe Shi and XinLei Li are regarded as joint first authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, Y., Shi, X., Li, X. et al. Prediction of interactiveness of proteins and nucleic acids based on feature selections. Mol Divers 14, 627–633 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-009-9198-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-009-9198-9