Summary
Sialic acids are a family of acidic sugars with a 9-carbon backbone, prominently expressed in animals of deuterostome lineage. Siglecs are the largest family of vertebrate endogenous receptors that recognize glycoconjugates containing sialic acids. Although a few Siglecs are well-conserved throughout vertebrate evolution and show similar binding preference regardless of the species of origin, most others, particularly the CD33-related subfamily of Siglecs, show marked inter-species differences in repertoire, sequence, and binding preference. The diversification of CD33-related Siglecs may be driven by direct competition against pathogens, and/or by necessity to catch up with the changing landscape of endogenous glycans, which may in turn be changing to escape exploitation by other pathogens.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
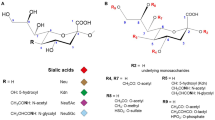
- Neu5Ac:
-
N-acetylneuraminic acid
- Neu5Gc:
-
N-glycolylneuraminic acid
- KDN:
-
2-keto-3-deoxy-d-glycero-d-galacto-nononic acid
- Sia:
-
sialic acid, type not specified
- CMP-Neu5Ac:
-
cytidine 5′-monophospho-Neu5Ac
- Gal:
-
d-galactose
- GalNAc:
-
N-acetyl-d-galactosamine
- GlcNAc:
-
N-acetyl-d-glucosamine
- HexNAc:
-
N-acetyl-d-hexosamine, i.e., GlcNAc or GalNAc
- Fuc:
-
l-fucose
- ITIM:
-
immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif
- Sn:
-
sialoadhesin
- MAG:
-
myelin-associated glycoprotein
- SMP:
-
Schwann cell myelin protein
- CD33rSiglec:
-
CD33/Siglec-3–related Siglec
- EST:
-
expressed sequence tag
References
Varki, A., Biological roles of oligosaccharides: All of the theories are correct, Glycobiology, 3 (1993) 97–130.
Gagneux, P. and Varki, A., Evolutionary considerations in relating oligosaccharide diversity to biological function, Glycobiology, 9 (1999) 747–755.
Freeze, H.H., Update and perspectives on congenital disorders of glycosylation, Glycobiology, 11 (2001) 129R–143R.
Jaeken, J. and Carchon, H., Congenital disorders of glycosylation: A booming chapter of pediatrics, Curr. Opin. Pediatr., 16 (2004) 434–439.
Aebi, M. and Hennet, T., Congenital disorders of glycosylation: Genetic model systems lead the way, Trends Cell Biol., 11 (2001) 136–141.
Angata, T. and Varki, A., Chemical diversity in the sialic acids and related alpha-keto acids: An evolutionary perspective, Chem. Rev., 102 (2002) 439–470.
Kelm, S. and Schauer, R., Sialic acids in molecular and cellular interactions, Int. Rev. Cytol., 175 (1997) 137–240.
Suzuki, Y., Sialobiology of influenza: Molecular mechanism of host range variation of influenza viruses, Biol. Pharm. Bull., 28 (2005) 399–408.
Holmgren, J., Lonnroth, I., Mansson, J. and Svennerholm, L., Interaction of cholera toxin and membrane GM1 ganglioside of small intestine, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 72 (1975) 2520–2524.
Mahdavi, J., Sonden, B., Hurtig, M., Olfat, F.O., Forsberg, L., Roche, N., Angstrom, J., Larsson, T., Teneberg, S., Karlsson, K.A., Altraja, S., Wadstrom, T., Kersulyte, D., Berg, D.E., Dubois, A., Petersson, C., Magnusson, K.E., Norberg, T., Lindh, F., Lundskog, B.B., Arnqvist, A., Hammarstrom, L. and Boren, T., Helicobacter pylori SabA adhesin in persistent infection and chronic inflammation, Science, 297 (2002) 573–578.
Orlandi, P.A., Klotz, F.W. and Haynes, J.D., A malaria invasion receptor, the 175-kilodalton erythrocyte binding antigen of Plasmodium falciparum recognizes the terminal Neu5Ac(alpha 2-3)Gal- sequences of glycophorin A, J. Cell Biol., 116 (1992) 901–909.
Kawano, T., Koyama, S., Takematsu, H., Kozutsumi, Y., Kawasaki, H., Kawashima, S., Kawasaki, T. and Suzuki, A., Molecular cloning of cytidine monophospho-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase. Regulation of species- and tissue-specific expression of N-glycolylneuraminic acid, J. Biol. Chem., 270 (1995) 16458–16463.
Kawano, T., Kozutsumi, Y., Kawasaki, T. and Suzuki, A., Biosynthesis of N-glycolylneuraminic acid-containing glycoconjugates. Purification and characterization of the key enzyme of the cytidine monophospho-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylation system, J. Biol. Chem., 269 (1994) 9024–9029.
Schwarzkopf, M., Knobeloch, K.P., Rohde, E., Hinderlich, S., Wiechens, N., Lucka, L., Horak, I., Reutter, W. and Horstkorte, R., Sialylation is essential for early development in mice, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 99 (2002) 5267–5270.
Eisenberg, I., Avidan, N., Potikha, T., Hochner, H., Chen, M., Olender, T., Barash, M., Shemesh, M., Sadeh, M., Grabov-Nardini, G., Shmilevich, I., Friedmann, A., Karpati, G., Bradley, W.G., Baumbach, L., Lancet, D., Asher, E.B., Beckmann, J.S., Argov, Z. and Mitrani-Rosenbaum, S., The UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase gene is mutated in recessive hereditary inclusion body myopathy, Nat. Genet., 29 (2001) 83–87.
Martinez-Duncker, I., Dupre, T., Piller, V., Piller, F., Candelier, J.J., Trichet, C., Tchernia, G., Oriol, R. and Mollicone, R., Genetic complementation reveals a novel human congenital disorder of glycosylation of type II, due to inactivation of the Golgi CMP-sialic acid transporter, Blood, 105 (2005) 2671–2676.
Crocker, P.R. and Varki, A., Siglecs, sialic acids and innate immunity, Trends Immunol., 22 (2001) 337–342.
Crocker, P.R., Siglecs in innate immunity, Curr. Opin. Pharmacol., 5 (2005) 431–437.
Varki, A. and Angata, T., iglecs - the major subfamily of I-type lectin, Glycobiology, 16 (2006) 1R–27R.
Crocker, P.R., Clark, E.A., Filbin, M., Gordon, S., Jones, Y., Kehrl, J.H., Kelm, S., Le Douarin, N., Powell, L., Roder, J., Schnaar, R.L., Sgroi, D.C., Stamenkovic, K., Schauer, R., Schachner, M., Van den Berg, T.K., Van der Merwe, P.A., Watt, S.M. and Varki, A., Siglecs: A family of sialic-acid binding lectins [letter], Glycobiology, 8 (1998)v.
Angata, T., Hingorani, R., Varki, N.M. and Varki, A., Cloning and characterization of a novel mouse Siglec, mSiglec-F: Differential evolution of the mouse and human (CD33) Siglec-3-related gene clusters, J. Biol. Chem., 276 (2001) 45128–45136.
Angata, T., Margulies, E.H., Green, E.D. and Varki, A., Large-scale sequencing of the CD33-related Siglec gene cluster in five mammalian species reveals rapid evolution by multiple mechanisms, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 101 (2004) 13251–13256.
Crocker, P.R. and Varki, A., Siglecs in the immune system, Immunology, 103 (2001) 137–145.
Patel, N., Brinkman-Van der Linden, E.C.M., Altmann, S.W., Gish, K., Balasubramanian, S., Timans, J.C., Peterson, D., Bell, M.P., Bazan, J.F., Varki, A. and Kastelein, R.A., OB-BP1/Siglec-6 - A leptin- and sialic acid-binding protein of the immunoglobulin superfamily, J. Biol. Chem., 274 (1999) 22729–22738.
May, A.P., Robinson, R.C., Vinson, M., Crocker, P.R. and Jones, E.Y., Crystal structure of the N-terminal domain of sialoadhesin in complex with 3′ sialyllactose at 1.85 A resolution, Mol. Cell., 1 (1998) 719–728.
Alphey, M.S., Attrill, H., Crocker, P.R. and Van Aalten, D.M., High resolution crystal structures of siglec-7. Insights into ligand specificity in the Siglec family, J. Biol. Chem., 278 (2003) 3372–3377.
Pedraza, L., Owens, G.C., Green, L.A. and Salzer, J.L., The myelin-associated glycoproteins: Membrane disposition, evidence of a novel disulfide linkage between immunoglobulin-like domains, and posttranslational palmitylation, J. Cell Biol., 111 (1990) 2651–2661.
Crocker, P.R., Mucklow, S., Bouckson, V., McWilliam, A., Willis, A.C., Gordon, S., Milon, G., Kelm, S. and Bradfield, P., Sialoadhesin, a macrophage sialic acid binding receptor for haemopoietic cells with 17 immunoglobulin-like domains, EMBO J., 13 (1994) 4490–4503.
Connolly, N.P., Jones, M. and Watt, S.M., Human Siglec-5: Tissue distribution, novel isoforms and domain specificities for sialic acid-dependent ligand interactions, Br. J. Haematol., 119 (2002) 221–238.
Domeniconi, M., Cao, Z.U., Spencer, T., Sivasankaran, R., Wang, K.C., Nikulina, E., Kimura, N., Cai, H., Deng, K.W., Gao, Y., He, Z.G. and Filbin, M.T., Myelin-associated glycoprotein interacts with the Nogo66 receptor to inhibit neurite outgrowth, Neuron, 35 (2002) 283–290.
Liu, B.P., Fournier, A., GrandPré, T. and Strittmatter, S.M., Myelin-associated glycoprotein as a functional ligand for the Nogo-66 receptor, Science, 297 (2002) 1190–1193.
Zhang, M. and Varki, A., Cell surface sialic acids do not affect primary CD22 interactions with CD45 and sIgM, nor the rate of constitutive CD22 endocytosis, Glycobiology, 14 (2004) 939–949.
Kumamoto, Y., Higashi, N., Denda-Nagai, K., Tsuiji, M., Sato, K., Crocker, P.R. and Irimura, T., Identification of sialoadhesin as a dominant lymph node counter-receptor for mouse macrophage galactose-type C-type lectin 1, J. Biol. Chem., 279 (2004) 49274–49280.
Martínez-Pomares, L., Crocker, P.R., Da Silva, R., Holmes, N., Colominas, C., Rudd, P., Dwek, R. and Gordon, S., Cell-specific glycoforms of sialoadhesin and CD45 are counter-receptors for the cysteine-rich domain of the mannose receptor, J. Biol. Chem., 274 (1999) 30325–30318.
Brinkman-Van der Linden, E.C.M., Sjoberg, E.R., Juneja, L.R., Crocker, P.R., Varki, N. and Varki, A., Loss of N-glycolylneuraminic acid in human evolution – Implications for sialic acid recognition by siglecs, J. Biol. Chem., 275 (2000) 8633–8640.
Blixt, O., Collins, B.E., Van Den Nieuwenhof, I.M., Crocker, P.R. and Paulson, J.C., Sialoside specificity of the Siglec family assessed using novel multivalent probes: Identification of potent inhibitors of myelin associated glycoprotein, J. Biol. Chem., 278 (2003) 31007–31019.
Van der Merwe, P.A., Crocker, P.R., Vinson, M., Barclay, A.N., Schauer, R. and Kelm, S., Localization of the putative sialic acid-binding site on the immunoglobulin superfamily cell-surface molecule CD22, J. Biol. Chem., 271 (1996) 9273–9280.
Kelm, S., Brossmer, R., Isecke, R., Gross, H.J., Strenge, K. and Schauer, R., Functional groups of sialic acids involved in binding to siglecs (sialoadhesins) deduced from interactions with synthetic analogues, Eur. J. Biochem., 255 (1998) 663–672.
Collins, B.E., Ito, H., Sawada, N., Ishida, H., Kiso, M. and Schnaar, R.L., Enhanced binding of the neural siglecs, myelin-associated glycoprotein and Schwann cell myelin protein, to Chol-1 (alpha-series) gangliosides and novel sulfated Chol-1 analogs, J. Biol. Chem., 274 (1999) 27899–27893.
Collins, B.E., Kiso, M., Hasegawa, A., Tropak, M.B., Roder, J.C., Crocker, P.R. and Schnaar, R.L., Binding specificities of the sialoadhesin family of I-type lectins – Sialic acid linkage and substructure requirements for binding of myelin-associated glycoprotein, Schwann cell myelin protein, and sialoadhesin, J. Biol. Chem., 272 (1997) 16889–16895.
Collins, B.E., Yang, L.J.S., Mukhopadhyay, G., Filbin, M.T., Kiso, M., Hasegawa, A. and Schnaar, R.L., Sialic acid specificity of myelin-associated glycoprotein binding, J. Biol. Chem., 272 (1997) 1248-1255.
Blixt, O., Head, S., Mondala, T., Scanlan, C., Huflejt, M.E., Alvarez, R., Bryan, M.C., Fazio, F., Calarese, D., Stevens, J., Razi, N., Stevens, D.J., Skehel, J.J., van Die, I., Burton, D.R., Wilson, I.A., Cummings, R., Bovin, N., Wong, C.H. and Paulson, J.C., Printed covalent glycan array for ligand profiling of diverse glycan binding proteins, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 101 (2004) 17033–17038.
Bochner, B.S., Alvarez, R.A., Mehta, P., Bovin, N.V., Blixt, O., White, J.R. and Schnaar, R.L., Glycan array screening reveals a candidate ligand for siglec-8, J. Biol. Chem., 280 (2005) 4307–4312.
Tateno, H., Crocker, P.R. and Paulson, J.C., Mouse Siglec-F and human Siglec-8 are functionally convergent paralogs that are selectively expressed on eosinophils and recognize 6′-sulfo-sialyl Lewis X as a preferred glycan ligand, Glycobiology, 15 (2005) 1125–1135.
Ito, A., Handa, K., Withers, D.A., Satoh, M. and Hakomori, S., Binding specificity of siglec7 to disialogangliosides of renal cell carcinoma: Possible role of disialogangliosides in tumor progression, FEBS Lett., 498 (2001) 116–120.
Miyazaki, K., Ohmori, K., Izawa, M., Koike, T., Kumamoto, K., Furukawa, K., Ando, T., Kiso, M., Yamaji, T., Hashimoto, Y., Suzuki, A., Yoshida, A., Takeuchi, M. and Kannagi, R., Loss of disialyl Lewis(a), the ligand for lymphocyte inhibitory receptor sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin-7 (Siglec-7) associated with increased sialyl Lewis(a) expression on human colon cancers, Cancer Res., 64 (2004) 4498–4505.
Ravetch, J.V. and Lanier, L.L., Immune inhibitory receptors, Science, 290 (2000) 84–89.
Doody, G.M., Justement, L.B., Delibrias, C.C., Matthews, R.J., Lin, J., Thomas, M.L. and Fearon, D.T., A role in B cell activation for CD22 and the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP, Science, 269 (1995) 242–244.
Blasioli, J., Paust, S. and Thomas, M.L., Definition of the sites of interaction between the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 and CD22, J. Biol. Chem., 274 (1999) 2303–2307.
Ulyanova, T., Blasioli, J., Woodford-Thomas, T.A. and Thomas, M.L., The sialoadhesin CD33 is a myeloid-specific inhibitory receptor, Eur. J. Immunol., 29 (1999) 3440–3449.
Paul, S.P., Taylor, L.S., Stansbury, E.K. and McVicar, D.W., Myeloid specific human CD33 is an inhibitory receptor with differential ITIM function in recruiting the phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2, Blood, 96 (2000) 483–490.
Falco, M., Biassoni, R., Bottino, C., Vitale, M., Sivori, S., Augugliaro, R., Moretta, L. and Moretta, A., Identification and molecular cloning of p75/AIRM1, a novel member of the sialoadhesin family that functions as an inhibitory receptor in human natural killer cells, J. Exp. Med., 190 (1999) 793–801.
Whitney, G., Wang, S.L., Chang, H., Cheng, K.Y., Lu, P., Zhou, X.D., Yang, W.P., McKinnon, M. and Longphre, M., A new siglec family member, siglec-10, is expressed in cells of the immune system and has signaling properties similar to CD33, Eur. J. Biochem., 268 (2001) 6083–6096.
Ulyanova, T., Shah, D.D. and Thomas, M.L., Molecular cloning of MIS, a myeloid inhibitory siglec, that binds protein-tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2, J. Biol. Chem., 276 (2001) 14451–14458.
Ikehara, Y., Ikehara, S.K. and Paulson, J.C., Negative regulation of T cell receptor signaling by Siglec-7 (p70/AIRM) and Siglec-9, J. Biol. Chem., 279 (2004) 43117–43125.
Kitzig, F., Martinez-Barriocanal, A., López-Botet, M. and Sayós, J., Cloning of two new splice variants of Siglec-10 and mapping of the interaction between Siglec-10 and SHP-1, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 296 (2002) 355–362.
Bonifacino, J.S. and Traub, L.M., Signals for sorting of transmembrane proteins to endosomes and lysosomes, Annu. Rev. Biochem., 72 (2003) 395–447.
John, B., Herrin, B.R., Raman, C., Wang, Y.N., Bobbitt, K.R., Brody, B.A. and Justement, L.B., The B cell coreceptor CD22 associates with AP50, a clathrin-coated pit adapter protein, via tyrosine-dependent interaction, J. Immunol., 170 (2003) 3534–3543.
Lanier, L.L. and Bakker, A.B., The ITAM-bearing transmembrane adaptor DAP12 in lymphoid and myeloid cell function, Immunol. Today, 21 (2000) 611–614.
Blasius, A.L., Cella, M., Takai, T. and Colonna, M., Siglec-H is an IPC-specific receptor that modulates type I IFN secretion through DAP12, Blood, 107 (2006) 2474–2476.
Jin, L., McLean, P.A., Neel, B.G. and Wortis, H.H., Sialic acid binding domains of CD22 are required for negative regulation of B cell receptor signaling, J. Exp. Med., 195 (2002) 1199–1205.
Kelm, S., Gerlach, J., Brossmer, R., Danzer, C.P. and Nitschke, L., The ligand-binding domain of CD22 is needed for inhibition of the B cell receptor signal, as demonstrated by a novel human CD22-specific inhibitor compound, J. Exp. Med., 195 (2002) 1207–1213.
Taylor, V.C., Buckley, C.D., Douglas, M., Cody, A.J., Simmons, D.L. and Freeman, S.D., The myeloid-specific sialic acid-binding receptor, CD33, associates with the protein-tyrosine phosphatases, SHP-1 and SHP-2, J. Biol. Chem., 274 (1999) 11505–11512.
Avril, T., Floyd, H., Lopez, F., Vivier, E. and Crocker, P.R., The membrane-proximal immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif is critical for the inhibitory signaling mediated by Siglecs-7 and -9, CD33-related Siglecs expressed on human monocytes and NK cells, J. Immunol., 173 (2004) 6841–6849.
Avril, T., Freeman, S.D., Attrill, H., Clarke, R.G. and Crocker, P.R., Siglec-5 (CD170) can mediate inhibitory signalling in the absence of immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif phosphorylation, J. Biol. Chem., 280 (2005) 19843–19851.
Grobe, K. and Powell, L.D., Role of protein kinase C in the phosphorylation of CD33 (Siglec-3) and its effect on lectin activity, Blood, 99 (2002) 3188–3196.
Powell, L.D., Jain, R.K., Matta, K.L., Sabesan, S. and Varki, A., Characterization of sialyloligosaccharide binding by recombinant soluble and native cell-associated CD22. Evidence for a minimal structural recognition motif and the potential importance of multisite binding, J. Biol. Chem., 270 (1995) 7523–7532.
Han, S., Collins, B.E., Bengston, P. and Paulson, J.C., Homomultimeric complexes of CD22 in B cells revealed by protein-glycan cross-linking, Nat. Chem. Biol., 1 (2005) 93–97.
Sgroi, D., Nocks, A. and Stamenkovic, I., A single N-linked glycosylation site is implicated in the regulation of ligand recognition by the I-type lectins CD22 and CD33, J. Biol. Chem., 271 (1996) 18803–18809.
Tropak, M.B. and Roder, J.C., Regulation of myelin-associated glycoprotein binding by sialylated cis-ligands, J. Neurochem., 68 (1997) 1753–1763.
Freeman, S., Birrell, H.C., D’Alessio, K., Erickson-Miller, C., Kikly, K. and Camilleri, P., A comparative study of the asparagine-linked oligosaccharides on siglec-5, siglec-7 and siglec-8, expressed in a CHO cell line, and their contribution to ligand recognition, Eur. J. Biochem., 268 (2001) 1228–1237.
Bartsch, U., Bandtlow, C.E., Schnell, L., Bartsch, S., Spillmann, A.A., Rubin, B.P., Hillenbrand, R., Montag, D., Schwab, M.E. and Schachner, M., Lack of evidence that myelin-associated glycoprotein is a major inhibitor of axonal regeneration in the CNS, Neuron, 15 (1995) 1375–1381.
Schachner, M. and Bartsch, U., Multiple functions of the myelin-associated glycoprotein MAG (siglec-4a) in formation and maintenance of myelin, Glia, 29 (2000) 154–165.
O’Keefe, T.L., Williams, G.T., Davies, S.L. and Neuberger, M.S., Hyperresponsive B cells in CD22-deficient mice, Science, 274 (1996) 798–801.
Otipoby, K.L., Andersson, K.B., Draves, K.E., Klaus, S.J., Farr, A.G., Kerner, J.D., Perlmutter, R.M., Law, C.L. and Clark, E.A., CD22 regulates thymus-independent responses and the lifespan of B cells, Nature, 384 (1996) 634–637.
Sato, S., Miller, A.S., Inaoki, M., Bock, C.B., Jansen, P.J., Tang, M.L. and Tedder, T.F., CD22 is both a positive and negative regulator of B lymphocyte antigen receptor signal transduction: Altered signaling in CD22-deficient mice, Immunity, 5 (1996) 551–562.
Nitschke, L., Carsetti, R., Ocker, B., Kohler, G. and Lamers, M.C., CD22 is a negative regulator of B-cell receptor signalling, Curr. Biol., 7 (1997) 133–143.
Brinkman-Van der Linden, E.C., Angata, T., Reynolds, S.A., Powell, L.D., Hedrick, S.M. and Varki, A., CD33/Siglec-3 binding specificity, expression pattern, and consequences of gene deletion in mice, Mol. Cell. Biol., 23 (2003) 4199–4206.
Jones, C., Virji, M. and Crocker, P.R., Recognition of sialylated meningococcal lipopolysaccharide by siglecs expressed on myeloid cells leads to enhanced bacterial uptake, Mol. Microbiol., 49 (2003) 1213–1225.
Vitale, C., Romagnani, C., Puccetti, A., Olive, D., Costello, R., Chiossone, L., Pitto, A., Bacigalupo, A., Moretta, L. and Mingari, M.C., Surface expression and function of p75/AIRM-1 or CD33 in acute myeloid leukemias: Engagement of CD33 induces apoptosis of leukemic cells, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 98 (2001) 5764–5769.
Nutku, E., Aizawa, H., Hudson, S.A. and Bochner, B.S., Ligation of Siglec-8: A selective mechanism for induction of human eosinophil apoptosis, Blood, 101 (2003) 5014–5020.
von Gunten, S., Yousefi, S., Seitz, M., Jakob, S.M., Schaffner, T., Seger, R., Takala, J., Villiger, P.M. and Simon, H.U., Siglec-9 transduces apoptotic and nonapoptotic death signals into neutrophils depending on the proinflammatory cytokine environment, Blood, 106 (2005) 1423–1431.
Vitale, C., Romagnani, C., Falco, M., Ponte, M., Vitale, M., Moretta, A., Bacigalupo, A., Moretta, L. and Mingari, M.C., Engagement of p75/AIRM1 or CD33 inhibits the proliferation of normal or leukemic myeloid cells, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 96 (1999) 15091–15096.
Dehal, P., Satou, Y., Campbell, R.K., Chapman, J., Degnan, B., De Tomaso, A., Davidson, B., Di Gregorio, A., Gelpke, M., Goodstein, D.M., Harafuji, N., Hastings, K.E., Ho, I., Hotta, K., Huang, W., Kawashima, T., Lemaire, P., Martinez, D., Meinertzhagen, I.A., Necula, S., Nonaka, M., Putnam, N., Rash, S., Saiga, H., Satake, M., Terry, A., Yamada, L., Wang, H.G., Awazu, S., Azumi, K., Boore, J., Branno, M., Chin-Bow, S., DeSantis, R., Doyle, S., Francino, P., Keys, D.N., Haga, S., Hayashi, H., Hino, K., Imai, K.S., Inaba, K., Kano, S., Kobayashi, K., Kobayashi, M., Lee, B.I., Makabe, K.W., Manohar, C., Matassi, G., Medina, M., Mochizuki, Y., Mount, S., Morishita, T., Miura, S., Nakayama, A., Nishizaka, S., Nomoto, H., Ohta, F., Oishi, K., Rigoutsos, I., Sano, M., Sasaki, A., Sasakura, Y., Shoguchi, E., Shin-i, T., Spagnuolo, A., Stainier, D., Suzuki, M.M., Tassy, O., Takatori, N., Tokuoka, M., Yagi, K., Yoshizaki, F., Wada, S., Zhang, C., Hyatt, P.D., Larimer, F., Detter, C., Doggett, N., Glavina, T., Hawkins, T., Richardson, P., Lucas, S., Kohara, Y., Levine, M., Satoh, N. and Rokhsar, D.S., The draft genome of Ciona intestinalis: Insights into chordate and vertebrate origins, Science, 298 (2002) 2157–2167.
Cameron, R.A., Mahairas, G., Rast, J.P., Martinez, P., Biondi, T.R., Swartzell, S., Wallace, J.C., Poustka, A.J., Livingston, B.T., Wray, G.A., Ettensohn, C.A., Lehrach, H., Britten, R.J., Davidson, E.H. and Hood, L., A sea urchin genome project: Sequence scan, virtual map, and additional resources, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 97 (2000) 9514–9518.
Poustka, A.J., Groth, D., Hennig, S., Thamm, S., Cameron, A., Beck, A., Reinhardt, R., Herwig, R., Panopoulou, G. and Lehrach, H., Generation, annotation, evolutionary analysis, and database integration of 20,000 unique sea urchin EST clusters, Genome. Res., 13 (2003) 2736–2746.
Lehmann, F., Gathje, H., Kelm, S. and Dietz, F., Evolution of sialic acid-binding proteins: Molecular cloning and expression of fish siglec-4, Glycobiology, 14 (2004) 959–968.
Lindblad-Toh, K., Wade, C.M., Mikkelsen, T.S., Karlsson, E.K., Jaffe, D.B., Kamal, M., Clamp, M., Chang, J.L., Kulbokas, E.J. III, Zody, M.C., Mauceli, E., Xie, X., Breen, M., Wayne, R.K., Ostrander, E.A., Ponting, C.P., Galibert, F., Smith, D.R., DeJong, P.J., Kirkness, E., Alvarez, P., Biagi, T., Brockman, W., Butler, J., Chin, C.W., Cook, A., Cuff, J., Daly, M.J., DeCaprio, D., Gnerre, S., Grabherr, M., Kellis, M., Kleber, M., Bardeleben, C., Goodstadt, L., Heger, A., Hitte, C., Kim, L., Koepfli, K.P., Parker, H.G., Pollinger, J.P., Searle, S.M., Sutter, N.B., Thomas, R., Webber, C., Broad Institute Genome Sequencing Platform and Lander, E.S., Genome sequence, comparative analysis and haplotype structure of the domestic dog, Nature, 438 (2005) 803–819.
Hayakawa, T., Angata, T., Lewis, A.L., Mikkelsen, T.S., Varki, N.M. and Varki, A., A human-specific gene in microglia, Science, 309 (2005) 1693.
Irie, A., Koyama, S., Kozutsumi, Y., Kawasaki, T. and Suzuki, A., The molecular basis for the absence of N-glycolylneuraminic acid in humans, J. Biol. Chem., 273 (1998) 15866–15871.
Chou, H.H., Hayakawa, T., Diaz, S., Krings, M., Indriati, E., Leakey, M., Paabo, S., Satta, Y., Takahata, N. and Varki, A., Inactivation of CMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase occurred prior to brain expansion during human evolution, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 99 (2002) 11736–11741.
Chou, H.H., Takematsu, H., Diaz, S., Iber, J., Nickerson, E., Wright, K.L., Muchmore, E.A., Nelson, D.L., Warren, S.T. and Varki, A., A mutation in human CMP-sialic acid hydroxylase occurred after the Homo-Pan divergence, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 95 (1998) 11751–11756.
Muchmore, E.A., Diaz, S. and Varki, A., A structural difference between the cell surfaces of humans and the great apes, Am. J. Phys. Anthropol., 107 (1998) 187–198.
Angata, T., Varki, N.M. and Varki, A., A second uniquely human mutation affecting sialic acid biology, J. Biol. Chem., 276 (2001) 40282–40287.
Yu, Z., Lai, C.M., Maoui, M., Banville, D. and Shen, S.H., Identification and characterization of S2V, a novel putative siglec that contains two V set Ig-like domains and recruits protein-tyrosine phosphatases SHPs, J. Biol. Chem., 276 (2001) 23816–23824.
Sonnenburg, J.L., Altheide, T.K. and Varki, A., A uniquely human consequence of domain-specific functional adaptation in a sialic acid-binding receptor, Glycobiology, 14 (2004) 339–346.
Varki, A., Loss of N-glycolylneuraminic acid in humans: Mechanisms, consequences and implications for hominid evolution, Yearbook Phys. Anthropol., 44 (2002) 54–69.
The Chimpanzee Sequencing and Analysis Consortium, Initial sequence of the chimpanzee genome and comparison with the human genome, Nature, 437 (2005) 69–87.
Vanderheijden, N., Delputte, P.L., Favoreel, H.W., Vandekerckhove, J., Van Damme, J., Van Woensel, P.A. and Nauwynck, H.J., Involvement of sialoadhesin in entry of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus into porcine alveolar macrophages, J. Virol., 77 (2003) 8207–8215.
Delputte, P.L. and Nauwynck, H.J., Porcine arterivirus infection of alveolar macrophages is mediated by sialic acid on the virus, J. Virol., 78 (2004) 8094–8101.
Galili, U., Clark, M.R., Shohet, S.B., Buehler, J. and Macher, B.A., Evolutionary relationship between the natural anti-Gal antibody and the Gal alpha1-3Gal epitope in primates, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 84 (1987) 1369–1373.
Galili, U., Shohet, S.B., Kobrin, E., Stults, C.L. and Macher, B.A., Man, apes, and Old World monkeys differ from other mammals in the expression of alpha-galactosyl epitopes on nucleated cells, J. Biol. Chem., 263 (1988) 17755–17762.
Galili, U. and Swanson, K., Gene sequences suggest inactivation of α-1,3-galactosyltransferase in catarrhines after the divergence of apes from monkeys, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 88 (1991) 7401–7404.
International Chicken Genome Sequencing Consortium, Sequence and comparative analysis of the chicken genome provide unique perspectives on vertebrate evolution, Nature, 432 (2004) 695–716.
Aparicio, S., Chapman, J., Stupka, E., Putnam, N., Chia, J.M., Dehal, P., Christoffels, A., Rash, S., Hoon, S., Smit, A., Gelpke, M.D., Roach, J., Oh, T., Ho, I.Y., Wong, M., Detter, C., Verhoef, F., Predki, P., Tay, A., Lucas, S., Richardson, P., Smith, S.F., Clark, M.S., Edwards, Y.J., Doggett, N., Zharkikh, A., Tavtigian, S.V., Pruss, D., Barnstead, M., Evans, C., Baden, H., Powell, J., Glusman, G., Rowen, L., Hood, L., Tan, Y.H., Elgar, G., Hawkins, T., Venkatesh, B., Rokhsar, D. and Brenner, S., Whole-genome shotgun assembly and analysis of the genome of Fugu rubripes, Science, 297 (2002) 1301–1310.
Jaillon, O., Aury, J.M., Brunet, F., Petit, J.L., Stange-Thomann, N., Mauceli, E., Bouneau, L., Fischer, C., Ozouf-Costaz, C., Bernot, A., Nicaud, S., Jaffe, D., Fisher, S., Lutfalla, G., Dossat, C., Segurens, B., Dasilva, C., Salanoubat, M., Levy, M., Boudet, N., Castellano, S., Anthouard, V., Jubin, C., Castelli, V., Katinka, M., Vacherie, B., Biemont, C., Skalli, Z., Cattolico, L., Poulain, J., De Berardinis, V., Cruaud, C., Duprat, S., Brottier, P., Coutanceau, J.P., Gouzy, J., Parra, G., Lardier, G., Chapple, C., McKernan, K.J., McEwan, P., Bosak, S., Kellis, M., Volff, J.N., Guigo, R., Zody, M.C., Mesirov, J., Lindblad-Toh, K., Birren, B., Nusbaum, C., Kahn, D., Robinson-Rechavi, M., Laudet, V., Schachter, V., Quetier, F., Saurin, W., Scarpelli, C., Wincker, P., Lander, E.S., Weissenbach, J. and Roest Crollius, H., Genome duplication in the teleost fish Tetraodon nigroviridis reveals the early vertebrate proto-karyotype, Nature, 431 (2004) 946–957.
Angata, T., Kerr, S.C., Greaves, D.R., Varki, N.M., Crocker, P.R. and Varki, A., Cloning and characterization of human Siglec-11. A recently evolved signaling molecule that can interact with SHP-1 and SHP-2 and is expressed by tissue macrophages, including brain microglia, J. Biol. Chem., 277 (2002) 24466–24474.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Angata, T. Molecular diversity and evolution of the Siglec family of cell-surface lectins. Mol Divers 10, 555–566 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-006-9029-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-006-9029-1