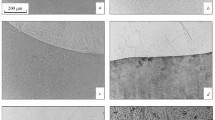
The effect of composition, structural state, excess phase precipitation, and manufacturing technology parameters on service property indices of high-strength, low-carbon steel of a main bimetal layer is studied in detail. For the low-carbon, high-strength steels developed primary importance is attached to strengthening mechanisms, connected with formation of different size carbonitride precipitates with different fineness, and secondary importance applies to the presence of strong structural components. A simultaneous improvement in strength properties and preparation of good steel weldability may be achieved by some increase in carbon content using a balanced microalloying system with a reduction in concentration of manganese, chromium, nickel, and copper, and effective alloying with boron. It is shown that the possibility of achieving high strength properties for the low-carbon steel developed with relatively slow cooling rates creates favorable conditions for obtaining a clad rolled product with a good and stable set of mechanical and other service properties, and quality indices.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. I. Zaitsev, I. G. Rodionova, A. A. Pavlov, et al., “Development of effective forms of corrosion-resistant clad rolled product based on a new generation of high-strength low-carbon microalloyed steels,” Metallurg, No. 10, 71–76 (2014).
S. Yu. Nastich, Development of Thermomechanical Treatment Technology for Strip and Sheet Rolled Product of Low-Alloy Steel Based on Controlled Formation of a Ferrite-Bainite Structure: Auth. Abstr. Diss. Cand. Techn. Sci., Bardin TsNIIshermet, Moscow (2013).
N. A. Arutyunyan, A. I. Zaistev, and O. N. Baklanova, “Study of principles of creation of steels for preparing highstrength, reliable objects by hot stamping,” Metallurg, No. 11, 55–61 (2014).
N. G. Shaposhnikov, B. M. Mogutnov, S. M. Polonskaya, et al., “Thermodynamic modeling as an instrument for improving steel 12Kh18N10T ingot heating technology for rolling,” Materialovedenie, No. 11, 2–9 (2004).
E. Kh. Shakhpazov, A. I. Zaistev, N. G. Shaposhnikov, and I. G. Rodionova, “Model for controlling steel ladle treatment processes,” Metallurg, No. 6, 30–35 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallurg, No. 8, pp. 50–58, August, 2015. Original article submitted April 24, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaitsev, A.I., Rodionova, I.G., Pavlov, A.A. et al. Effect of Composition, Structural State, and Manufacturing Technology on Service Properties of High-Strength Low-Carbon Steel Main Bimetal Layer. Metallurgist 59, 684–692 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-015-0159-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-015-0159-5