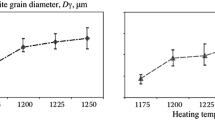
Principles are established for controlling low-alloy steel structure formation during thermomechanical treatment for the possibility of creating steels for different purposes from slabs of a single chemical composition. Technology is developed for manufacturing high-strength shipbuilding steels with a yield strength of 460 MPa and strength category K65 pipe steels of unified chemical composition.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
* An algorithm uniting a connected multitude of points to a single structural element is realized in accordance with previously prescribed grouping indices, the main one of which is tolerance angle θ t . In implementing this grouping algorithm, two neighboring points were assumed to be adjacent to the same structural element (grain), if the misorientation between them did not exceed θ t .
References
I. V. Gorynin, V. V. Rybin, V. A. Malyshevskii, and E. I. Khlusova, “Principles of alloying, phase transformation, structure, and properties of cold-resistant weldable shipbuilding steel,” MiTOM, No. 1, 9–15 (2007).
V. V. Orlov, “Principles of controlled creation of structural elements of nanosize scale in pipe steels with significant plastic deformation,” Vopr. Materialoved., No. 2(66), 5–17 (2011).
S. V. Korotovskaya, V. V. Orlov, and E. I. Khlusova, “Effect of fractional deformation on formation of ultrafine grained structure in low-carbon low-alloy steels,” Metallurg, No. 11, 78–82 (2013).
S. V. Korotovskaya, V. V. Orlov, and E. I. Khlusova, “Methods for forming ultrafine grained sub-microcrystalline structure in ferrite-bainite steel,” Proizv. Prokata, No. 1, 6–16 (2013).
E. Kh. Shakhpazov, Yu. D. Morozov, M. Yu. Matrosov, et al., “New generation of high-strength pipe steels with a ferrite-bainite structure,” Proc. Int. Semin. Contemporary Trends of Development and Manufacture of Steels and Pipes for Main Gas and Oil Pipelines, April 12–13, 2008, Moscow, Matallurgizdat, Moscow (2009).
M. Yu. Matrosov, L. I. Efron, A. A. Kichkina, and I. V. Lyasotskii, “Study of the microstructure of pipe steel microalloyed with niobium after different controlled rolling regimes with accelerated cooling,” MiTOM, No. 3(633), 44–49 (2008).
T. V. Soshina, A. A. Zisman, and E. I. Khlusova, “Revelation of previous austenite grains by thermal etching in a vacuum with simulation of TMT for low-carbon steels,” Metallurg, No. 7, 63–72 (2013).
A. A. Zisman, T. V. Soshina, and E. I. Khlusova, “Study of austenite recrystallization in steel 09KhM2MD under hot rolling conditions by stress relaxation,” Vopr. Materialoved., No. 2(70), 16–24 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallurg, No. 5, pp. 71–78, May, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korotovskaya, S.V., Orlov, V.V. & Khlusova, E.I. Control of Structure Formation During Thermomechanical Treatment of Shipbuilding and Pipe Steels of Unified Chemical Composition. Metallurgist 58, 406–414 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-014-9924-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-014-9924-0