Abstract
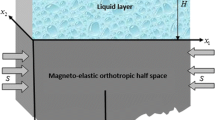
In the present time, self-reinforced materials are the basic requirement for civil engineering construction. These constructions encounter surface wave propagation during earthquakes and similar disturbances. Therefore, the study of surface wave propagation in such material is of great significance. The present paper, in the light of practical situation like dams, canals etc. aims to study the effect of gravity on the propagation of Rayleigh-type surface wave in a self-reinforced semi-infinite medium bounded and loaded by an inviscid liquid layer. Secular equation for the propagation of Rayleigh-type wave has been derived in closed form. The effect of gravity, reinforcement and liquid loading on phase velocity of Rayleigh-type wave has been distinctly observed. Numerical computation has been carried out and graphical illustration is provided for analysis of the presented study. Moreover, the effect of reinforced semi-infinite medium is compared to the effect of reinforced free semi-infinite medium on the phase velocity of Rayleigh-type surface wave to unravel the reinforcement effect. The effect of presence and absence of liquid loading on self-reinforced semi-infinite medium for Rayleigh-type wave propagation is also analysed and depicted by means of graphs.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rayleigh L (1885) On waves propagated along the plane surface of an elastic solid. Proc Lond Math Soc 17:4
Belfield AJ, Roger TG, Spencer AJM (1986) Stress in elastic plates reinforced by fibres lying in concentric circles. J Mech Phys Solids 31:25
Sengupta PR, Nath S (2001) Surface waves in fibre-reinforced anisotropic elastic media. Sãdhanã 26:363–370
Chattopadhyay A, Venkateswarlu RLK, Saha S (2002) Reflection of quasi-P and quasi-SV waves at the free and rigid boundaries of a fibre-reinforced medium. Sãdhanã 27:613–630
Chattopadhyay A, Gupta S, Sahu SA, Singh AK (2013) Dispersion of horizontally polarized shear waves in an irregular non-homogeneous self-reinforced crustal layer over a semi-infinite self-reinforced medium. J Vib Control 19:109–119
Baljeet S (2005) Wave propagation in thermally conducting linear fibre-reinforced composite materials. Arch Appl Mech 75:513–520
Baljeet S (2007) Wave propagation in an incompressible transversely isotropic fibre-reinforced elastic media. Arc Appl Mech 77:253–258
Sapan KS, Ranjan C (2011) Surface wave propagation in fiber-reinforced anisotropic elastic layer between liquid saturated porous half space and uniform liquid layer. Acta Geophys 59:470–482
Sapan KS, Ranjan C (2013) Love waves in the fiber-reinforced layer over a gravitating porous half-space. Acta Geophys 61:1170–1183
Bromwich TJ (1898) On the influence of gravity on elastic waves, and in particular, on the vibrations of an elastic glob. Proc Lond Math Soc 30:98–120
Love AEH (1965) Some problems of geodynamics. Cambridge University Press, London
De SK, Sengupta PR (1974) Influence of gravity on wave propagation in an elastic layer. J Acoust Soc Am 55:919–921
Biot MA (1965) Mechanics of Incremental Deformations. J. Willey
Wu J, Zhu Z (1992) The propagation of lamb waves in a plate bordered with layers of a liquid. J Acoust Soc Am 91:861–867
Sharma JN, Pathania V (2005) Propagation of leaky surface waves in thermoelastic solids due to inviscid fluid loadings. J Thermal Stresses 28:485–519
Sharma JN, Kumar S (2009) Lamb waves in micropolar thermoelastic solid plates immersed in liquid with varying temperature. Meccanica 44:305–319
Sharma V, Kumar S (2014) Velocity dispersion in an elastic plate with microstructure: effects of characteristic length in a couple stress model. Meccanica 49:1083–1090
Chattopadhyay A, Kumari Pato, Sharma VK (2014) Reflection and transmission of a three-dimensional plane qP-wave through a layered fluid medium between two distinct triclinic half-spaces. Int J Geomech 14:182–190
Ewing WM, Jardetzky WS (1957) Elastic waves in layered media. McGraw Hill, New York
Sharma JN, Kumar S, Sharma YD (2008) Propagation of rayleigh surface waves in microstretch thermoelastic continua under inviscid fluid loadings. J Therm Stresses 31:18–39
Markham MF (1970) Measurements of elastic constants of fibre composites by ultrasonics. Composites 1:145–149
Gubbins D (1990) Seismology and plate tectonics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 170
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, T., Sharma, S.K. & Singh, A.K. Effect of reinforcement, gravity and liquid loading on Rayleigh-type wave propagation. Meccanica 51, 2449–2458 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-016-0379-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-016-0379-1