Abstract
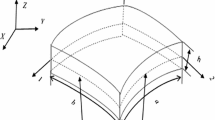
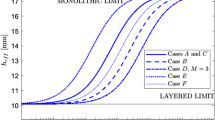
Laminated glass became a popular safety glass. The very soft interlayer of polymeric material impedes the slippage between glass layers, bending in parallel, by shear stress. The shear stress of the interlayer breaches the principle of straight normals remaining straight after deformation, on which is based the conventional shell elements in finite element (FE) analysis. As a result of this, the conventional finite elements are not capable to solve the laminated glass problems efficiently. Based on the assumption that the glass layers of a laminated glass obey Kirchoff’s plate theory and the interlayer transfer shear stress only, a finite element formulation is elaborated by introducing new degrees of freedom and implemented in a special rectangular triplex laminated glass plate FE. The element is validated by comparison with other computational FE models and experimental tests of a laminated glass strip in cylindrical bending and a laminated glass panel in transverse loading. The developed plate element or similar shell elements that could be developed on the same theory could solve the problem with laminated glass structures very efficiently and accurately, which is now usually solved by sacrificing the fidelity.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vallabhan CVG, Minor JE, Nagalla SR (1987) Stress in layered glass units and monolithic glass plates. J Struct Eng 113:36–43
Norville HS, King KW, Swofford JL (1998) Behavior and strength of laminated glass. J Eng Mech 124:46–53
Vallabhan CVG, Das YC, Magdi M, Aşik M, Bailey JR (1993) Analysis of laminated glass units. J Struct Eng 119:1572–1585
Aşik MZ (2003) Laminated glass plates: revealing of nonlinear behavior. Comput Struct 81:2659–2671
Aşik MZ, Tezcan S (2005) A mathematical model for the behavior of laminated glass beams. Comput Struct 83:1742–1753
Ivanov IV (2006) Analysis modelling and optimization of laminated glasses as plane beam. Int J Solids Struct 43:6887–6907
Duser AV, Jagota A, Bennison SJ (1999) Analysis of glass/polyvinyl butyral laminates subjected to uniform pressure. J Eng Mech 125:435–442
Schulze S-H, Pander M, Naumenko K, Altenbach H (2012) Analysis of laminated glass beams for photovoltaic applications. Int J Solids Struct 49:2027–2036
Weps M, Naumenko K, Altenbach H (2013) Unsymmetric three-layer laminate with soft core for photovoltaic modules. Compos Struct 105:332–339
Eisenträger J, Naumenko K, Altenbach H, Köppe H (2015) Application of the first-order shear deformation theory to the analysis of laminated glasses and photovoltaic panels. Int J Mech Sci 96–97:163–171
Zienkiewicz OC, Taylor RL (2000) The finite element method, solid mechanics, vol 2, 5th edn. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford
Jagota A, Bennison SJ, Smith CA (2000) Analysis of a compressive shear test for adhesion between elastomeric polymers and rigid substrates. Int J Fract 104:105–130
ABAQUS Analysis User’s Manual, ver. 6.11 (2011) Dassault Systèmes Simulia Corp., Providence, RI, USA
Acknowledgments
Financial support of Structural Funds in the Operational Programme - Innovative Economy (IE OP) financed from the European Regional Development Fund-Project “Modern material technologies in aerospace industry”, No. POIG.0101.02-00-015/08 is gratefully acknowledged (RT-15: Unconventional technologies of joining elements of aeronautical constructions). The support by National Science Fund of Bulgarian Ministry of Education and Science, Grant agreement No. DDVU 02/052- 20.12.2010, and the support by Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education, within the statutory research No. S/20/2015, are also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ivanov, I.V., Velchev, D.S., Georgiev, N.G. et al. A plate finite element for modelling of triplex laminated glass and comparison with other computational models. Meccanica 51, 341–358 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-015-0275-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-015-0275-0