Abstract
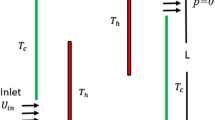
The Local Radial Basis Function-Differential Quadrature (RBF-DQ) method is applied to two-dimensional incompressible Navier-Stokes equations in primitive form. Numerical results of heatlines and entropy generation due to heat transfer and fluid friction have been obtained for laminar natural convection. The variations of the entropy generation for different Rayleigh numbers are also investigated. Comparison between the present results and previous works demonstrated excellent agreements which verify the accuracy and flexibility of the method in simulating the fluid mechanics and heat transfer problems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Be:
-
Bejan number
- c :
-
Shape parameter
- \(\bar{c}\) :
-
Constant in the transformed form of MQ test functions
- g :
-
Acceleration due to gravity (m s−2)
- H :
-
Length (m)
- K :
-
Thermal conductivity (W m−1 K−1)
- Nu:
-
Nusselt number
- P :
-
Dimensionless pressure
- Pr:
-
Prandtl number
- p :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- Ra:
-
Rayleigh number
- S :
-
Dimensionless entropy generation
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- T 0 :
-
Bulk temperature (T h +T c )/2 (K)
- t :
-
Time (s)
- U,V :
-
Dimensionless fluid velocities
- u,v :
-
Velocity components in x and y directions (m s−1)
- X,Y :
-
Dimensionless Cartesian coordinates
- x,y :
-
Cartesian coordinates (m)
- α :
-
Thermal diffusivity (m2 s−1)
- β :
-
Volumetric coefficient of thermal expansion (K−1)
- μ :
-
Viscosity (N s m−2)
- ν:
-
Kinematic viscosity (m2 s−1)
- ρ :
-
Fluid density (kg m−3)
- τ :
-
Dimensionless time
- φ :
-
Irreversibility distribution ratio
- c :
-
Cold
- f :
-
Fluid
- f.f :
-
Fluid friction
- h :
-
Hot
- h.t :
-
Heat transfer
- l :
-
Local
- t :
-
Total
References
Nayroles B, Touzot G, Villon P (1992) Generalizing the finite element method: diffuse approximation and diffuse elements. Comput Mech 10:307–318
Belytschko T, Lu YY, Gu L (1994) Element-free Galerkin methods. Int J Numer Methods Eng 37:229–256
Liu W, Jun S, Zhang Y (1995) Reproducing kernel particle methods. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 20:1081–1106
Atluri SN, Zhu T (1998) New meshless local Petrov–Galerkin (MLPG) approach in computational mechanics. Comput Mech 22:117–127
Hildebrand G (2009) Fracture analysis using an enriched meshless method. Meccanica 44:535–545
Kansa EJ (1990) Multiquadrics—A scattered data approximation scheme with applications to computational fluid dynamics—I. Surface approximations and partial derivative estimates. Comput Math Appl 19:127–145
Kansa EJ (1990) Multiquadrics—A scattered data approximation scheme with applications to computational fluiddynamics—II. Solutions to parabolic, hyperbolic, and elliptic partial differential equations. Comput Math Appl 19:147–161
Shu C, Ding H, Yeo KS (2003) Local radial basis function-based differential quadrature method and its application to solve two dimensional incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 192:941–954
Ding H, Shu C, Tang DB (2005) Error estimates of local multiquadric-based differential quadrature (LMQDQ) method through numerical experiments. Int J Numer Methods Eng 63:1513–1529
Shu C, Ding H, Chen HQ, Wang TG (2005) An upwind local RBF-DQ method for simulation of inviscid compressible flows. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 194:2001–2017
Bellman RE, Kashef BG, Casti J (1972) Differential quadrature: a technique for the rapid solution of nonlinear partial differential equations. J Comput Phys 10:40–52
Shu C, Richards BE (1992) Application of generalized differential quadrature to solve two-dimension incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 15:791–798
Shu C, Wee KHA (2002) Numerical simulation of natural convection in a square cavity by SIMPLE-generalized differential quadrature method. Comput Fluids 31:209–226
Tezer-Sezgin M (2004) Solution of magnetohydrodynamic flow in a rectangular duct by differential quadrature method. Comput Fluids 33:533–547
Soheil S, Jalaal M, Bararnia H, Ghasemi E, Ganji DD, Mohammadi F (2010) Local RBF-DQ method for two-dimensional heat conduction problems. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. doi:10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2010.06.033
Bararnia H, Jalaal M, Ghasemi E, Soheil S., Ganji DD, Mohammadi F (2010) Numerical simulation of Joule heating phenomenon using meshless RBF-DQ method. Int J Thermal Sci. doi:10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2010.06.008
Nithyadevi N, Sivasankaran S, Kandaswamy P (2007) Buoyancy-driven convection of water near its density maximum with time periodic partially active vertical walls. Meccanica 42:503–510
Saravanan S, Kandaswamy P (2002) Buoyancy convection in low Prandtl number liquids with large temperature variation. Meccanica 37:599–608
Ece MC, Elif B (2007) Natural convection flow under a magnetic field in an inclinedsquare enclosure differentially heated on adjacent walls. Meccanica 42:435–449
Zahmatkesh I (2008) On the importance of thermal boundary conditions in heat transfer and entropy generation for natural convection inside a porous enclosure. Int J Thermal Sci 47:339–346
Abu-Hijleh BAK, Abu-Qudais M, Abu-Nada E (1999) Numerical prediction of entropy generation due to natural convection from a horizontal cylinder. Energy 24:327–333
Magherbi M, Abbassi H, Brahim AB (2003) Entropy generation at the onset of natural convection. Int J Heat Mass Transf 46:3441–3450
Abu-Hijleh BAK, Heilen WN (1999) Entropy generation due to laminar natural convection over a heated rotating cylinder. Int J Heat Mass Transf 42:4225–4233
Mahmud S, Island AKS (2003) Laminar free convection and entropy generation inside an inclined wavy enclose. Int J Thermal Sci 42:1003–1012
Famouri M, Hooman K (2008) Entropy generation for natural convection by heated partitions in a cavity. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 35:492–502
Kimura S, Bejan A (1983) The heatline visualization of convective heat transfer. ASME J Heat Transf 105:916–919
Shan YY, Shu C, Lu ZL (2008) Application of local MQ-DQ method to solve 3D incompressible viscous flows with curved boundary. CMES Comput Model Eng Sci 25:99–113
de Vahl Davis G (1983) Natural convection of air in a square cavity: a benchmark numerical solution. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 3:249–264
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soleimani, S., Qajarjazi, A., Bararnia, H. et al. Entropy generation due to natural convection in a partially heated cavity by local RBF-DQ method. Meccanica 46, 1023–1033 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-010-9358-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-010-9358-0