Abstract
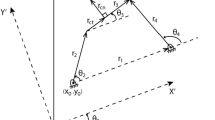
This article describes a method for optimizing the synthesis of a four-bar linkage mechanism to generate a definite mathematic function. In this research, the objective function was defined based on the least squares of error between the generated function and the desired function. Because of non-linearity of the objective function and the constraint, SQP method has been used to find the optimal mechanism. This method of optimization is a gradient-based method and its result is more trustable than heuristic methods. In this study, five precision points have been used to synthesize four-bar linkages; therefore, by using this amount of precision points, a set of non-linear equations was obtained for mechanism synthesis. Unlike the previous researches that dimensional parameters are used as optimization variables, precision points distribution was used in current research. The main innovation of this paper is presentation of some directions to have estimative prediction for distribution of precision points in optimal mechanism which maybe useful for designers. These directions were obtained based on the method that presented in current work and regard to shape of desired function and its first and second derivative.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martínez-Alfaro H (2008) Four-bar mechanism synthesis for n desired path points using simulated annealing. In: Siarry P, Michalewicz Z (eds) Advances in metaheuristics for hard optimization. Springer, Berlin, pp 23–37. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-72960-0_2
Freudenstein F (1959) Structural error analysis in plane kinematic synthesis. J Eng Ind Trans ASME 81B:15–22
Freudenstein F, Sandor GN (1959) Synthesis of path-generating mechanisms by means of a programmed digital computer. J Eng Ind 81B:159–168
Fox RL, Willmert KD (1967) Optimum design of curve generating linkages with inequality constraints. J Eng Ind 89B:144–152
Sutherland GH, Siddall JN (1974) Dimensional synthesis of linkages by multifactor optimization. Mech Mach Theory 9:81–95 doi:10.1016/0094-114X(74)90009-3
Levitskii NI, Sarkissyan YL, Gekchian GS (1972) Optimum synthesis of four-bar function generating mechanism. Mech Mach Theory 7(4):387–398. doi:10.1016/0094-114X(72)90048-1
Rao AC (1975) Kinematic design of four-bar function-generators with optimum sensitivity. Mech Mach Theory 10:531–535. doi:10.1016/0094-114X(75)90008-7
Rao AC (1979) Optimum design of four-bar function generators with minimum variance criterion. J Optim Theory Appl 29(1):147–153. doi:10.1007/BF00932641
Sun W (1982) Optimum design method for four-bar function generators. J Optim Theory Appl 38(2):287–293. doi:10.1007/BF00934089
Chen FY, Chan VL (1974) Dimensional synthesis of mechanisms for function generator using Marguardt’s compromise. J Eng Ind 96:131–137
Guj G, Dong ZY, Giacinto MD (1981) Dimensional synthesis of four bar linkage for function generation with velocity and acceleration constraints. Meccanica 16(4):210–219. doi:10.1007/BF02128323
Söylemez E, Freudenstein F (1982) Transmission optimization of spatial 4-link mechanisms. Mech Mach Theory 17(4):263–283. doi:10.1016/0094-114X(82)90050-7
Gosselin C, Angeles J (1989) Optimization of planar and spherical function generators as minimum-defect linkages. Mech Mach Theory 24(4):293–307. doi:10.1016/0094-114X(89)90049-9
Angeles J, Alivizatos A, Akhras R (1988) An unconstrained nonlinear least-square method of optimization of RRRR planar path generators. Mech Mach Theory 23(5):343–353. doi:10.1016/0094-114X(88)90048-1
Akhras R, Angeles J (1990) Unconstrained nonlinear least-square optimization of planar linkages for rigid-body guidance. Mech Mach Theory 25(1):97–118. doi:10.1016/0094-114X(90)90110-6
Choi JH, Lee SJ, Choi DH (1998) Tolerance optimization for mechanisms with lubricated joints. Multibody Syst Dyn 2(2):145–168. doi:10.1023/A:1009785211763
Yao J, Angeles J (2000) Computation of all optimum dyads in the approximate synthesis of planar linkages for rigid-body guidance. Mech Mach Theory 35(8):1065–1078. doi:10.1016/S0094-114X(99)00069-5
Vasiliu A, Yannou B (2001) Dimensional synthesis of planar mechanisms using neural networks: application to path generator linkages. Mech Mach Theory 36(2):299–310. doi:10.1016/S0094-114X(00)00037-9
Yan HS, Soong RC (2001) Kinematic and dynamic design of four-bar linkages by links counterweighing with variable input speed. Mech Mach Theory 36(9):1051–1071. doi:10.1016/S0094-114X(01)00032-5
Zhou H, EHM Cheung (2002) Analysis and optimal synthesis of adjustable linkages for path generation. Mechatronics 12(7):949–961. doi:10.1016/S0957-4158(01)00034-4
Simionescu PA, Beale D (2002) Optimum synthesis of the four-bar function generator in its symmetric embodiment: the Ackerman steering linkage. Mech Mach Theory 37(12):1487–1504. doi:10.1016/S0094-114X(02)00071-X
Sánchez Marín FT, Pérez González A (2003) Global optimization in path synthesis based on design space reduction. Mech Mach Theory 38(6):579–594. doi:10.1016/S0094-114X(03)00010-7
Zhou H, Cheung EHM (2004) Adjustable four-bar linkages for multi-phase motion generation. Mech Mach Theory 39(3):261–279. doi:10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2003.07.001
Sancibrian R, Viadero F, García P, Fernández A (2004) Gradient-based optimization of path synthesis problems in planar mechanisms. Mech Mach Theory 39(8):839–856. doi:10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2004.02.012
Erkaya S, Uzmay İ (2008) A neural–genetic (NN–GA) approach for optimising mechanisms having joints with clearance. Multibody Syst Dyn 20(1):69–83. doi:10.1007/s11044-008-9106-6
Bulatović RR, Dordević SR (2009) On the optimum synthesis of a four-bar linkage using differential evolution and method of variable controlled deviations. Mech Mach Theory 44(1):235–246. doi:10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2008.02.001
Nariman-Zadeh N, Felezi M, Jamali A, Ganji M (2009) Pareto optimal synthesis of four-bar mechanisms for path generation. Mech Mach Theory 44(1):180–191. doi:10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2008.02.006
Shen Q, Al-Smadi YM, Martin PJ, Russell K, Sodhi RS (2009) An extension of mechanism design optimization for motion generation. Mech Mach Theory 44(9):1759–1767. doi:10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2009.03.001
Acharyya SK, Mandal M (2009) Performance of EAS for four-bar linkage synthesis. Mech Mach Theory 44(9):1784–1794. doi:10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2009.03.003
Avilés R, Vallejo J, Fernández de Bustos I, Aguirrebeitia J, Ajuria G (2010) Optimum synthesis of planar linkages using a strain–energy error function under geometric constraints. Mech Mach Theory 45(1):65–79. doi:10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2009.08.002
Avilés R, Vallejo J, Aguirrebeitia J, Fernández de Bustos I, Ajuria G (2010) Optimization of linkages for generalized rigid-body guidance synthesis based on finite element models. Finite Elem Anal Des 46(9):721–731. doi:10.1016/j.finel.2010.03.010
Peng C, Sodhi RS (2010) Optimal synthesis of adjustable mechanisms generating multi-phase approximate paths. Mech Mach Theory 45(7):989–996. doi:10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2010.02.005
Hartenberg RS, Denavit J (1964) Kinematic synthesis of linkages. McGraw-Hill, New York
Waldron KJ, Kinzel GL (2003) Kinematics, dynamics, and design of machinery. Wiley, New York
Snyman JA (2005) Practical mathematical optimization: an introduction to basic optimization theory and classical and new gradient-based algorithms. Springer, New York
Biggs MC (1975) Constrained minimization using recursive quadratic programming. In: Dixon LCW, Szergo GP (eds) Towards global optimization. North-Holland, Amsterdam, pp 341–349
Han SP (1977) A globally convergent method for nonlinear programming. J Optim Theory Appl 22(3):297–309. doi:10.1007/BF00932858
Powell MJD (1979) Variable metric methods for constrained optimization. In: Glowinski R, Lions JL (eds) Computing methods in applied sciences and engineering. Springer, Berlin, pp 62–72. doi:10.1007/BFb0063615
Powell MJD (1978) A fast algorithm for nonlinearly constrained optimization calculations. In: Watson GA (ed) Numerical analysis. Springer, Berlin, pp 144–157. doi:10.1007/BFb0067703
Broyden CG (1970) The convergence of a class of double-rank minimization algorithms. J Inst Math Appl 6(1):76–90. doi:10.1093/imamat/6.1.76
Fletcher R (1970) A new approach to variable metric algorithms. Comput J 13(3):317–322. doi:10.1093/comjnl/13.3.317
Goldfarb D (1970) A family of variable metric updates derived by variational means. Math Comput 24:23–26
Shanno DF (1970) Conditioning of quasi-Newton methods for function minimization. Math Comput 24:647–656
Gill PE, Murray W, MA Saunders, Wright MH (1984) Procedures for optimization problems with a mixture of bounds and general linear constraints. ACM Trans Math Softw 10:282–298
Gill PE, Murray W, Wright MH (1991) Numerical linear algebra and optimization, vol 1. Addison-Wesley, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shariati, M., Norouzi, M. Optimal synthesis of function generator of four-bar linkages based on distribution of precision points. Meccanica 46, 1007–1021 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-010-9357-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-010-9357-1