Abstract
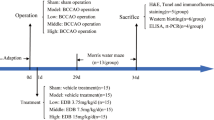
Vascular dementia (VaD) is the second cause of dementia after Alzheimer’s disease. Ligustilide (LIG) is one of the main active ingredients of traditional Chinese medicines, such as Angelica. Studies have reported that LIG could protect against VaD. However, the mechanism is still confused. In this study, we employed a bilateral common carotid artery occlusion rat model to study. LIG (20 or 40 mg/kg/day) and Nimodipine (20 mg/kg) were orally administered to the VaD rats for four weeks. Morris water maze test showed that LIG effectively ameliorated learning and memory impairment in VaD rats. LIG obviously reduced neuronal oxidative stress damage and the level of homocysteine in the brain of VaD rats. Western blot results showed that pro-apoptotic protein Bax and cleaved caspase 3 increased and anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 decreased in the hippocampi of VaD rats. But after LIG treatment, these changes were reversed. Moreover, Nissl staining result showed that LIG could reduce neuronal degeneration in VaD rats. Furthermore, LIG enhanced the expressions of P-AMPK and Sirtuin1(SIRT1) in VaD rats. In conclusion, these studies indicated that LIG could ameliorate cognitive impairment in VaD rats, which might be related to AMPK/SIRT1 pathway activation.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Allan LM, Rowan EN, Firbank MJ, Thomas AJ, Parry SW, Polvikoski TM, O’Brien JT, Kalaria RN (2011) Long term incidence of dementia, predictors of mortality and pathological diagnosis in older stroke survivors. Brain 134:3716–3727. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awr273
Almeida M, Porter RM (2019) Sirtuins and FoxOs in osteoporosis and osteoarthritis. Bone 121:284–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2019.01.018
Amenta F, Di Tullio MA, Tomassoni D (2002) The cholinergic approach for the treatment of vascular dementia: evidence from pre-clinical and clinical studies. Clin Exp Hypertens 24:697–713. https://doi.org/10.1081/ceh-120015346
Bennett S, Grant MM, Aldred S (2009) Oxidative stress in vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease: a common pathology. J Alzheimers Dis 17:245–257. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-2009-1041
Bromley-Brits K, Deng Y, Song W (2011) Morris water maze test for learning and memory deficits in Alzheimer’s disease model mice. J Vis Exp. 53:2920. https://doi.org/10.3791/2920
Cantó C, Gerhart-Hines Z, Feige JN, Lagouge M, Noriega L, Milne JC, Elliott PJ, Puigserver P, Auwerx J (2009) AMPK regulates energy expenditure by modulating NAD + metabolism and SIRT1 activity. Nature 458:1056–1060. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07813
Chen C, Zhou M, Ge Y, Wang X (2020a) SIRT1 and aging related signaling pathways. Mech Ageing Dev 187:111215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2020.111215
Chen XY, Cai CZ, Yu ML, Feng ZM, Zhang YW, Liu PH, Zeng H, Yu CH (2019) LB100 ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via the AMPK/Sirt1 pathway. World J Gastroenterol 25:6607–6618. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i45.6607
Chen Z, Yu J, Fu M, Dong R, Yang Y, Luo J, Hu S, Li W, Xu X, Tu L (2020b) Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition improves endothelial senescence by activating AMPK/SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol 177:113951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113951
Dai Z, Lu XY, Zhu WL, Liu XQ, Li BY, Song L, Liu HF, Cai WW, Deng YX, Xu TT, Wang Q, Zhang SJ (2020) Carnosine ameliorates age-related dementia via improving mitochondrial dysfunction in SAMP8 mice. Food Funct 11:2489–2497. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9fo02453k
Draper HH, Hadley M (1990) Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 186:421–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(90)86135-i
Duan J, Cui J, Yang Z, Guo C, Cao J, Xi M, Weng Y, Yin Y, Wang Y, Wei G, Qiao B, Wen A (2019) Neuroprotective effect of Apelin 13 on ischemic stroke by activating AMPK/GSK-3β/Nrf2 signaling. J Neuroinflammation 16:24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-019-1406-7
Duprez L, Wirawan E, Vanden Berghe T, Vandenabeele P (2009) Major cell death pathways at a glance. Microbes Infect 11:1050–1062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micinf.2009.08.013
Feng Z, Lu Y, Wu X, Zhao P, Li J, Peng B, Qian Z, Zhu L (2012) Ligustilide alleviates brain damage and improves cognitive function in rats of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. J Ethnopharmacol 144:313–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2012.09.014
Firbank MJ, Teodorczuk A, van der Flier WM, Gouw AA, Wallin A, Erkinjuntti T, Inzitari D, Wahlund LO, Pantoni L, Poggesi A, Pracucci G, Langhorne P, O’Brien JT (2012) Relationship between progression of brain white matter changes and late-life depression: 3-year results from the LADIS study. Br J Psychiatry 201:40–45. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.bp.111.098897
Fuhrmann DC, Brüne B (2017) Mitochondrial composition and function under the control of hypoxia. Redox Biol 12:208–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.02.012
Guo J, Shang EX, Duan JA, Tang Y, Qian D (2011) Determination of ligustilide in the brains of freely moving rats using microdialysis coupled with ultra performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Fitoterapia 82:441–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2010.12.002
Hainsworth AH, Yeo NE, Weekman EM, Wilcock DM (2016) Homocysteine, hyperhomocysteinemia and vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia (VCID). Biochim Biophys Acta 1862:1008–1017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.11.015
Hardie DG (2007) AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinases: conserved guardians of cellular energy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:774–785. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2249
Hardie DG, Ross FA, Hawley SA (2012) AMPK: a nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13:251–262. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3311
Heijnen HF, van Donselaar E, Slot JW, Fries DM, Blachard-Fillion B, Hodara R, Lightfoot R, Polydoro M, Spielberg D, Thomson L, Regan EA, Crapo J, Ischiropoulos H (2006) Subcellular localization of tyrosine-nitrated proteins is dictated by reactive oxygen species generating enzymes and by proximity to nitric oxide synthase. Free Radic Biol Med 40:1903–1913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.09.006
Himeno E, Ohyagi Y, Ma L, Nakamura N, Miyoshi K, Sakae N, Motomura K, Soejima N, Yamasaki R, Hashimoto T, Tabira T, LaFerla FM, Kira J (2011) Apomorphine treatment in Alzheimer mice promoting amyloid-β degradation. Ann Neurol 69:248–256. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22319
Hu M, Liu Z, Lv P, Wang H, Zhu Y, Qi Q, Xu J (2017) Autophagy and Akt/CREB signalling play an important role in the neuroprotective effect of nimodipine in a rat model of vascular dementia. Behav Brain Res 325:79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2016.11.053
Hu T, Shi JJ, Fang J, Wang Q, Chen YB, Zhang SJ (2020) Quercetin ameliorates diabetic encephalopathy through SIRT1/ER stress pathway in db/db mice. Aging 12:7015–7029. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103059
Huo T, Jia Y, Yin C, Luo X, Zhao J, Wang Z, Lv P (2019) Iron dysregulation in vascular dementia: Focused on the AMPK/autophagy pathway. Brain Res Bull 153:305–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.09.006
Iadecola C (2004) Neurovascular regulation in the normal brain and in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:347–360. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1387
Iadecola C (2013) The pathobiology of vascular dementia. Neuron 80:844–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.10.008
Iadecola C, Gorelick PB (2003) Converging pathogenic mechanisms in vascular and neurodegenerative dementia. Stroke 34:335. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.0000054050.51530.76
Iadecola C, Nedergaard M (2007) Glial regulation of the cerebral microvasculature. Nat Neurosci 10:1369–1376. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn2003
Jian WX, Zhang Z, Zhan JH, Chu SF, Peng Y, Zhao M, Wang Q, Chen NH (2020) Donepezil attenuates vascular dementia in rats through increasing BDNF induced by reducing HDAC6 nuclear translocation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 41:588–598. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-019-0334-5
Joosten E (2001) Homocysteine, vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Chem Lab Med 39:717–720. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm.2001.119
Jorm AF, Jolley D (1998) The incidence of dementia: a meta-analysis. Neurology 51:728–733. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.51.3.728
Justin BN, Turek M, Hakim AM (2013) Heart disease as a risk factor for dementia. Clin Epidemiol 5:135–145. https://doi.org/10.2147/clep.S30621
Kisler K, Nelson AR, Montagne A, Zlokovic BV (2017) Cerebral blood flow regulation and neurovascular dysfunction in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 18:419–434. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2017.48
Kuang X, Du JR, Liu YX, Zhang GY, Peng HY (2008) Postischemic administration of Z-Ligustilide ameliorates cognitive dysfunction and brain damage induced by permanent forebrain ischemia in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 88:213–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2007.08.006
Li H, Peng D, Zhang SJ, Zhang Y, Wang Q, Guan L (2021) Buyang Huanwu Decoction promotes neurogenesis via sirtuin 1/autophagy pathway in a cerebral ischemia model. Mol Med Rep 24:79124. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2021.12431
Li M, Meng N, Guo X, Niu X, Zhao Z, Wang W, Xie X, Lv P (2020) Dl-3-n-Butylphthalide Promotes Remyelination and Suppresses Inflammation by Regulating AMPK/SIRT1 and STAT3/NF-κB Signaling in Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion. Front Aging Neurosci 12:137. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2020.00137
Marshall RS, Festa JR, Cheung YK, Chen R, Pavol MA, Derdeyn CP, Clarke WR, Videen TO, Grubb RL, Adams HP, Powers WJ, Lazar RM (2012) Cerebral hemodynamics and cognitive impairment: baseline data from the RECON trial. Neurology 78:250–255. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e31824365d3
Maxwell AJ (2002) Mechanisms of dysfunction of the nitric oxide pathway in vascular diseases. Nitric Oxide 6:101–124. https://doi.org/10.1006/niox.2001.0394
Pendlebury ST, Rothwell PM (2009) Prevalence, incidence, and factors associated with pre-stroke and post-stroke dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 8:1006–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(09)70236-4
Popa-Wagner A, Buga AM, Popescu B, Muresanu D (2015) Vascular cognitive impairment, dementia, aging and energy demand. A vicious cycle. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 122(Suppl 1):S47–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-013-1129-3
Raz L, Knoefel J, Bhaskar K (2016) The neuropathology and cerebrovascular mechanisms of dementia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36:172–186. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2015.164
Ren C, Li N, Gao C, Zhang W, Yang Y, Li S, Ji X, Ding Y (2020a) Ligustilide provides neuroprotection by promoting angiogenesis after cerebral ischemia. Neurol Res 42:683–692. https://doi.org/10.1080/01616412.2020.1782122
Ren H, Shao Y, Wu C, Ma X, Lv C, Wang Q (2020b) Metformin alleviates oxidative stress and enhances autophagy in diabetic kidney disease via AMPK/SIRT1-FoxO1 pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol 500: 110628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2019.110628
Rizzi L, Rosset I, Roriz-Cruz M (2014) Global epidemiology of dementia: Alzheimer’s and vascular types. Biomed Res Int 2014: 908915. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/908915
Sachdev P, Kalaria R, O’Brien J, Skoog I, Alladi S, Black SE, Blacker D, Blazer DG, Chen C, Chui H, Ganguli M, Jellinger K, Jeste DV, Pasquier F, Paulsen J, Prins N, Rockwood K, Roman G, Scheltens P (2014) Diagnostic criteria for vascular cognitive disorders: a VASCOG statement. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 28:206–218. https://doi.org/10.1097/wad.0000000000000034
Sairanen T, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, Paetau A, Ijäs P, Lindsberg PJ (2006) Apoptosis dominant in the periinfarct area of human ischaemic stroke–a possible target of antiapoptotic treatments. Brain 129:189–199. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awh645
Saposnik G, Ray JG, Sheridan P, McQueen M, Lonn E (2009) Homocysteine-lowering therapy and stroke risk, severity, and disability: additional findings from the HOPE 2 trial. Stroke 40:1365–1372. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.108.529503
Sarubbo F, Esteban S, Miralles A, Moranta D (2018) Effects of Resveratrol and other Polyphenols on Sirt1: Relevance to Brain Function During Aging. Curr Neuropharmacol 16:126–136. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159x15666170703113212
Sergi C, Shen F, Liu SM (2019) Insulin/IGF-1R, SIRT1, and FOXOs Pathways-An Intriguing Interaction Platform for Bone and Osteosarcoma. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 10::93. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00093
Siddiqui WA, Ahad A, Ahsan H (2015) The mystery of BCL2 family: Bcl-2 proteins and apoptosis: an update. Arch Toxicol 89:289–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1448-7
Tomassoni D, Lanari A, Silvestrelli G, Traini E, Amenta F (2008) Nimodipine and its use in cerebrovascular disease: evidence from recent preclinical and controlled clinical studies. Clin Exp Hypertens 30:744–766. https://doi.org/10.1080/10641960802580232
Wang L, Wang F, Liu S, Yang X, Yang J, Ming D (2018) VEGF attenuates 2-VO induced cognitive impairment and neuronal injury associated with the activation of PI3K/Akt and Notch1 pathway. Exp Gerontol 102:93–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2017.12.010
Wang XX, Zhang B, Xia R, Jia QY (2020) Inflammation, apoptosis and autophagy as critical players in vascular dementia. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24:9601–9614. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202009_23048
Washida K, Hattori Y, Ihara M (2019) Animal Models of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion: From Mouse to Primate. Int J Mol Sci 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246176
Wolburg H, Noell S, Mack A, Wolburg-Buchholz K, Fallier-Becker P (2009) Brain endothelial cells and the glio-vascular complex. Cell Tissue Res 335:75–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-008-0658-9
Wu S, Wang N, Li J, Wang G, Seto SW, Chang D, Liang H (2019) Ligustilide Ameliorates the Permeability of the Blood-Brain Barrier Model In Vitro During Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation Injury Through HIF/VEGF Pathway. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 73:316–325. https://doi.org/10.1097/fjc.0000000000000664
Wyllie AH (2010) “Where, O death, is thy sting?“ A brief review of apoptosis biology. Mol Neurobiol 42:4–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-010-8125-5
Xu YJ, Mei Y, Qu ZL, Zhang SJ, Zhao W, Fang JS, Wu J, Yang C, Liu SJ, Fang YQ, Wang Q, Zhang YB (2018) Ligustilide Ameliorates Memory Deficiency in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice via Restoring Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Biomed Res Int 2018: 4606752. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4606752
Yang L, Jiang Y, Shi L, Zhong D, Li Y, Li J, Jin R (2020) AMPK: Potential Therapeutic Target for Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr Protein Pept Sci 21:66–77. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389203720666190819142746
Zhang XL, Zheng SL, Dong FR, Wang ZM (2012) Nimodipine improves regional cerebral blood flow and suppresses inflammatory factors in the hippocampus of rats with vascular dementia. J Int Med Res 40:1036–1045. https://doi.org/10.1177/147323001204000322
Zhou X, Xiao W, Su Z, Cheng J, Zheng C, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Wang L, Xu B, Li S, Yang X, Pui Man Hoi M (2019) Hippocampal Proteomic Alteration in Triple Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease and Implication of PINK 1 Regulation in Donepezil Treatment. J Proteome Res 18::1542–1552. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00818
Zhu WL, Zheng JY, Cai WW, Dai Z, Li BY, Xu TT, Liu HF, Liu XQ, Wei SF, Luo Y, Wang H, Pan HF, Wang Q, Zhang SJ (2020) Ligustilide improves aging-induced memory deficit by regulating mitochondrial related inflammation in SAMP8 mice. Aging 12:3175–3189. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102793
Zlokovic BV (2008) The blood-brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron 57:178–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2008.01.003
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82004430 and 81673717); the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong (2021A1515011478 and 2018A0303130053) and Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Research on Emergency in TCM (2017B030314176).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shi-Jie Zhang designed the experiments. Dong Peng carried out the experiments and wrote the manuscript. Dan Luo supported the animal work. Han-Zi Qiao, Hong-Yu Tan, Yi-Xue Wang, Li-Jun Qiao supported the materials. Dong Peng, Ye-Feng Cai and Shi-Jie Zhang modified the manuscript. Qi Wang supported the experimental platform. Li Guan and Shi-Jie Zhang supervised this work
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Committee for Animal Research of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine.
Consent to Participate and Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, D., Qiao, HZ., Tan, HY. et al. Ligustilide ameliorates cognitive impairment via AMPK/SIRT1 pathway in vascular dementia rat. Metab Brain Dis 37, 1401–1414 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-00947-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-00947-0