Abstract
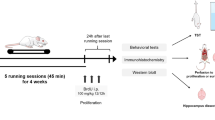
3, 4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) or ecstasy is a derivative of amphetamine that leads to long term potentiation (LTP) disruption in the hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG). Exercise has been accepted as a treatment for the improvement of neurodegenerative disease. Herein, the effects of exercise on the MDMA- induced neurotoxicity were assessed. Male Wistar rats received intraperitoneal injection of MDMA (10 mg/kg) and exercised for one month on a treadmill (Simultaneously or asynchronously with MDMA). LTP and expression of BDNF were assessed using electrophysiology and western blotting methods, respectively. MDMA attenuated the field excitatory post-synaptic potential (fEPSP) slope in comparison with the control group, whereas treadmill exercise increased this parameter when compared to MDMA group. Furthermore, BDNF expression significantly decreased in MDMA group and treadmill exercise could increase that. In conclusion, results of this study suggest that synchronous exercise is able to improve MDMA-induced LTP changes through increase of BDNF expression in the hippocampus of rats.



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
25 September 2017
In the original publication of the article, author name Masoumeh Asadbegi was incorrectly written as Masoumeh Asadbeigi. The authors regret the oversight.
References
Alomari MA et al (2016) Combining restricted diet with forced or voluntary exercises improves hippocampal BDNF and cognitive function in rats. Int J Neurosci 126:366–373
Arias-Cavieres A et al (2010) MDMA (“ecstasy”) impairs learning in the Morris water maze and reduces hippocampal LTP in young rats. Neurosci Lett 469:375–379
Bolla KI, McCann UD, Ricaurte GA (1998) Memory impairment in abstinent MDMA (" ecstasy") users. Neurology 51:1532–1537
Christie BR et al (2005) Voluntary exercise rescues deficits in spatial memory and long-term potentiation in prenatal ethanol-exposed male rats. Eur J Neurosci 21:1719–1726
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) 2015. World drug report 2015, Vol., United Nations Publications.
Fantegrossi WE et al (2003) Pharmacological characterization of the effects of 3, 4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (" ecstasy") and its enantiomers on lethality, core temperature, and locomotor activity in singly housed and crowded mice. Psychopharmacology 166:202–211
Fernandez, S.P., et al., 2016. Constitutive and acquired serotonin deficiency alters memory and hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Neuropsychopharmacology.
Ferreira TA, Iacono LL, Gross CT (2010) Serotonin receptor 1A modulates actin dynamics and restricts dendritic growth in hippocampal neurons. Eur J Neurosci 32:18–26
Grider M et al (2005) In situ expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor or neurotrophin-3 promotes sprouting of cortical serotonergic axons following a neurotoxic lesion. J Neurosci Res 82:404–412
Griesbach GS et al (2004) Voluntary exercise following traumatic brain injury: brain-derived neurotrophic factor upregulation and recovery of function. Neuroscience 125:129–139
Karimi SA et al (2013) Effect of high-fat diet and antioxidants on hippocampal long-term potentiation in rats: an in vivo study. Brain Res 1539:1–6
Kim S-E et al (2013) Treadmill exercise and wheel exercise enhance expressions of neutrophic factors in the hippocampus of lipopolysaccharide-injected rats. Neurosci Lett 538:54–59
Kojima M, Mizui T (2017) Chapter two-BDNF propeptide: a novel modulator of synaptic plasticity. Vitam Horm 104:19–28
Kovalchuk Y et al (2002) Postsynaptic induction of BDNF-mediated long-term potentiation. Science 295:1729–1734
Kuipers SD et al (2016) BDNF-induced LTP is associated with rapid Arc/Arg3. 1-dependent enhancement in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Sci Rep 6:21222
Lu, B., Nagappan, G., Lu, Y., 2014. BDNF and synaptic plasticity, cognitive function, and dysfunction. In: neurotrophic factors. Vol., ed.^eds. Springer, pp. 223-250.
Madhav T, Pei Q, Zetterström T (2001) Serotonergic cells of the rat raphe nuclei express mRNA of tyrosine kinase B (trkB), the high-affinity receptor for brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Mol Brain Res 93:56–63
Martínez-Turrillas R et al (2006) Differential effects of 3, 4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA,“ecstasy”) on BDNF mRNA expression in rat frontal cortex and hippocampus. Neurosci Lett 402:126–130
Mattson MP, Maudsley S, Martin B (2004) BDNF and 5-HT: a dynamic duo in age-related neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. Trends Neurosci 27:589–594
Mazer C et al (1997) Serotonin depletion during synaptogenesis leads to decreased synaptic density and learning deficits in the adult rat: a possible model of neurodevelopmental disorders with cognitive deficits. Brain Res 760:68–73
Mirzamohammadi S et al (2015) Effect of 17β-estradiol on mediators involved in mesenchymal stromal cell trafficking in cell therapy of diabetes. Cytotherapy 17:46–57
Morimoto K, Otani S, Goddard GV (1987) Effects of acute and long-term treatment with amphetamine on evoked responses and long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus of anesthetized rats. Brain Res 407:137–143
Morini R et al (2011) Enhanced hippocampal long-term potentiation following repeated MDMA treatment in dark–agouti rats. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 21:80–91
Morris R et al (1982) Place navigation impaired in rats with hippocampal lesions. Nature 297:681–683
Nicoll RA (2017) A brief history of long-term potentiation. Neuron 93:281–290
Otsuka S et al (2016) The neuroprotective effects of preconditioning exercise on brain damage and neurotrophic factors after focal brain ischemia in rats. Behav Brain Res 303:9–18
Parrott A (2002) Recreational ecstasy/MDMA, the serotonin syndrome, and serotonergic neurotoxicity. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:837–844
Paxinos G et al (1985) Bregma, lambda and the interaural midpoint in stereotaxic surgery with rats of different sex, strain and weight. J Neurosci Methods 13:139–143
Radak Z et al (2006) The effects of training and detraining on memory, neurotrophins and oxidative stress markers in rat brain. Neurochem Int 49:387–392
Radák Z et al (2001) Regular exercise improves cognitive function and decreases oxidative damage in rat brain. Neurochem Int 38:17–23
Rauskolb S et al (2010) Global deprivation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the CNS reveals an area-specific requirement for dendritic growth. J Neurosci 30:1739–1749
Reisi P et al (2010) Treadmill running improves long-term potentiation (LTP) defects in streptozotocin-induced diabetes at dentate gyrus in rats. Pathophysiology 17:33–38
Roberts CA, Jones A, Montgomery C (2016) Meta-analysis of molecular imaging of serotonin transporters in ecstasy/polydrug users. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 63:158–167
Sakalem ME et al (2017) Environmental enrichment and physical exercise revert behavioral and electrophysiological impairments caused by reduced adult neurogenesis. Hippocampus 27:36–51
Shariati MBH et al (2014) Acute effects of ecstasy on memory are more extensive than chronic effects. Basic Clin Neurosci 5:225
Soleimani Asl S et al (2015) Attenuation of ecstasy-induced neurotoxicity by N-acetylcysteine. Metab Brain Dis 30:171–181
Sprague JE et al (2003) Hippocampal serotonergic damage induced by MDMA (ecstasy): effects on spatial learning. Physiol Behav 79:281–287
Tong L et al (2001) Effects of exercise on gene-expression profile in the rat hippocampus. Neurobiol Dis 8:1046–1056
Tuon T et al (2014) Physical training prevents depressive symptoms and a decrease in brain-derived neurotrophic factor in Parkinson's disease. Brain Res Bull 108:106–112
Van Praag H et al (2005) Exercise enhances learning and hippocampal neurogenesis in aged mice. J Neurosci 25:8680–8685
Vedder LC, Savage LM (2017) BDNF regains function in hippocampal long-term potentiation deficits caused by diencephalic damage. Learn Mem 24:81–85
Zargooshnia S et al (2015) The protective effect of Borago officinalis extract on amyloid β (25–35)-induced long term potentiation disruption in the dentate gyrus of male rats. Metab Brain Dis 30:151–156
Acknowledgements
The data used in this paper was extracted from M.Sc. thesis of Azam Sajadi and supported by Hamadan University of Medical Sciences No.9410015475.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors of this paper have a financial interest to report.
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-0114-1.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sajadi, A., Amiri, I., Gharebaghi, A. et al. Treadmill exercise alters ecstasy- induced long- term potentiation disruption in the hippocampus of male rats. Metab Brain Dis 32, 1603–1607 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-0046-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-0046-9