Abstract
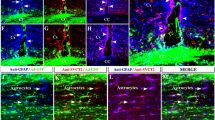
Glia activation and neuroinflamation are major factors implicated in the aetiology of most neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs). Several agents and toxins have been known to be capable of inducing glia activation an inflammatory response; most of which are active substances that can cause oxidative stress by inducing production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Neurogenesis on the other hand involves metabolic and structural interaction between neurogenic and glia cells of the periventricular zone (PVZ); a region around the third ventricle. This study investigates glia activation (GFAP), cell proliferation (Ki-67) and neuronal metabolism (NSE) during neurogenesis and oxidative stress by comparing protein expression in the PVZ against that of the parietal cortex. Adult Wistar Rats were treated with normal saline and 20 mg/Kg KCN for 7 days. The tissue sections were processed for immunohistochemistry to demonstrate glia cells (anti Rat-GFAP), cell proliferation (anti Rat-Ki-67) and neuronal metabolism (anti Rat-NSE) using the antigen retrieval method. The sections from Rats treated with cyanide showed evidence of neurodegeneration both in the PVZ and cortex. The distribution of glia cells (GFAP), Neuron specific Enolase (NSE) and Ki-67 increased with cyanide treatment, although the increases were more pronounced in the neurogenic cell area (PVZ) when compared to the cortex. This suggests the close link between neuronal metabolism and glia activation both in neurogenesis and oxidative stress.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PVZ:
-
Periventricular zone
- GFAP:
-
Glia fibrillary acidic protein
- NSE:
-
Neuron specific enolase
- Ki:
-
67- Antigen Ki-67
- KCN:
-
Potassium Cyanide
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen Species
- RNS:
-
Reactive nitrogen species
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- ACSF:
-
Accessory cerebrospinal fluid
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- DAB:
-
3′3′ Diaminobenzidine Tetrachloride
References
Béraud D, Hathaway HA, Trecki J, Chasovskikh S, Johnson DA, Johnson JA, Federoff HJ, Shimoji M, Mhyre TR, Maguire-Zeiss KA (2012) Microglial activation and antioxidant responses induced by the Parkinson’s disease protein α-Synuclein. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 8(1):94–117
Campanini B, Spyrakis F, Peracchi A, Mozzarelli A (2013) Serine racemase: a key player in neuron activity and in neuropathologies. Front Biosci 18:1112–28
Chunyan L, Pradeep KT, William EA (2007) Differences in Spike train variability in rat vasopressin and oxytocin neuronsand their relationship to synaptic activity. J Physiol 2007(581):221–240
Contestabile A, Monti B, Polazzi E (2012) Neuronal-glial interactions define the role of nitric oxide in neural functional processes. Curr Neuropharmacol 10(4):303–10
Devos SL, Miller TM (2013) Direct intraventricular delivery of drugs to the rodent central nervous system. J Vis Exp (75):e50326. doi:10.3791/50326
Eid T, Tu N, Lee TS, Lai JC (2013) Regulation of astrocyte glutamine synthetase in epilepsy. Neurochem Int. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2013.06.008
Episcopo FL, Tirolo C, Testa N, Caniglia S, Morale MC, Marchetti B (2013) Reactive astrocytes are key players in nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurorepair in the mptp mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: focus on endogenous neurorestoration. Curr Aging Sci 6(1):45–55
Geissler M, Gottschling C, Aguado A, Rauch U, Wetzel CH, Hatt H, Faissner A (2013) Primary hippocampal neurons, which lack four crucial extracellular matrix molecules, display abnormalities of synaptic structure and function and severe deficits in perineuronal net formation. J Neurosci 33(18):7742–7755. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3275-12.2013
Hui J, Zhang ZJ, Zhang X, Shen Y, Gao YJ (2013) Repetitive hyperbaric oxygen treatment attenuates complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced pain and reduces glia-mediated neuroinflammation in the spinal cord. J Pain 14(7):747–58
Jungenitz T, Radic T, Jedlicka P, Schwarzacher SW (2013) High-frequency stimulation induces gradual immediate early gene expression in maturing adult-generated hippocampal granule cells. Cereb Cortex. doi:10.1093/cercor/bht035
Khozhaĭ LI, Otellin VA (2013) Reactive microglial changes in rat neocortex and hippocampus after exposure to acute perinatal hypoxia. Morfologiia 143(1):23–7
Kim JH, Choi JS, Lee BH (2012) PI3K/Akt and MAPK pathways evoke activation of FoxO transcription factor to undergo neuronal apoptosis in brain of the silkworm Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) Suppl.58:OL1780–OL1785
Knolhoff AM, Nautiyal KM, Nemes P, Kalachikov S, Morozova I, Silver R, Sweedler JV (2013) Combining small-volume metabolomic and transcriptomic approaches for assessing brain chemistry. Anal Chem 85(6):3136–43. doi:10.1021/ac3032959
Knuckles P, Vogt MA, Lugert S, Milo M, Chong MM, Hautbergue GM, Wilson SA, Littman DR, Taylor V (2012) Drosha regulates neurogenesis by controlling neurogenin 2 expression independent of microRNAs. Nat Neurosci 15(7):962–9. doi:10.1038/nn.3139
Madeira JM, Renschler CJ, Mueller B, Hashioka S, Gibson DL, Klegeris A (2013) Novel protective properties of auranofin: inhibition of human astrocyte cytotoxic secretions and direct neuroprotection. Life Sci 92(22):1072–80. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2013.04.005
Magistretti PJ, Pellerin L (1996) Cellular mechanisms of brain energy metabolism. Relevance to functional brain imaging and to neurodegenerative disorders. Ann N Y Acad Sci 777:380–387, Issue Bio artificial Organs: Science, Medicine, and Technology
May D, Tress O, Seifert G, Willecke K (2013) Connexin47 protein phosphorylation and stability in oligodendrocytes depend on expression of Connexin43 protein in astrocytes. J Neurosci 33(18):7985–96. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5874-12.2013
Morte MI, Carreira BP, Machado V, Carmo A, Nunes-Correia I, Carvalho CM, Araújo IM (2013) Evaluation of proliferation of neural stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Curr Protoc Stem Cell Biol. 2:Unit2D.14. doi:10.1002/9780470151808.sc02d14s24
Murphy BL, Hofacer RD, Faulkner CN, Loepke AW, Danzer SC (2012) Abnormalities of granule cell dendritic structure are a prominent feature of the intrahippocampal kainic acid model of epilepsy despite reduced postinjury neurogenesis. Epilepsia 53(5):908–21. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2012.03463.x
Mutso AA, Radzicki D, Baliki MN, Huang L, Banisadr G, Centeno MV, Radulovic J, Martina M, Miller RJ, Apkarian AV (2012) Abnormalities in hippocampal functioning with persistent pain. J Neurosci 32(17):5747–56. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0587-12.2012
Nazarenko I, Hedrén A, Sjödin H, Orrego A, Andrae J, Afink GB, Nistér M, Lindström MS (2011) Brain abnormalities and glioma-like lesions in mice overexpressing the long isoform of PDGF-A in astrocytic cells. PLoS One 6(4):e18303
Nikolakopoulou AM, Dutta R, Chen Z, Miller RH, Trapp BD (2013) Activated microglia enhance neurogenesis via trypsinogen secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(21):8714–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.1218856110
Oliva I, Fernández M, Martín ED (2013) Dopamine release regulation by astrocytes during cerebral ischemia. Neurobiol Dis. 58:231–41. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2013.06.007
Perederiy JV, Westbrook GL (2013) Structural plasticity in the dentate gyrus- revisiting a classic injury model. Front Neural Circ 7:17
Poluch S, Juliano SL (2013) Fine-tuning of neurogenesis is essential for the evolutionary expansion of the cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex. doi:10.1093/cercor/bht232
Robins SC, Stewart I, McNay DE, Taylor V, Giachino C, Goetz M, Ninkovic J, Briancon N, Maratos-Flier E, Flier JS, Kokoeva MV, Placzek M (2013) Α-Tantacytes of the adult hypothalamic third ventricle includes distinct populations of FGF-responsive neural progenitors. Nature Communications 4, Article number: 2049, doi:10.1038/ncomms3049
Shi M, Majumdar D, Gao Y, Brewer BM, Goodwin CR, McLean JA, Li D, Webb DJ (2013) Glia co-culture with neurons in microfluidic platforms promotes the formation and stabilization of synaptic contacts. Lab Chip 13(15):3008–21. doi:10.1039/c3lc50249j
Skaper SD, Facci L, Giusti P (2013) Glia and mast cells as targets for palmitoylethanolamide, an anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective lipid mediator. Mol Neurobiol 48(2):340–52. doi:10.1007/s12035-013-8487-6
Sykora P, Wilson DM 3rd, Bohr VA (2013) Base excision repair in the mammalian brain: implication for age related neurodegeneration. Mech Ageing Dev. doi:10.1016/j.mad.2013.04.005
Terazawa R, Akimoto N, Kato T, Itoh T, Fujita Y, Hamada N, Deguchi T, Iinuma M, Noda M, Nozawa Y, Ito M (2013) A kavalactone derivative inhibits lipopolysaccharide-stimulated iNOS induction and NO production through activation of Nrf2 signaling in BV2 microglial cells. Pharmacol Res. 71:34–43. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2013.02.002
Wang Y, Liu HK, Schütz G (2013) Role of the nuclear receptor Tailless in adult neural stem cells. Mech Dev. doi:10.1016/j.mod.2013.02.001
Xiong Y, Bai Y, Leong N, Laughlin TS, Rothberg PG, Xu H, Nong L, Zhao J, Dong Y, Li T (2013) Immunohistochemical detection of mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in lung adenocarcinomas using mutation-specific antibodies. Diagn Pathol 8(1):27–1
Xu Y, Tamamaki N, Noda T, Kimura K, Itokazu Y, Matsumoto N, Dezawa M, Ide C (2013) Neurogenesis in the ependymal layer of the adult rat 3rd ventricle. Exp Neurol 192(2):251–64
Zabel MK, Kirsch WM (2013) From development to dysfunction: Microglia and the complement cascade in CNS homeostasis. Ageing Res Rev. 12(3):749–56. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2013.02.001
Zhang ZZ, Gong YY, Shi YH, Zhang W, Qin XH, Wu XW (2012) Valproate promotes survival of retinal ganglion cells in a rat model of optic nerve crush. Neuroscience 224:282–93. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.07.056
Zhang HY, Wang ND, Song N, Xu HM, Shi LM, Jiang H, Xie JX (2013) 6-Hydroxydopamine promotes iron traffic in primary cultured astrocytes. Biometals. 26(5):705–14. doi:10.1007/s10534-013-9647-x
Zhou Y, Xu Q, Li D, Zhao L, Wang Y, Liu M, Gu X, Liu Y (2012) Early neurogenesis during caudal spinal cord regeneration in adult Gekko japonicus. J Mol Histol. 44(3):291–7. doi:10.1007/s10735-012-9466-3
Zou Y, Corniola R, Leu D, Khan A, Sahbaie P, Chakraborti A, Clark DJ, Fike JR, Huang TT (2012) Extracellular superoxide dismutase is important for hippocampal neurogenesis and preservation of cognitive functions after irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(52):21522–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.1216913110
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the contributions of Mr. Madukwe Jonathan of the Department of Histopathology, National Hospital Abuja. We will also like to appreciate Mr. Oso of the Department of Chemical Sciences, Mrs. Olaiya of the Physiology Laboratory, Afe Babalola University for their assistance in regent preparation and treatment of the animals throughout the duration of the experiment.
Conflict of interest
The Authors hereby declare there is no conflict of interest associated with this study or any of the procedures and materials used for the purpose of the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highlights
1. Structural evidence reveals neuronal damage cytoplasmic fragmentation and loss of axonal projections in neuronal cells for the treatment group
2. Glia activation increased with cyanide treatment and oxidative stress
3. Neuronal metabolism increased both in oxidative stress and neurogenesis as shown by NSE immunopositivity and was more prominent in neurogenic cells of the PVZ both in the control and treatment category
4. Cell proliferation increased in PVZ and parietal cortex with cyanide treatment. The increase was much more prominent in neurogenic cells of the PVZ. The cortical cell increase was found to be glia (GFAP immunopositive) rather than neuronal
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogundele, O.M., Omoaghe, A.O., Ajonijebu, D.C. et al. Glia activation and its role in oxidative stress. Metab Brain Dis 29, 483–493 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-013-9446-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-013-9446-7