Abstract
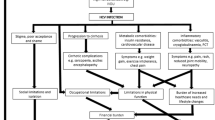
There is growing evidence that hepatitis C virus (HCV)-infection may affect the brain. About half of the HCV-infected patients complain of chronic fatigue irrespective of their stage of liver disease or virus replication rate. Even after successful antiviral therapy fatigue persists in about one third of the patients. Many patients, in addition, report of deficits in attention, concentration and memory, some also of depression. Psychometric testing revealed deficits in attention and verbal learning ability as characteristic for HCV-afflicted patients with normal liver function. Magnetic resonance spectroscopic studies showed alterations of the cerebral choline, N-acetyl-aspartate, and creatine content in the basal ganglia, white matter and frontal cortex, respectively. Recently, pathologic cerebral serotonin and dopamine transporter binding and regional alterations of the cerebral glucose utilisation compatible with alterations of the dopaminergic attentional system were observed. Several studies detected HCV in brain samples or cerebro-spinal fluid. Interestingly, viral sequences in the brain often differed from those in the liver, but were closely related to those found in lymphoid tissue. Therefore, the Trojan horse hypothesis emerged: HCV-infected mononuclear blood cells enter the brain, enabling the virus to reside within the brain (probably in microglia) and to infect brain cells, especially astrocytes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adair D, Wilkinson J, Scheck A, Radkowski M, Rakela J, Laskus T (2004) Differential display and microarray analysis show differentially expressed genes in central nervous system in HCV infected patients and laser capture microscopy points to brain microglia as cells harboring HCV. Hepatology 40:433A
Chaudhuri A, Behan PO (2004) Fatigue in neurological disorders. Lancet 363:978–988
Cordoba J, Flavia M, Jacas C, Sauleda S, Esteban JI, Vargas V, Esteban R, Guardia J (2003) Quality of life and cognitive function in hepatitis C at different stages of liver disease. J Hepatol 39:231–238
Cozzi A, Zignego AL, Carpendo R, Biagiotti T, Aldinucci A, Monti M, Giannini C, Rosselli M, Laffi G, Moroni F (2006) Low serum tryptophan levels, reduced macrophage IDO activity and high frequency of psychopathology in HCV patients. J Viral Hepatitis 13:402–408
Fishman SL, Murray JM, Eng FJ, Walewski JL, Morgello S, Branch AD (2008) Molecular and bioinformatic evidence of hepatitis C virus evolution in brain. J Infectious Diseases 197:597–607
Fontana RJ, Bieliauskas LA, Back-Madruga C, Lindsay KL, Kronfol Z, Lok AS, Padmanabhan L, the HALT C trial group (2005) Cognitive function in hepatitis C patients with advanced fibrosis enrolled in the HALT-C trial. J Hepatol 43: 614–623
Fontana RJ, Bieliauskas LA, Lindsay KL, Back-Madruga C, Wright EC, Snow KK, Lok ASF, Kronfol Z, Padmanabhan L, the HALT-C Trial Group (2007) Cognitive function does not worsen during pegylated interferon and ribavirin retreatment of chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 45:1154–1163
Forton DM (2006). Altered monoaminergic transporter binding in hepatitis C related cerebral dysfunction: a neuroimmunological condition? GUT 55 (11): 1535–1537
Forton DM, Allsop JM, Main J, Foster GR, Thomas HC, Taylor-Robinson SD (2001) Evidence for a cerebral effect of the hepatitis C virus. Lancet 358:38-39
Forton DM, Thomas HC, Murphy CA, Allsop JM, Foster GR, Main J, Wesnes KA, Taylor-Robinson SD (2002) Hepatitis C and cognitive impairment in a cohort of patients with mild liver disease. Hepatology 35:433–439
Forton DM, Karayianni P, Mahmud N, Taylor-Robinson SD, Thomas HC (2004) Identification of unique hepatitis C virus quasispecies in the central nervous system and comparative analysis of internal translational efficiency of brain, liver, and serum variants. J Virology 78(10):5170–5183
Forton DM, Taylor-Robinson S, Thoma HC (2006) Central nervous system changes in hepatitis C virus infection. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 18:333–338
Foster GR, Goldin RD, Thomas HC (1998) Chronic hepatitis C virus infection causes a significant reduction in quality of life in the absence of cirrhosis. Hepatology 27:209–212
Hassoun Z, Willems B, Deslauriers J, Nguyen BN, Huet PM (2002) Assessment of fatigue in patients with chronic hepatitis C using the fatigue impact scale. Dig Dis Sci 47(12):2674–2681
Hüppe D, Zehnter E, Mauss S, Böker K, Lutz T, Racky S, Schmidt W, Ullrich J, Sbrijer I, Heyne R, Schober A, John C, Hey KH, Bokemeyer B, Kallinowski B, Miller B, Pape S, Gutmann M, Alshuth U, Niederau C (2008) Epidemiolgie der chronischen Hepatitis C in Deutschland—Eine Analyse von 10326 Hepatitis C-Virus-Infizierten aus Schwerpunktpraxen und—ambulanzen. Z Gastrenterol 46:34–44
Jones EA (1999) Relief from profound fatigue associated with chronic liver disease by long-term ondansetron therapy. Lancet 354:397
Jüngling FD, Ebert D, Gut O, Engelbrecht MA, Rasenack J, Nitzsche EU, Bauer J, Lieb K. (2000) Prefrontal cortical hypometabolism during low-dose interferon alpha treatment. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 152(4): 383–389
Kallman J, O’Neil MM, Larive B, Boparai N, Calabrese L, Younossi ZM (2007) Fatigue and health-related quality of life (HRQL) in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Dig Dis Sci 52:2531–2539
Karaivazoglou K, Assimakopoulos K, Thomopoulos K, Theocharis G, Messinis L, Sakellaropoulos G, Labropoulou-Karatza C (2007) Neuropsychological function in Greek patients with chronic hepatitis C. Liver International 27(6):798–805
Kenny-Walsh E (1999) Clinical outcomes after hepatitis C infection from contaminated anti-D immune globulin. Irish Hepatology Research Group. N Engl J Med 340(16):1228–1233
Laskus T, Radkowski M, Adair DM, Wilkinson J, Scheck AC, Rakela J (2005) Emerging evidence of hepatitis C virus neuroinvasion. AIDS 19(suppl 3):S140–S144
Laskus T, Radkowski M, Bednarska A, Wikinson J, Adair D, Nowicki M, Nikolopoulou GB, Vargas H, Rakela J (2002) Detection and analysis of hepatitis C virus sequences in cerebrospinal fluid. J Virol. 76:10064–10068
McAndrews MP, Farcnik K, Carlen P, Damyanovich A, Mrkonjic M, Jones S, Heathcote EJ (2005) Prevalence and significance of neurocognitive dysfunction in hepatitis C in the absence of correlated risk factors. Hepatology 2005; 41(4): 801–808
Niederau C, Bemba G, Kautz A (2006) Sozioökonomische Charakteristika, Lebensqualität und Wissensstand bei Patienten mit Hepatitis C-Virusinfektion in Deutschland. Z Gastroenterol 44:305–317
Niederau C, Fischer C, Kautz A (2007) Sozioökonomische Charakteristika, Lebensqualität und Wissensstand bei Patienten mit Hepatitis B-Virusinfektion in Deutschland. Sozioökonomische Aspekte der Hepatitis B. Z Gastroenterol 45:355–368
Niederau C, Bemba G, Kautz A (2008) Entwicklung von sozioökonomischen Charakteristika, Lebensqualität und Wissensstand bei patienten mit Hepatitis C während des Projektes Kompetenznetz Hepatitis. Z Gastroenterologie 46:22–33
Piche T, Vanbiervliet G, Cherikh F, Antoun Z, Huet PM, Gelsi E, Damarquay J-F, Caroli-Bosc F-X, Benzaken S, Rigault M-C, Renou C, Rampal P, Tran A (2005) Effect of ondansetron, a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, on fatigue in chronic hepatitis C: a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled study. Gut 54:1169–1173
Poynard T, Cacoub P, Ratziu V, Myers RP, Dezailles MH, Mercadier A, Ghillani P, Charlotte F, Piette JC, Moussalli J (2002) Fatigue in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Journal of Viral Hepatitis 2002; 9: 295–303
Provencher SW (1995) Automated estimation of metabolite concentrations from localized proton MRS. New prospects in psychiatry. The bio-clinical interface:405–413.
Radkowski M, Wilkinson J, Nowicki M, Adair D, Vargas H, Ingui C, Rakela J, Laskus T (2002) Search for hepatitis c virus negative-strand RNA sequences and analysis of viral sequences in the central nervous system: evidence of replication. J Virol 76(2):600–608
Rodger AJ, Jolley D, Thompson SC, Lanigan A, Crofts N (1999) The impact of diagnosis of hepatitis C virus on quality of life. Hepatology 30:1299–1301
Seeff LB (2002) Natural history of chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 36:S35–S46
Soogoor M, Lynn HS, Donfield SM, Gomperts E, Bell TS, Daar ES, for the Hemophilia Growth and Development Study (2006) Hepatitis C virus infection and neurocognitive function. Neurology 67:1482–1485
Weissenborn K, Ennen JC, Schomerus H, Ruckert N, Hecker H (2001) Neuropsychological characterization of hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol 34(5):768–773
Weissenborn K, Krause J, Bokemeyer M, Hecker H, Schüler A, Ennen JC, Ahl B, Manns MP, Böker KW (2004) Hepatitis C virus infection affects the brain—evidence from psychometric studies and magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Hepatol 41(5):845–851
Weissenborn K, Ennen JC, Bokemeyer M, Ahl B, Wurster U, Tillmann H, Trebst C, Hecker H, Berding G (2006) Monoaminergic neurotransmission is altered in hepatitis C virus infected patients with chronic fatigue and cognitive impairment. GUT 55(11):1624–1630
Wiese M, Berr F, Lafrenz M, Porst H, Oesen U (2000) Low frequency of cirrhosis in a hepatitis C (genotype 1b) single-source outbreak in germany: a 20-year multicenter study. Hepatology 32:91–96
Wiese M, Grüngreiff K, Güthoff W, Lafrenz M, Oesen U, Porst H, for the East German Hepatitis C Study Group (2005) Outcome in a hepatitis C (genotype 1b). Single source outbreak in Germany—a 25 year multicenter study. J Hepatology 43(4):590–598
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weissenborn, K., Tryc, A.B., Heeren, M. et al. Hepatitis C virus infection and the brain. Metab Brain Dis 24, 197–210 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-008-9130-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-008-9130-5