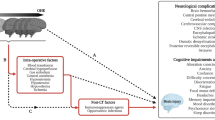
Abstract
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) refers to the reversible neuropsychiatric disorders observed in acute liver failure and as a complication of cirrhosis and/or portal hypertension. This review aims to describe the pathophysiology of HE, the rationale for the use of artificial liver support in the treatment of HE, the different concepts of artificial liver support and the results obtained. Ammonia has been considered central to its pathogenesis but recently an important role for its interaction with inflammatory responses and auto-regulation of cerebral hemodynamics has been suggested. Artificial liver support might be able to decrease ammonia and modulate inflammatory mediators and cerebral hemodynamics. Bioartificial liver support systems use hepatocytes in an extracorporeal device connected to the patient’s circulation. Artificial liver support is intended to remove protein-bound toxins and water-soluble toxins without providing synthetic function. Both systems improve clinical and biochemical parameters and can be applied safely to patients. Clinical studies have shown that artificial liver support, especially albumin dialysis, is able to improve HE in acute and acute-on-chronic liver failure. Further studies are required to better understand the mechanism, however, artificial liver support can be added to the therapeutic bundle in treating HE.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal S et al (2005) Cerebral hemodynamic and metabolic profiles in fulminant hepatic failure: relationship to outcome. Liver Transpl 11:1353–1360
Ash SR et al (2000) Push-pull sorbent-based pheresis and hemodiabsorption in the treatment of hepatic failure: preliminary results of a clinical trial with the BioLogic-DTPF System. Ther Apher 4:218–228
Bernal W et al (2007) Arterial ammonia and clinical risk factors for encephalopathy and intracranial hypertension in acute liver failure. Hepatology 46:1844–1852
Bhatia V et al (2006) Predictive value of arterial ammonia for complications and outcome in acute liver failure. Gut 55:98–104
Bustamante J et al (1999) Prognostic significance of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol 30:890–895
Cauli O, Rodrigo R, Piedrafita B, Boix JB, Felipo V (2007) inflammation and hepatic encephalopathy: ibuprofen restores learning ability in rats with chronic liver failure. Hepatology 46(2):514–519
Clemmesen JO et al (1999) Cerebral herniation in patients with acute liver failure is correlated with arterial ammonia concentration. Hepatology 29:648–53
Cordoba J et al (1996) Determinants of ammonia clearance by hemodialysis. Artif Organs 20:800–803
Davies NA et al (2005) Serum albumin shows conformational, structural and functional abnormalities in cirrhotic patients, which worsens with severity of liver disease and are unaffescted by albumin dialysis. Hepatology 42:A66
Desjardins P et al (1999) Effect of portacaval anastomosis on glutamine synthetase protein and gene expression in brain, liver and skeletal muscle. Metab Brain Dis 14:273–280
Eiseman B (1966) Treatment of hepatic coma by extracorporeal liver perfusion. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 38:329–348
Ellis AJ et al (1999) Temporary extracorporeal liver support for severe acute alcoholic hepatitis using the biologic-DT. Int J Artif Organs 22:27–34
Falkenhagen D et al (1999) Fractionated plasma separation and adsorption system: a novel system for blood purification to remove albumin bound substances. Artif Organs 23:81–86
Ferenci P et al (2002) Hepatic encephalopathy—definition, nomenclature, diagnosis, and quantification: final report of the working party at the 11th World Congresses of Gastroenterology, Vienna, 1998. Hepatology 35:716–721
Gabduzda GJ, Hall PW 3rd (1966) Relation of potassium depletion to renal ammonium metabolism and hepatic coma. Medicine (Baltimore) 45:481–490
Hassanein TI et al (2007) Randomized controlled study of extracorporeal albumin dialysis for hepatic encephalopathy in advanced cirrhosis. Hepatology 46:1853–1862
Haussinger D et al (2000) Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: a clinical manifestation of astrocyte swelling and low-grade cerebral edema? J Hepatol 32:1035–1038
Heemann U et al (2002) Albumin dialysis in cirrhosis with superimposed acute liver injury: a prospective, controlled study. Hepatology 36:949–958
Hiroma T et al (2002) Continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration in neonatal onset hyperammonemia. Am J Perinatol 19:221–224
Hughes RD (2002) Review of methods to remove protein-bound substances in liver failure. Int J Artif Organs 25:911–917
Hughes RD et al (1994) Evaluation of the biologic-DT sorbent-suspension dialyser in patients with fulminant hepatic failure. Int J Artif Organs 17:657–662
Jalan R, Kapoor D (2004) Reversal of diuretic-induced hepatic encephalopathy with infusion of albumin but not colloid. Clin Sci (Lond) 106:467–474
Jalan R et al (1997) Elevation of intracranial pressure following transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent-shunt for variceal haemorrhage. J Hepatol 27:928–933
Jalan R et al (2002) Liver derived pro-inflammatory cytokines may be important in producing intracranial hypertension in acute liver failure. J Hepatol 37:536–538
Jalan R et al (2004) Pathogenesis of intracranial hypertension in acute liver failure: inflammation, ammonia and cerebral blood flow. J Hepatol 41:613–620
Jover R et al (2006) Brain edema and inflammatory activation in bile duct ligated rats with diet-induced hyperammonemia: A model of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis. Hepatology 43:1257–1266
Jurgens G et al (2002) Investigation into the interaction of recombinant human serum albumin with Re-lipopolysaccharide and lipid A. J Endotoxin Res 8:115–126
Kiley JE et al (1956) Removal of blood ammonia by hemodialysis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 91:489–490
Krisper P et al (2005) In vivo quantification of liver dialysis: comparison of albumin dialysis and fractionated plasma separation. J Hepatol 43:451–457
Laleman W et al (2006) Effect of the molecular adsorbent recirculating system and Prometheus devices on systemic haemodynamics and vasoactive agents in patients with acute-on-chronic alcoholic liver failure. Crit Care 10:R108
Lepore MJ, Martel AJ (1970) Plasmapheresis with plasma exchange in hepatic coma. Methods and results in five patients with acute fulminant hepatic necrosis. Ann Intern Med 72:165–174
Lockwood AH et al (1979) The dynamics of ammonia metabolism in man. Effects of liver disease and hyperammonemia. J Clin Invest 63:449–460
Master S et al (1999) Cerebral blood flow and the development of ammonia-induced brain edema in rats after portacaval anastomosis. Hepatology 30:876–880
Mitzner SR et al (2000) Improvement of hepatorenal syndrome with extracorporeal albumin dialysis MARS: results of a prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Liver Transpl 6:277–286
Mitzner SR et al (2001) Improvement of multiple organ functions in hepatorenal syndrome during albumin dialysis with the molecular adsorbent recirculating system. Ther Apher 5:417–422
Mitzner S et al (2002) Improvement in central nervous system functions during treatment of liver failure with albumin dialysis MARS—a review of clinical, biochemical, and electrophysiological data. Metab Brain Dis 17:463–475
Mookerjee R et al. (2007) Neutrophil dysfunction in alcoholic hepatitis superimposed on cirrhosis is reversible and predicts outcome. Hepatology.Aug 6 [epub ahead of print]
Muto Y et al (1988) Enhanced tumour necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in fulminant hepatic failure. Lancet 2:72–74
Oettl K et al. (2006). Redox state of serum albumin and carbonyl content of plasma proteins in advanced liver disease. Proceedings of the 13th Biennal Congress of the Society for Free Radical Research International:265–268
O’Grady JG (2005) Acute liver failure. Postgrad Med J 81:148–154
O’Grady JG et al (1989) Early indicators of prognosis in fulminant hepatic failure. Gastroenterology 97:439–445
Olde Damink SW et al (2003) The kidney plays a major role in the hyperammonemia seen after simulated or actual GI bleeding in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 37:1277–1285
Opolon P et al (1976) Hepatic failure coma (HFC) treated by polyacrylonitrile membrane (PAN) hemodialysis (HD). Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs 22:701–710
Ortega R et al (2002) Terlipressin therapy with and without albumin for patients with hepatorenal syndrome: results of a prospective, nonrandomized study. Hepatology 36:941–948
Pedersen HR et al (2007) Hyperammonemia acts synergistically with lipopolysaccharide in inducing changes in cerebral hemodynamics in rats anaesthetised with pentobarbital. J Hepatol 47:245–252
Peszynski P et al (2002) Albumin dialysis: single pass vs. recirculation (MARS). Liver 22(Suppl 2):40–42
Prass K et al (2003) Stroke-induced immunodeficiency promotes spontaneous bacterial infections and is mediated by sympathetic activation reversal by poststroke T helper cell type 1-like immunostimulation. J Exp Med 198:725–736
Quinlan GJ et al (2005) Albumin: biochemical properties and therapeutic potential. Hepatology 41:1211–1219
Rifai K et al (2003) Prometheus—a new extracorporeal system for the treatment of liver failure. J Hepatol 39:984–990
Rifai K et al (2006) Removal selectivity of Prometheus: a new extracorporeal liver support device. World J Gastroenterol 12:940–944
Rolando N et al (1990) Prospective study of bacterial infection in acute liver failure: an analysis of fifty patients. Hepatology 11:49–53
Rolando N et al (2000) The systemic inflammatory response syndrome in acute liver failure. Hepatology 32:734–739
Romero-Gomez M et al (2004a) Intestinal glutaminase activity is increased in liver cirrhosis and correlates with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol 41:49–54
Romero-Gomez M et al (2004b) Prognostic value of altered oral glutamine challenge in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 39:939–943
Rose CL, Ytrebø LM, Davies NA, Sen S, Nedredal GI, Belanger M, Williams R, Revhaug A, Jalan R (2007) Reduction of extracellular ammonia and lactate is associated with attenuation of intracranial hypertension in acute liver failure pigs. Hepatology 46(6):1883–1892
Rozga J (2006) Liver support technology—an update. Xenotransplantation 13:380–389
Sabin S, Merritt JA (1968) Treatment of hepatic coma in cirrhosis by plasmapheresis and plasma infusion (plasma exchange). Ann Intern Med 68:1–7
Sauer IM et al (2004) In vitro comparison of the molecular adsorbent recirculation system (MARS) and single-pass albumin dialysis (SPAD). Hepatology 39:1408–1414
Schmidt LE et al (2001a) Cerebral blood flow velocity increases during a single treatment with the molecular adsorbents recirculating system in patients with acute on chronic liver failure. Liver Transpl 7:709–712
Schmidt LE et al (2001b) Hemodynamic changes during a single treatment with the molecular adsorbents recirculating system in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure. Liver Transpl 7:1034–1039
Schmidt LE et al (2003) Systemic hemodynamic effects of treatment with the molecular adsorbents recirculating system in patients with hyperacute liver failure: a prospective controlled trial. Liver Transpl 9:290–297
Sen S et al (2004a) Albumin dialysis: a new therapeutic strategy for intoxication from protein-bound drugs. Intensive Care Med 30:496–501
Sen S et al (2004b) Pathophysiological effects of albumin dialysis in acute-on-chronic liver failure: a randomized controlled study. Liver Transpl 10:1109–1119
Sen S et al (2006) Effect of albumin dialysis on intracranial pressure increase in pigs with acute liver failure: a randomized study. Crit Care Med 34:158–164
Shawcross DL et al (2004) Systemic inflammatory response exacerbates the neuropsychological effects of induced hyperammonemia in cirrhosis. J Hepatol 40:247–254
Shawcross DL et al (2007a) Role of ammonia and inflammation in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 22:125–138
Shawcross D et al (2007b) Ammonia and hyponatremia impairs neutrophil function by inducing swelling and is modulated by the p38_MAPK pathway. Gastroenterology 46:A841
Sorkine P et al (2001) Role of the molecular adsorbent recycling system (MARS) in the treatment of patients with acute exacerbation of chronic liver failure. Crit Care Med 29:1332–1336
Sort P et al (1999) Effect of intravenous albumin on renal impairment and mortality in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. N Engl J Med 341:403–409
Stadlbauer V et al (2006) Effect of extracorporeal liver support by MARS and Prometheus on serum cytokines in acute-on-chronic liver failure. Crit Care 10:R169
Stadlbauer V et al (2008) Artificial liver support systems in the management of complications of cirrhosis. Semin Liver Dis 28:96–109
Stange J, Mitzner S (1996) A carrier-mediated transport of toxins in a hybrid membrane. Safety barrier between a patients blood and a bioartificial liver. Int J Artif Organs 19:677–691
Stange J et al (1993) Dialysis against a recycled albumin solution enables the removal of albumin-bound toxins. Artif Organs 17:809–813
Stange J et al (1999) Molecular adsorbent recycling system (MARS): clinical results of a new membrane-based blood purification system for bioartificial liver support. Artif Organs 23:319–330
Stewart CA et al (2007) Hepatic encephalopathy as a predictor of survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Liver Transpl 13:1366–1371
Thalheimer U et al (2005) Infection, coagulation, and variceal bleeding in cirrhosis. Gut 54:556–563
Vaquero J et al (2003) Infection and the progression of hepatic encephalopathy in acute liver failure. Gastroenterology 125:755–764
Wright G, Jalan R (2007) Management of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 21:95–110
Wright G et al (2007) Endotoxemia produces coma and brain swelling in bile duct ligated rats. Hepatology 45(6):1517–1526
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stadlbauer, V., Wright, G.A.K. & Jalan, R. Role of artificial liver support in hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 24, 15–26 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-008-9117-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-008-9117-2