Abstract
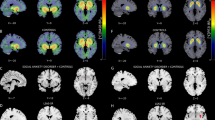
Background: Disgust and fear are basic emotions that have different elicitors and expressions, and that appear to be mediated by different neurocircuits. Although obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is classified as an anxiety disorder, disgust may be involved in its pathogenesis. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies of disgust-inducing visual stimuli in OCD have suggested disorder specific alterations in brain activation during these tasks. Methods: Subjects with OCD and healthy controls (HC) underwent positron emission tomography (PET) brain scanning after injection of H2 15O. During PET, subjects either watched slides designed to evoke feelings of disgust (OCD = 5, HC = 11), expected the delivery of an electrical shock (OCD = 11, HC = 13), or rested (OCD = 11, HC = 14). After the anticipatory anxiety and resting tasks, anxiety ratings, heart rate, and electrodermal measures were obtained. Statistical parametric mapping (SPM) was used to analyze regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) data. Results: Comparison of OCD subjects with controls on differences in rCBF across the disgust-inducing and resting tasks showed that OCD was characterized by greater rCBF in the left insula. In OCD the disgust-inducing task increased right lateral orbitofrontal cortex rCBF compared to resting, whereas in controls there was no difference in rCBF between these tasks. Anxiety ratings, heart rate, and electrodermal activity increased during anticipatory anxiety in both groups, and comparison of rCBF in OCD subjects with controls in anticipatory anxiety versus resting state also found no significant differences. Conclusions: OCD may be characterized by a disruption in disgust processing, such that there is a decrease in appropriate disgust (such as that evoked by observing disgust in others) and an increase in inappropriate disgust (such as that evoked by contamination stimuli). The insula may play a particularly important role in mediating such putative disruptions. The sample studied here was small, and further work is required to determine whether disgust-induced activation patterns in OCD are more apparent in specific subtypes of this disorder, whether they are specific to OCD, and whether they are normalized by treatment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolphs R, Tranel D, Damasio AR (2003) Dissociable neural systems for recognizing emotions. Brain and Cogn 52:61–69
Adolphs R, Tranel D, Damasio AR (2003) Dissociable neural systems for recognizing emotions. Brain and Cogn 52:61–69
Calder AJ, Keane J, Manes F, Antoun N, Young AW (2000) Impaired recognition and experience of disgust following brain injury. Nat Neurosci 3:1077–1078
Carson RE, Berg GW, Finn RD, Patlak CS, Daube-Witherspoon ME, Stein SD, Simpson NR, Green MV, Larson SM (1987) Tomographic comparison of LCBF with high-resolution PET and H2 15O: comparison of methods. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 7:S578
Chua P, Krams M, Toni I, Passingham R, Dolan R (1999) A Functional Anatomy of Anticipatory Anxiety. Neuroimage 9:563–571
Collet C, Vernet-Maury E, Delhomme G, Dittmar A (1997) Autonomic nervous system response patterns specificity to basic emotions. J Auton Nerv Syst 62:45–57
Darwin C (1965) The expression of emotion in man and animals. Chicago University Press, Chicago, IL, 1872
Davidson RJ, Ekman P, Saron CD, Senulis JA, Friesen WV (1990) Approach-withdrawal and cerebral asymmetry: emotional expression and brain physiology. I. J Pers Soc Psychol 58:330–341
Davis M (1997) Neurobiology of fear responses: The role of the amygdala. J Neuropsychiatry and Clin Neurosci 9:382–402
Davis M, Whalen PJ (2001) The amygdala: Vigilance and emotion. Mol Psychiatry 6:13–34
Friston KJ, Frith CD, Liddle PF, Frackowiak RSJ (1991) Comparing functional (PET) images: The assessment of significant change. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 11:690–699
Gorman JM, Kent JM, Sullivan GM, Coplan JD (2000) Neuroanatomical hypothesis of panic disorder, revised. Am J Psychiatry 157:493–505
Gorno-Tempini ML, Pradelli S, Serafini M, Pagnoni G, Baraldi P, Porro C, Nicoletti R, Umita C, Nichelli P (2001) Explicit and incidental facial expression processing: An fMRI study. Neuroimage 14:465–473
Kim J, Myung Chul L, Kim J, In Young K, Kim SI, Moon Hee H, Chang K, Jun Soo K (2001) Grey matter abnormalities in obsessive-compulsive disorder: Statistical parametric mapping of segmented magnetic resonance images. Br J Psychiatry 179:330–334
Kim JJ, Youn T, Lee JM, Kim IY, Kim SI, Kwon JS (2003) Morphometric abnormality of the insula in schizophrenia: a comparison with obsessive-compulsive disorder and normal control using MRI. Schizophrenia Res 60:191–198
Le Doux J (1998) Fear and the brain: Where have we been, and where are we going? Biol Psychiatry 44:1229–1238
Mancini F, Gragnani A, D’Olimpio F (2001) The connection between disgust and obsessions and compulsions in a non-clinical sample. Pers Individ Differences 31:1173–1180
Mancini F, Gragnani A, D’Olimpio F (2001) The connection between disgust and obsessions and compulsions in a non-clinical sample. Pers Individ Differences 31:1173–1180
Matochik JA, London ED, Eldreth DA, Cadet J-L, Bolla KI (2003) Frontal cortical tissue composition in abstinent cocaine abusers: a magnetic resonance imaging study. Neuroimage 19:1095–1102
McKay D (2002) Introduction to the special issue: the role of disgust in anxiety disorders. J Anxiety Disord 16:475–476
Muris P, Merckelbach H, Schmidt H, Tierney S (1999) Disgust sensitivity, trait anxiety and anxiety disorders symptoms in normal children. Behav Res Ther 37:953–961
Olatunji BO, Sawchuk CN, Lohr JM, de Jong PJ (2004) Disgust domains in the prediction of contamination fear. Behav Res Ther 42:93--104
Phan KL, Wager T, Taylor SF, Liberzon I (2002) Functional Neuroanatomy of Emotion: A Meta-Analysis of Emotion Activation Studies in PET and fMRI*1. Neuroimage 16:331–348
Phillips ML, Drevets WC, Rauch SL, Lane R (2003) Neurobiology of emotion perception I: The neural basis of normal emotion perception. Biol Psychiatry 54:504–514
Phillips ML, Marks IM, Senior C, Lythgoe D, O’Dwyer AM, Meehan O, Williams SC, Brammer MJ, Bullmore ET, McGuire PK (2000) A differential neural response in obsessive-compulsive disorder patients with washing compared with checking symptoms to disgust. Psychol Med 30:1037–1050
Phillips ML, Senior C, Fahy T, David AS (1998) Disgust—the forgotten emotion of psychiatry. The Br J Psychiatry: The Journal Mental Sci 172:373–375
Phillips ML, Young AW, Scott SK, Calder AJ, Andrew C, Giampietro V, Williams SC, Bullmore ET, Brammer M, Gray JA (1998) Neural responses to facial and vocal expressions of fear and disgust. Proc Royal Soc London: Series B. Biol Sci 265:1809–1817
Phillips ML, Young AW, Senior C, Brammer M, Andrew C, Calder AJ, Bullmore ET, Perrett DI, Rowland D, Williams SC, Gray JA, David AS (1997) A specific neural substrate for perceiving facial expressions of disgust. Nature 389:495–498
Power M, Dalgleish T (1997) Cognition and emotion: from order to disorder. Psychology Press, Hove, UK
Rachman S (1994) Pollution of the mind. Behav Res Ther 32:311–314
Rauch SL, Shin LM, Whalen PJ, Pitman RK (1998) Neuroimaging and the neuroanatomy of posttraumatic stress disorder. CNS Spectrums 3:31–41
Reiman EM (1997) The application of positron emission tomography to the study of normal and pathologic emotions. J Clin Psychiatry 58(Suppl 16):4–12
Rolls ET (1994) Central taste anatomy and physiology. In: Doty RL (ed) Handbook of clinical olfaction and gustation. Marcel Dekker, New York, NY
Rozin P, Fallon AE (1987) A perspective on disgust. Psychol Rev 94:23–41
Rozin P, Lowery L, Imada S, Haidt J (1999) The CAD triad hypothesis: a mapping between three moral emotions (contempt, anger, disgust) and three moral codes (community, autonomy, divinity). J Pers Soc Psychol 76:574–586
Shapira NA, Shapira NA, Liu Y, He AG, Bradley MM, Lessig MC, James GA, Stein DJ, Lang PJ,Goodman WK (2003) Brain activation by disgust-inducing pictures in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 54:751–756.
Simpson JR Jr, Drevets WC, Snyder AZ, Gusnard DA, Raichle ME (2001) Emotion-induced changes in human medial prefrontal cortex: II. During anticipatory anxiety. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98:688–693
Spitzer RL, First MB, Gibbon M, Williams JB (1987) Structured clinical interview for Axis I DSM-III-R disorders. New York State Psychiatric Institute, Biometrics Research Department
Sprengelmeyer R, Rausch M, Eysel UT, Przuntek H (1998) Neural structures associated with recognition of facial expressions of basic emotions. Proc Royal Soc London: Series B. Biol Sci 265:1927–1931
Sprengelmeyer R, Rausch M, Eysel UT, Przuntek H (1998) Neural structures associated with recognition of facial expressions of basic emotions. Proc R Soc London. Series B: Biol Sci 265:1927–1931
Sprengelmeyer R, Young AW, Calder AJ, Karnat A, Lange H, Homberg V, Perrett DI, Rowland D (1996) Loss of disgust: Perception of faces and emotions in Huntington's disease. Brain 119:1647–1665
Sprengelmeyer R, Young AW, Pundt I, Sprengelmeyer A, Calder AJ, Berrios G, Winkel R, Vollmoeller W, Kuhn W, Sartory G, Przuntek H (1997) Disgust implicated in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 264:1767–1773
Stark R, Schienle A, Walter B, Kirsch P, Sammer G, Ott U, Blecker C, Vaitl D (2003) Hemodynamic responses to fear and disgust-inducing pictures: an fMRI study. Int J Psychophysiol 50:225–234
Stein DJ, Liu Y, Shapira NA, Goodman WK (2001) The psychobiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder: how important is the role of disgust? Curr Psychiatry Rep 3:281–287
Surguladze SA, Brammer MJ, Young AW, Andrew C, Travis MJ, Williams SCR, Phillips ML (2003) A preferential increase in the extrastriate response to signals of danger. Neuroimage 19:1317–1328
Thorpe SJ, Patel SP, Simonds LM (2003) The relationship between disgust sensitivity, anxiety and obsessions. Behav Res Ther 41:1397–1409
Thorpe SJ, Patel SP, Simonds LM (2003) The relationship between disgust sensitivity, anxiety and obsessions. Behav Res Ther 41:1397–1409
Tsao SD, McKay D (2004) Behavioral avoidance tests and disgust in contamination fears: distinctions from trait anxiety. Behav Res Ther 42:207–216
Wicker B, Keysers C, Plailly J, Royet JP, Gallese V, Rizzolatti G (2003) Both of Us Disgusted in My Insula: The Common Neural Basis of Seeing and Feeling Disgust. Neuron 40:655–664
Wright CI, Martis B, McMullin K, Shin LM, Rauch SL (2003) Amygdala and insular responses to emotionally valenced human faces in small animal specific phobia. Biol Psychiatry 54:1067–1076
Yartz AR, Hawk J (2002) Addressing the specificity of affective startle modulation: fear versus disgust*1. Biol Psychol 59:55–68
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the help of Jordan Grafman and Paul Rozin (study design), Margaret Pekar, Catherine Stayer, and John Matochik (data analysis), and Kathleen McKenna and Albert J. Allen (data acquisition).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stein, D.J., Arya, M., Pietrini, P. et al. Neurocircuitry of disgust and anxiety in obsessive-compulsive disorder: A positron emission tomography study. Metab Brain Dis 21, 255–265 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-006-9021-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-006-9021-6