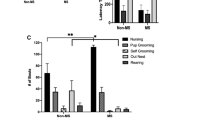
Maternal separation in non-human primates has been proposed as a model of early adversity. The symptoms of separation anxiety were studied in vervet monkeys, during the weaning period, when psychotropic medications were administered. The control group received a normal diet and treatment groups received citalopram, reboxetine or lamotrigine in their food daily. Treatment was given for 7 weeks starting 1 month prior to weaning. Behavior was recorded twice weekly for 8 weeks, and was rated for anxiety and depression. Cerebrospinal fluid was collected at the beginning and end of the trial and analyzed for monoamines and metabolites using High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Citalopram pretreatment prevented the reduction of affiliation behavior and reduced stereotypies after weaning, and both citalopram and reboxetine abolished the increase in activity seen in control monkeys after weaning, but no statistically significant differences were found between groups. Citalopram pretreatment also significantly increased noradrenaline and 5-hydroxyindolacetic acid (5-HIAA) levels and reboxetine significantly decreased dopamine levels over time. The 5-HIAA levels of reboxetine and lamotrigine treated monkeys were significantly lower than that of the control group at the end of the trial. Although limited by a small sample size, this study demonstrates the possibility of investigating the psychopharmacology of early adversity in a non-human primate model.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson GM, Bennett AJ, Weld KP, Pushkas JG, Ocarne DM, Higley JD (2002) Serotonin in cerebrospinal fluid of rhesus monkeys: basal levels and effects of sertraline administration. Psychopharmacology 161:95–99
Carpenter LL, Anderson GM, Siniscalchi JM, Chappell PB, Price LH (2003) Acute changes in cerebrospinal fluid 5-HIAA following oral paroxetine challenge in healthy humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:339–347
Charney DS, Drystal JJ, Southwick SM, Nagy LM, Woods SW, Heninger GR (1990) Serotonin function in panic and generalized anxiety disorders. Psychiatr Ann 20:593–604
David DJP, Bourin M, Jego G, Przybylski C, Jolliet P, Gardier AM (2003) Effects of acute treatment with paroxetine, citalopram and venlafaxine in vivo on noradrenaline and serotonin outflow: a microdialysis study in Swiss mice. Br J Pharmacol 140:1128–1136
Gorman JM, Mathew S, Coplan J (2002) Neurobiology of early life stress: nonhuman primate models. Semin Clin Neuropsychiatry 7:96–103
Harvey BH, Brand L, Jeeva Z, Stein DJ (2006) Cortical/hippocampal monoamines, HPA-axis changes and aversive behavior following stress and re-stress in an animal model of post traumatic stress disorder. Physiology and Behavior (in press)
Hinde RA, Spencer-Booth Y (1971) Effects of brief separation from mother on rhesus monkeys. Science 173:111–118
Hughes ZA, Stanford SC (1998) Evidence from microdialysis and synaptosomal studies of rat cortex for noradrenaline uptake sites with different sensitivities to SSRIs. Br J Pharmacol 124:1141–1148
Hugo C, Seier J, Mdhluli C, Daniels W, Harvey B, Du Toit D, Wolfe-Coote S, Nel D, Stein D (2003) Fluoxetine decreases stereotypic behaviour in primates. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 27:639–643
Hugo CJ, Seier J, Mdhluli C, van Niekerk C, Daniels W, du Toit DF, Wolfe-Coote S, Stein DJ (2001) Use of fluoxetine for separation anxiety in primates. Paper presented at the Psychopharmacology Congress, Stellenbosch, South Africa
Insel TR (1990) Serotonin in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatr Ann 20:558–559
Kalin NH, Shelton SE, Barksdale CM (1988) Opiate modulation of separation-induced distress in non-human primates. Brain Res 440:285–292
Kraemer GW, Ebert MH, Schmidt DE, McKinney WT (1991) Strangers in a strange land: a psychobiological study of infant monkeys before and after separation from real or inanimate mothers. Child Dev 62:548–566
Kraemer GW, Ebert MH, Schmidt DE, McKinney WT (1989) A longitudinal study of the effect of different social rearing conditions on cerebrospinal fluid norepinephrine and biogenic amine metabolites in rhesus monkeys. Neuropsychopharmacology 2:175–189
Koch S, Perry KW, Nelson DL, Conway RG, Threlkeld PG, Bymaster FP (2002) R-fluoxetine increases extracellular DA, NE, as well as 5-HT in rat prefrontal cortex and hypothalamus: an in vivo microdialysis and receptor binding study. Neuropsychopharmacol 27:949–959
Laudenslager ML, Held PE, Boccia ML, Cohen JJ (1990) Behavioural and immunology consequences of brief maternal separation: a species comparison. Dev Psychobiol 23:247–264
Leger L, Descarries L (1978) Serotonin nerve terminals in the locus coeruleus of adult rat: a radioautographic study. Brain Res 145:1–13
Luckett WP, Szalay FS (1975) Phylogeny of the Primates. Plenum Press, New York and London
Maj J, Dziedzicka-Wasylewska M, Rogoz R, Rogoz Z (1998) Effect of antidepressant drugs administered repeatedly on the dopamine D3 receptors in the rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 351:31–37
Maj J, Dziedzicka-Wasylewska M, Rogoz R, Rogoz Z, Skuza G (1996) Antidepressant drugs given repeatedly change the binding of dopamine D2 receptor agonist, [3H]N-0437, to dopamine D2 receptors in the rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 304:49–54
Meltzer HY, Lowy MT (1987) The serotonin hypotheses of depression. In: Meltzer HY (ed) Psychopharmacology: The Third Generation of Progress. Raven Press, New York, pp. 513–526
Meyer JS, Novak MA, Bowman RE, Harlow HF (1975) Behavioral and hormonal effects of attachment object separation in surrogate-peer-reared and mother-reared infant rhesus monkeys. Dev Psychobiol 8:425–435
Millan MJ, Dekeyne A, Gobert A (1998) Serotonin (5-HT)2C receptors tonically inhibit dopamine (DA) and noradrenaline (NA), but not 5-HT, release in the frontal cortex in vivo. Neuropharmacol 37:953–955
Morgane JP, Jacobs MS (1979) Raphe projections to the locus coeruleus in the rat. Brain Res Bull 4:519–534
Owens MJ, Knight DL, Nemeroff CB (2001) Second-generation SSRIs: human monoamine transporter binding profile of Escitalopram and R-flouxetine. Biol Psychiatr 50:345–350
Pickel VM, Joh TH, Reis DJ (1977) A serotonergic innervation of noradrenergic neurons in nucleus locus coeruleus: demonstration by immunocytochemical localization of the transmitter specific enzymes tyrosine and tryptophan hydroxylase. Brain Res 131:197–214
Rogoz Z, Margas W, Skuza G, Solich J, Kusmider M, Dziedzicka-Wasylewska M (2002) Effect of repeated treatment with reboxetine on the central α1-adrenergic and dopaminergic receptors. Pol J Pharmacol 54:593–603
Rosenblum LA, Andrews MW (1994) Influences of environmental demand on maternal behavior and infant development. Acta Paediatr Suppl 397:57–63
Sanchez MM, Ladd CO, Plotsky PM (2001) Early adverse experience as a developmental risk factor for later psychopathology: evidence from rodent and primate models. Dev Psychopathol 13:419–449
Smith TD, Kuczenski R, George-Friedman K, Malley JD, Foote SL (2000) In vivo microdialysis assessment of extracellular serotonin and dopamine levels in awake monkeys during sustained fluoxetine administration. Synapse 38:460–470
Sulser F (1984) Antidepressant treatments and regulation of norepenephrine-receptor-coupled adenylate cyclase systems in brain. In: Usdin E (ed) Frontiers in Biochemical and Pharmacological Research in Depression. Raven Press, New York, pp. 249–261
Sulser F (1989) New perspectives on the molecular pharmacology of affective disorder. Eur Arch Psychiatry Neurol Sci 238:231–239
Zohar J, Insel TR (1987) Obsessive-compulsive disorder: psychobiological approaches to diagnosis, treatment, and pathophysiology. Biol Psychiatry 22:667–87
Acknowledgements
We thank Jürgen Seier, Ali Dhansay, Charon de Villiers and the staff of the Primate Facility for their help with the procedures for this experiment. Reboxetine was supplied by Pharmacia (South Africa) and citalopram by Lundbeck (Denmark). This project was funded by the Medical Research Council of South Africa.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marais, L., Daniels, W., Brand, L. et al. Psychopharmacology of maternal separation anxiety in vervet monkeys. Metab Brain Dis 21, 191–200 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-006-9011-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-006-9011-8