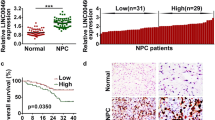
Abstract
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is one of the most common head and neck malignancies. It has obvious ethnic and regional specificity. Long non-coding RNAs (LncRNAs) are a class of non-protein coding RNA molecules. Emerging research shows that lncRNAs play a key role in tumor development, prognosis, and treatment. With the deepening of sequence analysis, a large number of functional LncRNAs have been found in NPC, which interact with coding genes, miRNAs, and proteins to form a complex regulatory network. However, the specific role and mechanism of abnormally expressed lncRNAs in the pathogenesis of NPC is not fully understood. This article briefly introduced the concept, classification, and functional mechanism of lncRNAs and reviewed their biological functions and their clinical applications in NPC. Specifically, we described lncRNAs related to the occurrence, growth, invasion, metastasis, angiogenesis, and cancer stem cells of NPC; discussed lncRNAs related to Epstein-Barr virus infection; and summarized the role of lncRNAs in NPC treatment resistance. We have also sorted out lncRNAs related to Chinese medicine treatment. We believe that with the deepening of lncRNAs research, tumor-specific lncRNAs may become a new target for the treatment and a biomarker for predicting prognosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included in the article.
References
Chua M, Wee J, Hui E, Chan A (2016) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet (London, England) 387:1012–1024. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(15)00055-0
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I et al (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clin 68:394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Wang K, Chang H (2011) Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell 43:904–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2011.08.018
Ransohoff J, Wei Y, Khavari P (2018) The functions and unique features of long intergenic non-coding RNA. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19:143–157. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2017.104
Yao R, Wang Y, Chen L (2019) Cellular functions of long noncoding RNAs. Nat Cell Biol 21:542–551. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-019-0311-8
Zhang K, Tan X, Guo L (2020) The long non-coding RNA DANCR regulates the inflammatory phenotype of breast cancer cells and promotes breast cancer progression via EZH2-dependent suppression of SOCS3 transcription. Mol Oncol 14:309–328. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12622
Yuan S, Wang J, Yang F et al (2016) Long noncoding RNA DANCR increases stemness features of hepatocellular carcinoma by derepression of CTNNB1. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 63:499–511. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.27893
Jiang N, Wang X, Xie X et al (2017) lncRNA DANCR promotes tumor progression and cancer stemness features in osteosarcoma by upregulating AXL via miR-33a-5p inhibition. Cancer Lett 405:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.06.009
Wang Y, Zeng X, Wang N et al (2018) Long noncoding RNA DANCR, working as a competitive endogenous RNA, promotes ROCK1-mediated proliferation and metastasis via decoying of miR-335-5p and miR-1972 in osteosarcoma. Mol Cancer 17:89. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0837-6
Zhang X, Zhou Y, Mehta K et al (2003) A pituitary-derived MEG3 isoform functions as a growth suppressor in tumor cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:5119–5126. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2003-030222
Benetatos L, Vartholomatos G, Hatzimichael E (2011) MEG3 imprinted gene contribution in tumorigenesis. Int J Cancer 129:773–779. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.26052
Han T, Zhuo M, Yuan C et al (2020) Coordinated silencing of the Sp1-mediated long noncoding RNA MEG3 by EZH2 and HDAC3 as a prognostic factor in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Biol Med 17:953–969. https://doi.org/10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2019.0427
Ji Y, Feng G, Hou Y et al (2020) Long noncoding RNA MEG3 decreases the growth of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the expression of miR-421 and E-cadherin. Cancer Med 9:3954–3963. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.3002
Zhang Y, Wu J, Jing H et al (2019) Long noncoding RNA MEG3 inhibits breast cancer growth via upregulating endoplasmic reticulum stress and activating NF-κB and p53. J Cell Biochem 120:6789–6797. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27982
Chak W, Lung R, Tong J et al (2017) Downregulation of long non-coding RNA MEG3 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Carcinog 56:1041–1054. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.22569
Farrell P (2019) Epstein-Barr virus and cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 14:29–53. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-012418-013023
You R, Liu Y, Lin M et al (2019) Relationship of circulating tumor cells and Epstein-Barr virus DNA to progression-free survival and overall survival in metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Int J Cancer 145:2873–2883. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.32380
Chan A, Lo Y, Zee B et al (2002) Plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA and residual disease after radiotherapy for undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 94:1614–1619. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/94.21.1614
Kanda T, Yajima M, Ikuta K (2019) Epstein-Barr virus strain variation and cancer. Cancer Sci 110:1132–1139. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13954
Lu T, Guo Q, Lin K et al (2020) Circulating Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs BART7-3p and BART13-3p as novel biomarkers in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Sci 111:1711–1723. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.14381
Xu M, Yao Y, Chen H et al (2019) Genome sequencing analysis identifies Epstein-Barr virus subtypes associated with high risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Nat Genet 51:1131–1136. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-019-0436-5
Li Z, Tsai M, Shumilov A et al (2019) Epstein-Barr virus ncRNA from a nasopharyngeal carcinoma induces an inflammatory response that promotes virus production. Nat Microbiol 4:2475–2486. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-019-0546-y
Guo R, Tang L, Mao Y et al (2019) Proposed modifications and incorporation of plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA improve the TNM staging system for Epstein-Barr virus-related nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer 125:79–89. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.31741
Zhang J, Zhang S, Zuo L et al (2019) Differential expression profiling of lncRNAs related to Epstein-Barr virus infection in the epithelial cells. J Med Virol 91:1845–1855. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25516
Wang H, Liu W, Luo B (2021) The roles of miRNAs and lncRNAs in Epstein-Barr virus associated epithelial cell tumors. Virus Res 291:198217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198217
Marquitz A, Mathur A, Edwards R, Raab-Traub N (2015) Host gene expression is regulated by two types of noncoding RNAs transcribed from the Epstein-Barr virus BamHI A rightward transcript region. J Virol 89:11256–11268. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.01492-15
Park R, Miller G (2018) Epstein-Barr virus-induced nodules on viral replication compartments contain RNA processing proteins and a viral long noncoding RNA. J Virol. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.01254-18
Verhoeven R, Tong S, Mok B et al (2019) Epstein-Barr virus BART long non-coding RNAs Function as epigenetic modulators in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Front Oncol 9:1120. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.01120
Verhoeven R, Tong S, Zhang G et al (2016) NF-κB signaling regulates expression of Epstein-Barr virus BART MicroRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Virol 90:6475–6488. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.00613-16
Song K, Yang S, Hwang J, Kim J, Kang M (2015) The full-length DNA sequence of Epstein Barr virus from a human gastric carcinoma cell line, SNU-719. Virus Genes 51:329–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-015-1248-z
Tan C, Peng C, Huang Y et al (2002) Effects of NPC-associated gene NAG7 on cell cycle and apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Ai zheng Chinese J Cancer 21:449–55
Huang C, Wu M, Tang Y et al (2009) NAG7 promotes human nasopharyngeal carcinoma invasion through inhibition of estrogen receptor alpha and up-regulation of JNK2/AP-1/MMP1 pathways. J Cell Physiol 221:394–401. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.21867
Samanta M, Takada K (2010) Modulation of innate immunity system by Epstein-Barr virus-encoded non-coding RNA and oncogenesis. Cancer Sci 101:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01377.x
Zhang W, Huang C, Gong Z et al (2013) Expression of LINC00312, a long intergenic non-coding RNA, is negatively correlated with tumor size but positively correlated with lymph node metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Mol Histol 44:545–554. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-013-9503-x
He B, Li W, Wu Y et al (2016) Epstein-Barr virus-encoded miR-BART6-3p inhibits cancer cell metastasis and invasion by targeting long non-coding RNA LOC553103. Cell Death Dis 7:e2353. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2016.253
Wu Y, Tang M, Wu Y et al (2014) A combination of paclitaxel and siRNA-mediated silencing of Stathmin inhibits growth and promotes apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Cell Oncol (Dordr) 37:53–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-013-0163-3
Wang D, Zeng Z, Zhang S et al (2020) Epstein-Barr virus-encoded miR-BART6-3p inhibits cancer cell proliferation through the LOC553103-STMN1 axis. FASEB J 34:8012–8027. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202000039RR
Chuang W, Chang S, Yu W et al (2020) Successful identification of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in nasopharyngeal biopsies using deep learning. Cancers (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020507
Wu P, Zhao Y, Xiang L, Yang L (2020) Management of chemotherapy for stage II nasopharyngeal carcinoma in the intensity-modulated radiotherapy era: a review. Cancer Manag Res 12:957–963. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.S239729
Lee N, Harris J, Garden A et al (2009) Intensity-modulated radiation therapy with or without chemotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: radiation therapy oncology group phase II trial 0225. J Clin Oncol 27:3684–3690. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2008.19.9109
Lee A, Chow J, Lee N (2020) Treatment deescalation strategies for nasopharyngeal cancer: a review. JAMA Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.6154
Liu S, Sun X, Lu Z et al (2020) Nomogram predicting the benefits of adding concurrent chemotherapy to intensity-modulated radiotherapy after induction chemotherapy in stages II-IVb nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Front Oncol 10:539321. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.539321
Zheng R, Yao Q, Ren C et al (2016) Upregulation of long noncoding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 18 promotes radioresistance of glioma by repressing semaphorin 5A. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 96:877–887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.07.036
Wang B, Zheng J, Li R et al (2019) Long noncoding RNA LINC02582 acts downstream of miR-200c to promote radioresistance through CHK1 in breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis 10:764. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1996-0
Xiao J, Lin L, Luo D et al (2020) Long noncoding RNA TRPM2-AS acts as a microRNA sponge of miR-612 to promote gastric cancer progression and radioresistance. Oncogenesis 9:29. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41389-020-0215-2
Huang D, Zhu X, Wang Y, Yu H, Pu Y (2020) Long non-coding RNA FAM133B-2 represses the radio-resistance of nasopharyngeal cancer cells by targeting miR-34a-5p/CDK6 axis. Aging 12:16936–16950. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103600
Peng J, Liu F, Zheng H, Wu Q, Liu S (2020) IncRNA ZFAS1 contributes to the radioresistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by sponging hsa-miR-7–5p to upregulate ENO2. Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex). https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2020.1864128
Han Y, Li F, Xie J, Wang Y, Zhang H (2020) PVT1 mediates cell proliferation, apoptosis and radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through regulating miR-515-5p/PIK3CA Axis. Cancer Manag Res 12:10077–10090. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.S257583
Han Y, Liu K, Xie J et al (2020) LINC00114 promoted nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression and radioresistance in vitro and in vivo through regulating ERK/JNK signaling pathway via targeting miR-203. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24:2491–2504. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202003_20517
Liu H, Zheng W, Chen Q et al (2021) lncRNA CASC19 contributes to radioresistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by promoting autophagy via AMPK-mTOR pathway. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031407
Guo Z, Wang Y, Xu H et al (2021) LncRNA linc00312 suppresses radiotherapy resistance by targeting DNA-PKcs and impairing DNA damage repair in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell Death Dis 12:69. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-03302-2
Zhang Y, Chen L, Hu G et al (2019) Gemcitabine and cisplatin induction chemotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. N Engl J Med 381:1124–1135. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1905287
Li W, Chen N, Zhang N et al (2019) Concurrent chemoradiotherapy with/without induction chemotherapy in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Long-term results of phase 3 randomized controlled trial. Int J Cancer 145:295–305. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.32099
Chen Y, Ismaila N, Chua M et al (2021) Chemotherapy in Combination With Radiotherapy for Definitive-Intent Treatment of Stage II-IVA Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: CSCO and ASCO Guideline. J Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.20.03237
Ren S, Li G, Liu C et al (2016) Next generation deep sequencing identified a novel lncRNA n375709 associated with paclitaxel resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncol Rep 36:1861–1867. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2016.4981
Li L, Gu M, You B et al (2016) Long non-coding RNA ROR promotes proliferation, migration and chemoresistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Sci 107:1215–1222. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.12989
Wang Q, Zhang W, Hao S (2017) LncRNA CCAT1 modulates the sensitivity of paclitaxel in nasopharynx cancers cells via miR-181a/CPEB2 axis. Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.) 16:795–801. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2017.1301334
Gao L, Cheng X, Cao H (2018) LncRNA THOR attenuates cisplatin sensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via enhancing cells stemness. Biochimie 152:63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2018.06.015
Lin F, Lin X, Xu L, Zhu S (2020) Long noncoding RNA HOXA11-AS modulates the resistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells to Cisplatin via miR-454-3p/c-Met. Mol Cells 43:856–869. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2020.0133
Zheng Z, Li Z, Guan J et al (2020) Long noncoding RNA TINCR-mediated regulation of Acetyl-CoA metabolism promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression and chemoresistance. Cancer Res 80:5174–5188. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-19-3626
Zhu H (2020) Silencing long non-coding RNA H19 combined with paclitaxel inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 138:110249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2020.110249
Liu F, Tai Y, Ma J (2018) LncRNA NEAT1/let-7a-5p axis regulates the cisplatin resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting Rsf-1 and modulating the Ras-MAPK pathway. Cancer Biol Ther 19:534–542. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2018.1450119
Li H, Huang J, Yu S, Lou Z (2020) Long Non-Coding RNA DLEU1 Up-Regulates BIRC6 Expression by Competitively Sponging miR-381-3p to Promote Cisplatin Resistance in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther 13:2037–2045. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.S237456
Yuan F, Lou Z, Zhou Z, Yan X (2021) Long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell cisplatin resistance via the miR-454/USP47 axis. Int J Mol Med 47:1. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2021.4887
Wang Y, Guo Z, Zhao Y et al (2017) Genetic polymorphisms of lncRNA-p53 regulatory network genes are associated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy toxicities and efficacy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Sci Rep 7:8320. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08890-2
Guo Z, Wang Y, Zhao Y et al (2017) Genetic polymorphisms of long non-coding RNA GAS5 predict platinum-based concurrent chemoradiotherapy response in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Oncotarget 8:62286–62297. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19725
Liu Y, Yang S, Wang K et al (2020) Cellular senescence and cancer: Focusing on traditional Chinese medicine and natural products. Cell Prolif 53:e12894. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12894
Liu Y, Hsiao C, Tzang B, Hsu T (2019) In vitro and in vivo effects of traditional Chinese medicine formula T33 in human breast cancer cells. BMC Complement Altern Med 19:211. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-019-2630-5
Bao H, Gao J, Huang T et al (2010) Relationship between traditional Chinese medicine syndrome differentiation and imaging characterization to the radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chin J Cancer 29:937–945. https://doi.org/10.5732/cjc.010.10209
Lou J, Yao P, Tsim K (2018) Cancer treatment by using traditional Chinese medicine: probing active compounds in anti-multidrug resistance during drug therapy. Curr Med Chem 25:5128–5141. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867324666170920161922
Cho W, Chen H (2009) Clinical efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine as a concomitant therapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Invest 27:334–344. https://doi.org/10.1080/07357900802392683
Wang Q, Fan H, Liu Y et al (2014) Curcumin enhances the radiosensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells involving the reversal of differentially expressed long non-coding RNAs. Int J Oncol 44:858–864. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2013.2237
Shao M, Lou D, Yang J et al (2020) Curcumin and wikstroflavone B, a new biflavonoid isolated from Wikstroemia indica, synergistically suppress the proliferation and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via blocking FAK/STAT3 signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 79:153341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153341
Heger M, van Golen R, Broekgaarden M, Michel M (2014) The molecular basis for the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of curcumin and its metabolites in relation to cancer. Pharmacol Rev 66:222–307. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.110.004044
Gao W, Chan J, Wong T (2014) Curcumin exerts inhibitory effects on undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma by inhibiting the expression of miR-125a-5p. Clinical science (London, England: 1979) 127:571–9. https://doi.org/10.1042/cs20140010
Yang J, Zhu D, Liu S et al (2020) Curcumin enhances radiosensitization of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by regulating circRNA network. Mol Carcinog 59:202–214. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.23143
Wu X, Wang Y, Cheng J, Zhao Y (2006) Calcium channel blocking activity of calycosin, a major active component of Astragali Radix, on rat aorta. Acta Pharmacol Sin 27:1007–1012. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7254.2006.00349.x
Li J, Harata-Lee Y, Denton M et al (2017) Astragalus membranaceusLong read reference genome-free reconstruction of a full-length transcriptome from reveals transcript variants involved in bioactive compound biosynthesis. Cell discovery 3:17031. https://doi.org/10.1038/celldisc.2017.31
Tian J, Wang Y, Zhang X et al (2017) Calycosin inhibits the in vitro and in vivo growth of breast cancer cells through WDR7-7-GPR30 Signaling. Journal of experimental & clinical cancer research : CR 36:153. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-017-0625-y
El-Kott A, Al-Kahtani M, Shati A (2019) Calycosin induces apoptosis in adenocarcinoma HT29 cells by inducing cytotoxic autophagy mediated by SIRT1/AMPK-induced inhibition of Akt/mTOR. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 46:944–954. https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1681.13133
Kong L, Li X, Wang H, He G, Tang A (2018) Calycosin inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by influencing EWSAT1 expression to regulate the TRAF6-related pathways. Biomed Pharmacother 106:342–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.143
Wang S, Lv Y, Xu X et al (2019) Triptonide inhibits human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell growth via disrupting Lnc-RNA THOR-IGF2BP1 signaling. Cancer Lett 443:13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.11.028
Hong F, Gu W, Jiang J, Liu X, Jiang H (2019) Anticancer activity of polyphyllin I in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by modulation of lncRNA ROR and P53 signalling. J Drug Target 27:806–811. https://doi.org/10.1080/1061186x.2018.1561887
Zhou R, Chen K, Zhang J et al (2018) The decade of exosomal long RNA species: an emerging cancer antagonist. Mol Cancer 17:75. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0823-z
Zuo Z, Hu H, Xu Q et al (2020) BBCancer: an expression atlas of blood-based biomarkers in the early diagnosis of cancers. Nucleic Acids Res 48:D789–D796. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz942
Nie Y, Liu X, Qu S et al (2013) Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is an independent prognostic marker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression and survival. Cancer Sci 104:458–464. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.12092
Yang L, Tang Y, He Y et al (2017) High expression of LINC01420 indicates an unfavorable prognosis and modulates cell migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Cancer 8:97–103. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.16819
He B, Zeng J, Chao W et al (2017) Serum long non-coding RNAs MALAT1, AFAP1-AS1 and AL359062 as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget 8:41166–41177. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17083
Yao L, Wang T, Wang X (2021) LncRNA FOXP4-AS1 serves as a biomarker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma diagnosis and prognosis. 3 Biotech 11:25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02593-8
Li Q, Jiang Y, Zhong G et al (2020) Long noncoding RNA DANCR regulates cell proliferation by stabilizing SOX2 mRNA in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Am J Pathol 190:2343–2354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.09.005
Zhang X, Yang J, Bian Z, Shi D, Cao Z (2019) Long noncoding RNA DANCR promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by interacting with STAT3, enhancing IL-6/JAK1/STAT3 signaling. Biomed Pharmacother 113:108713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108713
Hao Y, Zhao H, Jin X et al (2019) Long non-coding RNA DANCR promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation and migration. Mol Med Rep 19:2883–2889. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.9906
Wen X, Liu X, Mao Y et al (2018) Long non-coding RNA DANCR stabilizes HIF-1α and promotes metastasis by interacting with NF90/NF45 complex in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Theranostics 8:5676–5689. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.28538
Zhao C, Bai X, Hu X (2020) Knockdown of lncRNA XIST inhibits hypoxia-induced glycolysis, migration and invasion through regulating miR-381-3p/NEK5 axis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24:2505–2517. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202003_20518
Shi J, Tan S, Song L, Song L, Wang Y (2020) LncRNA XIST knockdown suppresses the malignancy of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma through XIST/miRNA-148a-3p/ADAM17 pathway in vitro and in vivo. Biomed Pharmacother 121:109620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109620
Cheng Q, Xu X, Jiang H, Xu L, Li Q (2018) Knockdown of long non-coding RNA XIST suppresses nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by activating miR-491-5p. J Cell Biochem 119:3936–3944. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26535
Song P, Ye L, Zhang C, Peng T, Zhou X (2016) Long non-coding RNA XIST exerts oncogenic functions in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting miR-34a-5p. Gene 592:8–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2016.07.055
Peng J, Liu F, Zheng H, Wu Q, Liu S (2020) Long noncoding RNA ZFAS1 promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by sponging miR-892b to up-regulate LPAR1 expression. J Cell Mol Med 24:1437–1450. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14823
Wang X, Jin Q, Wang X, Chen W, Cai Z (2019) LncRNA ZFAS1 promotes proliferation and migration and inhibits apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via the PI3K/AKT pathway in vitro. Cancer biomarkers : section A of Disease markers 26:171–182. https://doi.org/10.3233/cbm-182080
Wang M, Ji Y, Song Z et al (2019) Knockdown of lncRNA ZFAS1 inhibits progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by sponging miR-135a. Neoplasma 66:939–945. https://doi.org/10.4149/neo_2018_181213N963
Chen X, Li J, Li C, Lu X (2018) Long non-coding RNA ZFAS1 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma through activation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:3423–3429. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201806_15165
Li X, Lin Y, Yang X, Wu X, He X (2016) Long noncoding RNA H19 regulates EZH2 expression by interacting with miR-630 and promotes cell invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 473:913–919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.03.150
Zhang T, Lei F, Jiang T et al (2019) H19/miR-675-5p targeting SFN enhances the invasion and metastasis of nasalpharyngeal cancer cells. Curr Mol Pharmacol 12:324–333. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874467212666190719120446
Zhang Y, Zhu R, Wang J et al (2019) Upregulation of lncRNA H19 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma proliferation and metastasis in let-7 dependent manner. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47:3854–3861. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1669618
Hu W, Xu W, Shi Y, Dai W (2018) lncRNA HOTAIR upregulates COX-2 expression to promote invasion and migration of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by interacting with miR-101. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 505:1090–1096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.09.190
Ma D, Yuan L, Lin L (2017) LncRNA HOTAIR contributes to the tumorigenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via up-regulating FASN. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 21:5143–5152. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201711_13831
Fu W, Lu Y, Hu B et al (2016) Long noncoding RNA Hotair mediated angiogenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by direct and indirect signaling pathways. Oncotarget 7:4712–4723. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6731
Hu W, Li H, Wang S (2020) LncRNA SNHG7 promotes the proliferation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by miR-514a-5p/ELAVL1 axis. BMC Cancer 20:376. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-020-06775-8
Dai Y, Zhang X, Xing H et al (2020) Downregulated long non-coding RNA SNHG7 restricts proliferation and boosts apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by elevating microRNA-140–5p to suppress GLI3 expression. Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.) 19:448–463. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2020.1712033
Cheng N, Guo Y (2017) Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression through regulation of miR-124/NF-κB pathway. Onco Targets Ther 10:5843–5853. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.S151800
Ji Y, Wang M, Li X, Cui F (2019) The long noncoding RNA NEAT1 targets miR-34a-5p and drives nasopharyngeal Carcinoma progression via Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Yonsei Med J 60:336–345. https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2019.60.4.336
Shi B, Wang Y, Yin F (2017) MALAT1/miR-124/Capn4 axis regulates proliferation, invasion and EMT in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther 18:792–800. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2017.1373214
Zheng Y, Zhao J, Liang T et al (2019) Long noncoding RNA SMAD5-AS1 acts as a microRNA-106a-5p sponge to promote epithelial mesenchymal transition in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. FASEB J 33:12915–12928. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201900803R
Li S, Zhao B, Zhao H et al (2019) Silencing of long non-coding RNA SMAD5-AS1 reverses epithelial mesenchymal transition in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via microRNA-195-dependent inhibition of SMAD5. Front Oncol 9:1246. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.01246
Chen S, Lv L, Zhan Z et al (2020) Silencing of long noncoding RNA SRRM2-AS exerts suppressive effects on angiogenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via activating MYLK-mediated cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol 235:7757–7768. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29382
Zhang E, Li C, Xiang Y (2020) LncRNA FOXD3-AS1/miR-135a-5p function in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Open medicine (Warsaw, Poland) 15:1193–1201. https://doi.org/10.1515/med-2020-0177
Hu J, Pan J, Luo Z, Duan Q, Wang D (2020) Long non-coding RNA FOXD3-AS1 silencing exerts tumor suppressive effects in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by downregulating FOXD3 expression via microRNA-185-3p upregulation. Cancer Gene Ther. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00242-z
Fang M, Zhang M, Wang Y et al (2020) Long noncoding RNA AFAP1-AS1 Is a critical regulator of nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumorigenicity. Front Oncol 10:601055. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.601055
Lian Y, Xiong F, Yang L et al (2018) Long noncoding RNA AFAP1-AS1 acts as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-423-5p to facilitate nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis through regulating the Rho/Rac pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37:253. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0918-9
Zhong Q, Wang Z, Liao X, Wu R, Guo X (2020) LncRNA GAS5/miR-4465 axis regulates the malignant potential of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting COX2. Cell Cycle (Georgetown, Tex.) 19:3004–3017. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2020.1816280
Zhou L, Liu R, Liang X et al (2020) lncRNA RP11-624L4.1 Is Associated with Unfavorable Prognosis and Promotes Proliferation via the CDK4/6-Cyclin D1-Rb-E2F1 Pathway in NPC. Molecular therapy Nucleic acids 22:1025–1039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2020.10.017
Fan C, Wang J, Tang Y et al (2020) Upregulation of long non-coding RNA LOC284454 may serve as a new serum diagnostic biomarker for head and neck cancers. BMC Cancer 20:917. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-020-07408-w
He S, Xu C, Li Y et al (2020) AR-induced long non-coding RNA LINC01503 facilitates proliferation and metastasis via the SFPQ-FOSL1 axis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncogene 39:5616–5632. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-01388-8
Yao H, Yang L, Tian L, Guo Y, Li Y (2020) LncRNA MSC-AS1 aggravates nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by targeting miR-524-5p/nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 2 (NR4A2). Cancer Cell Int 20:138. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-01202-1
Tang T, Yang L, Cao Y et al (2020) LncRNA AATBC regulates Pinin to promote metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Oncol 14:2251–2270. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12703
Liao B, Wang Z, Zhu Y, Wang M, Liu Y (2019) Long noncoding RNA DRAIC acts as a microRNA-122 sponge to facilitate nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion via regulating SATB1. Artificial cells, nanomedicine, and biotechnology 47:3585–3597. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1656638
Hu X, Liu W, Jiang X et al (2019) Long noncoding RNA LINC00460 aggravates invasion and metastasis by targeting miR-30a-3p/Rap1A in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Hum Cell 32:465–476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-019-00262-4
Kong Y, Cui M, Chen S et al (2018) LncRNA-LINC00460 facilitates nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumorigenesis through sponging miR-149-5p to up-regulate IL6. Gene 639:77–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2017.10.006
Zheng Z, Li Z, Zhou G et al (2019) Long noncoding RNA FAM225A promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumorigenesis and metastasis by acting as ceRNA to sponge miR-590-3p/miR-1275 and upregulate ITGB3. Cancer Res 79:4612–4626. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-19-0799
Gao C, Lu W, Lou W, Wang L, Xu Q (2019) Long noncoding RNA HOXC13-AS positively affects cell proliferation and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via modulating miR-383-3p/HMGA2 axis. J Cell Physiol 234:12809–12820. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27915
Zhang E, Li X (2019) LncRNA SOX2-OT regulates proliferation and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through miR-146b-5p/HNRNPA2B1 pathway. J Cell Biochem 120:16575–16588. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28917
Lan X, Liu X (2019) LncRNA SNHG1 functions as a ceRNA to antagonize the effect of miR-145a-5p on the down-regulation of NUAK1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell. J Cell Mol Med 23:2351–2361. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13497
Zou Z, Ma C, Medoro L et al (2016) LncRNA ANRIL is up-regulated in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and promotes the cancer progression via increasing proliferation, reprograming cell glucose metabolism and inducing side-population stem-like cancer cells. Oncotarget 7:61741–61754. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.11437
Song P, Yin S (2016) Long non-coding RNA EWSAT1 promotes human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell growth in vitro by targeting miR-326/-330-5p. Aging 8:2948–2960. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101103
Chen X, Huang Y, Shi D et al (2020) ZNF667-AS1LncRNA promotes expression by adsorbing to suppress nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell progression. Onco Targets Ther 13:4397–4409. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.S245554
Zhang W, Guo Q, Liu G et al (2019) NKILA represses nasopharyngeal carcinoma carcinogenesis and metastasis by NF-κB pathway inhibition. PLoS Genet 15:e1008325. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1008325
Sun Q, Liu H, Li L et al (2015) Long noncoding RNA-LET, which is repressed by EZH2, inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell. Medical Oncol (Northwood, London, England) 32:226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-015-0673-0
Chen L, Sun L, Dong L et al (2017) The role of long noncoding RNA-LET in cell proliferation and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and its mechanism. Onco Targets Ther 10:2769–2778. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.S126907
Guo J, Ma J, Zhao G et al (2017) Long Noncoding RNA LINC0086 Functions as a Tumor Suppressor in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by Targeting miR-214. Oncol Res 25:1189–1197. https://doi.org/10.3727/096504017x14865126670075
Gong Z, Zhang S, Zeng Z et al (2014) LOC401317, a p53-regulated long non-coding RNA, inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in the nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line HNE2. PLoS One 9:e110674. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0110674
Funding
This work was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81172575).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YT: Data Curation, Visualization and Writing—Original Draft; XH: Writing—Review & Editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Y., He, X. Long non-coding RNAs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: biological functions and clinical applications. Mol Cell Biochem 476, 3537–3550 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-021-04176-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-021-04176-4