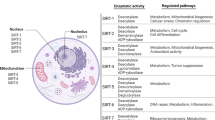
Abstract
Zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1) is an important transcription factor in epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) which participates in the numerous life processes, such as embryonic development, fibrosis and tumor progression. ZEB1 has multiple functions in human body and plays a crucial part in some life processes. ZEB1 is vital for the formation and development of the organs in the embryonic period. The abnormal expression of ZEB1 is a predictor for the poor prognosis or the poor survival in several cancers. ZEB1 contributes to the occurrence of fibrosis, cancer and even chemoresistance. Some research is indicated that fibrosis is finally developed into the cancers. Therefore, ZEB1 is probably taken as a biomarker in fibrosis or cancer. In this review, it is predicted of the structure of ZEB1 and the protein binding sites of ZEB1 with some protein, and it is discussed about the roles of ZEB1 in fibrosis and cancer progression to elaborate the potential applications of ZEB1 in clinic.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lehmann W, Mossmann D, Kleemann J et al (2016) ZEB1 turns into a transcriptional activator by interacting with YAP1 in aggressive cancer types. Nat Commun 7:10498
Sánchez-Tilló E, Siles L, de Barrios O et al (2011) Expanding roles of ZEB factors in tumorigenesis and tumor progression. Am J Cancer Res 1(7):897–912
Roche J, Nasarre P, Gemmill R et al (2016) Global decrease of histone H3K27 acetylation in ZEB1-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells. Cancers (Basel) 8(12):114
Peinado H, Olmeda D, Cano A (2007) Snail, Zeb and bHLH factors in tumour progression: an alliance against the epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer 7(6):415–428
Zhang P, Sun Y, Ma L (2015) ZEB1: at the crossroads of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, metastasis and therapy resistance. Cell Cycle 14(4):481–487
Zhang H, Li G, Sheng X et al (2019) Upregulation of miR-33b promotes endometriosis via inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and ZEB1 expression. Mol Med Rep 19(3):2144–2152
Chockley PJ, Chen J, Chen G et al (2018) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition leads to NK cell-mediated metastasis-specific immunosurveillance in lung cancer. J Clin Invest 128(4):1384–1396
Holohan C, Van Schaeybroeck S, Longley DB et al (2013) Cancer drug resistance: an evolving paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer 13(10):714–726
Takeyama Y, Sato M, Horio M et al (2010) Knockdown of ZEB1, a master epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) gene, suppresses anchorage-independent cell growth of lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett 296(2):216–224
Behnke J, Kremer S, Shahzad T et al (2020) MSC based therapies-new perspectives for the injured lung. J Clin Med 9(3):682
Chapman HA (2011) Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in pulmonary fibrosis. Annu Rev Physiol 73:413–435
Lee JG, Jung E, Heur M (2018) Fibroblast growth factor 2 induces proliferation and fibrosis via SNAI1-mediated activation of CDK2 and ZEB1 in corneal endothelium. J Biol Chem 293(10):3758–3769
Yuan X, Pan J, Wen L et al (2020) MiR-590-3p regulates proliferation, migration and collagen synthesis of cardiac fibroblast by targeting ZEB1. J Cell Mol Med 24(1):227–237
Yao L, Conforti F, Hill C et al (2019) Paracrine signalling during ZEB1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition augments local myofibroblast differentiation in lung fibrosis. Cell Death Differ 26(5):943–957
Xu X, Cao L, Zhang Y et al (2018) MicroRNA-1246 inhibits cell invasion and epithelial mesenchymal transition process by targeting CXCR4 in lung cancer cells. Cancer Biomark 21(2):251–260
Jose CC, Jagannathan L, Tanwar VS et al (2018) Nickel exposure induces persistent mesenchymal phenotype in human lung epithelial cells through epigenetic activation of ZEB1. Mol Carcinog 57(6):794–806
Qian W, Cai X, Qian Q et al (2019) lncRNA ZEB1-AS1 promotes pulmonary fibrosis through ZEB1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition by competitively binding miR-141-3p. Cell Death Dis 10(2):129
Park JS, Park HJ, Park YS et al (2014) Clinical significance of mTOR, ZEB1, ROCK1 expression in lung tissues of pulmonary fibrosis patients. BMC Pulm Med 14:168
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ et al (2008) The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 133(4):704–715
Chilosi M, Caliò A, Rossi A et al (2017) Epithelial to mesenchymal transition-related proteins ZEB1, β-catenin, and β-tubulin-III in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Mod Pathol 30(1):26–38
Li L, Zheng YL, Jiang C et al (2019) HN1L-mediated transcriptional axis AP-2γ/METTL13/TCF3-ZEB1 drives tumor growth and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Differ 26(11):2268–2283
Sinigaglia A, Lavezzo E, Trevisan M et al (2015) Changes in microRNA expression during disease progression in patients with chronic viral hepatitis. Liver Int 35(4):1324–1333
Li LY, Yang CC, Yang JF et al (2020) ZEB1 regulates the activation of hepatic stellate cells through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 869:172848
Song Y, Liu C, Liu X et al (2017) H19 promotes cholestatic liver fibrosis by preventing ZEB1-mediated inhibition of epithelial cell adhesion molecule. Hepatology 66(4):1183–1196
Zhang P, Sun Y, Ma L (2015) ZEB1: at the crossroads of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, metastasis and therapy resistance. Cell Cycle 14(4):481–487
Chen Y, Lu X, Montoya-Durango DE et al (2017) ZEB1 regulates multiple oncogenic components involved in uveal melanoma progression. Sci Rep 7(1):45
Chen XJ, Deng YR, Wang ZC et al (2019) Hypoxia-induced ZEB1 promotes cervical cancer progression via CCL8-dependent tumour-associated macrophage recruitment. Cell Death Dis 10(7):508
Zhang W, Shi X, Peng Y et al (2015) HIF-1α promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis through direct regulation of ZEB1 in colorectal cancer. PLoS One 10(6):e0129603
Rankin EB, Giaccia AJ (2016) Hypoxic control of metastasis. Science 352(6282):175–180
Chen XJ, Deng YR, Wang ZC et al (2019) Hypoxia-induced ZEB1 promotes cervical cancer progression via CCL8-dependent tumour-associated macrophage recruitment. Cell Death Dis 10(7):508
Cortés M, Sanchez-Moral L, de Barrios O et al (2017) Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) depend on ZEB1 for their cancer-promoting roles. EMBO J 36(22):3336–3355
Zhang X, Zhang Z, Zhang Q et al (2018) ZEB1 confers chemotherapeutic resistance to breast cancer by activating ATM. Cell Death Dis 9(2):57
Hou LK, Yu Y, Xie YG et al (2016) miR-340 and ZEB1 negative feedback loop regulates TGF-β- mediated breast cancer progression. Oncotarget 7(18):26016–26026
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY et al (2009) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 139(5):871–890
Larsen JE, Nathan V, Osborne JK et al (2016) ZEB1 drives epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer. J Clin Invest 126(9):3219–3235
Manshouri R, Coyaud E, Kundu ST et al (2019) ZEB1/NuRD complex suppresses TBC1D2b to stimulate E-cadherin internalization and promote metastasis in lung cancer. Nat Commun 10(1):5125
Zhang M, Miao F, Huang R et al (2018) RHBDD1 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis through the Wnt signaling pathway and its downstream target ZEB1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37(1):60
Ni X, Ding Y, Yuan H et al (2020) Long non-coding RNA ZEB1-AS1 promotes colon adenocarcinoma malignant progression via miR-455-3p/PAK2 axis. Cell Prolif 53(1):e12723
Su W, Xu M, Chen X et al (2017) Long noncoding RNA ZEB1-AS1 epigenetically regulates the expressions of ZEB1 and downstream molecules in prostate cancer. Mol Cancer 16(1):142
Zheng L, Xu M, Xu J et al (2018) ELF3 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by protecting ZEB1 from miR-141-3p-mediated silencing in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis 9(3):387
Jiang R, Zhang C, Liu G et al (2017) MicroRNA-126 inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT in osteosarcoma by targeting ZEB1. J Cell Biochem 118(11):3765–3774
Murata M, Ito T, Tanaka Y et al (2020) OVOL2-mediated ZEB1 downregulation may prevent promotion of actinic keratosis to cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Med 9(3):618
Liu C, Pan C, Cai Y et al (2017) Interplay between long noncoding RNA ZEB1-AS1 and miR-200s regulates osteosarcoma cell proliferation and migration. J Cell Biochem 118(8):2250–2260
Edwards LA, Li A, Berel D et al (2017) ZEB1 regulates glioma stemness through LIF repression. Sci Rep 7(1):69
Chen H, Zhu D, Zheng Z et al (2019) CEP55 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal cell carcinoma through PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Clin Transl Oncol 21(7):939–949
Liu Y, Lu C, Fan L et al (2020) MiR-199a-5p targets ZEB1 to inhibit the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of ovarian ectopic endometrial stromal cells via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signal pathway in vitro and in vivo. Reprod Sci 27(1):110–118
Furuya M, Masuda H, Hara K et al (2017) ZEB1 expression is a potential indicator of invasive endometriosis. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 96(9):1128–1135
Baumann M, Krause M, Hill R (2008) Exploring the role of cancer stem cells in radioresistance. Nat Rev Cancer 8(7):545–554
Yi Y, Xie H, Xiao X et al (2018) Ultraviolet A irradiation induces senescence in human dermal fibroblasts by down-regulating DNMT1 via ZEB1. Aging (Albany NY) 10(2):212–228
Zhang P, Wei Y, Wang L et al (2014) ATM-mediated stabilization of ZEB1 promotes DNA damage response and radioresistance through CHK1. Nat Cell Biol 16(9):864–875
Siebzehnrubl FA, Silver DJ, Tugertimur B et al (2013) The ZEB1 pathway links glioblastoma initiation, invasion and chemoresistance. EMBO Mol Med 5(8):1196–1212
Sreekumar R, Emaduddin M, Al-Saihati H et al (2019) Protein kinase C inhibitors override ZEB1-induced chemoresistance in HCC. Cell Death Dis 10(10):703
Hanrahan K, O'Neill A, Prencipe M et al (2017) The role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition drivers ZEB1 and ZEB2 in mediating docetaxel-resistant prostate cancer. Mol Oncol 11(3):251–265
Drápela S, Bouchal J, Jolly MK et al (2020) ZEB1: a critical regulator of cell plasticity, DNA damage response, and therapy resistance. Front Mol Biosci 7:36
Meidhof S, Brabletz S, Lehmann W et al (2015) ZEB1-associated drug resistance in cancer cells is reversed by the class I HDAC inhibitor mocetinostat. EMBO Mol Med 7(6):831–847
Borrelli GM, Abrão MS, Taube ET et al (2015) Immunohistochemical investigation of metastasis-related chemokines in deep-infiltrating endometriosis and compromised pelvic sentinel lymph nodes. Reprod Sci 22(12):1632–1642
Wang H, Xiao Z, Zheng J et al (2019) ZEB1 represses neural differentiation and cooperates with CTBP2 to dynamically regulate cell migration during neocortex development. Cell Rep 27(8):2335–2353
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY et al (2009) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 139(5):871–890
Kalluri R, Weinberg RA (2010) The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest 120(5):1786
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ et al (2008) The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 133(4):704–715
Liu Y, El-Naggar S, Darling DS et al (2008) Zeb1 links epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cellular senescence. Development 135(3):579–588
Wang Y, Bu F, Royer C et al (2014) ASPP2 controls epithelial plasticity and inhibits metastasis through β-catenin-dependent regulation of ZEB1. Nat Cell Biol 16(11):1092–1104
Funding
This study was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81973404, 81503058), Department of Education of Liaoning Province (No. JC2019034), Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (No. 2014021065).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Lin Cheng had the idea for the article, Lin Cheng, Ming-Yuan Zhou, Ying-Jian Gu, Lei Chen performed the literature search and data analysis, Lin Cheng drafted the work, and Yun Wang critically revised the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, L., Zhou, MY., Gu, YJ. et al. ZEB1: New advances in fibrosis and cancer. Mol Cell Biochem 476, 1643–1650 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-04036-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-04036-7