Abstract
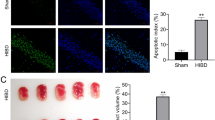
Hypoxic-ischemic (HI) brain damage (HIBD) leads to high neonatal mortality and severe neurologic morbidity. Autophagy is involved in the pathogenesis of HIBD. This study aims to investigate the effect of long non-coding RNA colorectal neoplasia differentially expressed (CRNDE) on HIBD and to validate whether autophagy is involved in this process. A HIBD model in rat pups and a HI model in rat primary cerebrocortical neurons were established. Autophagy was evaluated by western blot. The HIBD in rats was evaluated by hematoxylin and eosin staining, TUNEL staining, triphenyl tetrazolium chloride staining, and morris water maze test. The HI injury in vitro was evaluated by determining cell viability and apoptosis. The results showed that CRNDE expression was time-dependently increased in the brain after HIBD. Administration with CRNDE shRNA-expressing lentiviruses alleviated pathological injury and apoptosis in rat hippocampus, decreased infarct volume, and improved behavior performance of rats subjected to HIBD. Furthermore, CRNDE silencing promoted cell viability and inhibited cell apoptosis in neurons exposed to HI. Moreover, CRNDE silencing promoted autophagy and the autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine counteracted the neuroprotective effect of CRNDE silencing on HI-induced neuronal injury both in vivo and in vitro. Collectively, CRNDE silencing alleviates HIBD, at least partially, through promoting autophagy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yildiz EP, Ekici B, Tatli B (2017) Neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy: an update on disease pathogenesis and treatment. Expert Rev Neurother 17:449–459. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737175.2017.1259567
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM, Klionsky DJ (2008) Autophagy fights disease through cellular self-digestion. Nature 451:1069–1075. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06639
Carloni S, Buonocore G, Balduini W (2008) Protective role of autophagy in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia induced brain injury. Neurobiol Dis 32:329–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2008.07.022
Xu Y, Tian Y, Tian Y, Li X, Zhao P (2016) Autophagy activation involved in hypoxic-ischemic brain injury induces cognitive and memory impairment in neonatal rats. J Neurochem 139:795–805. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13851
Ye L, Feng Z, Doycheva D, Malaguit J, Dixon B, Xu N, Zhang JH, Tang J (2018) CpG-ODN exerts a neuroprotective effect via the TLR9/pAMPK signaling pathway by activation of autophagy in a neonatal HIE rat model. Exp Neurol 301:70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.12.008
Kwok ZH, Tay Y (2017) Long noncoding RNAs: lincs between human health and disease. Biochem Soc Trans 45:805
Fang H, Li HF, He MH, Yan JY, Yang M, Zhang FX, Wang RR, Wang QY, Zhang JP (2019) Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 sponges microRNA-429 to regulate apoptosis of hippocampal neurons in hypoxic-ischemic brain damage by regulating WNT1. Brain Res Bull 152:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.06.004
Zhou XM, Liu J, Wang Y, Zhang MH (2018) Silencing of long noncoding RNA MEG3 enhances cerebral protection of dexmedetomidine against hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal mice by binding to miR-129-5p. J Cell Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28075
Zhao RB, Zhu LH, Shu JP, Qiao LX, Xia ZK (2018) GAS5 silencing protects against hypoxia/ischemia-induced neonatal brain injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 497:285–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.070
Shen S, Liu H, Wang Y, Wang J, Ni X, Ai Z, Pan H, Liu H, Shao Y (2016) Long non-coding RNA CRNDE promotes gallbladder carcinoma carcinogenesis and as a scaffold of DMBT1 and C-IAP1 complexes to activating PI3K-AKT pathway. Oncotarget 7:72833–72844. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12023
Zheng J, Liu X, Wang P, Xue Y, Ma J, Qu C, Liu Y (2016) CRNDE promotes malignant progression of glioma by attenuating miR-384/PIWIL4/STAT3 Axis. Mol Ther 24:1199–1215. https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2016.71
Yi M, Dai X, Li Q, Xu X, Chen Y, Wang D (2019) Downregulated lncRNA CRNDE contributes to the enhancement of nerve repair after traumatic brain injury in rats. Cell Cycle 18:2332–2343. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2019.1647024
Zhao F, Qu Y, Zhu J, Zhang L, Huang L, Liu H, Li S, Mu D (2017) miR-30d-5p plays an important role in autophagy and apoptosis in developing rat brains after hypoxic-ischemic injury. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 76:709–719. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnen/nlx052
Ichimura Y, Komatsu M (2010) Selective degradation of p62 by autophagy. Semin Immunopathol 32:431–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-010-0220-1
Graham LD, Pedersen SK, Brown GS, Ho T, Kassir Z, Moynihan AT, Vizgoft EK, Dunne R, Pimlott L, Young GP, Lapointe LC, Molloy PL (2011) Colorectal neoplasia differentially expressed (CRNDE), a novel gene with elevated expression in colorectal adenomas and adenocarcinomas. Genes Cancer 2:829–840. https://doi.org/10.1177/1947601911431081
Ding J, Li J, Wang H, Tian Y, Xie M, He X, Ji H, Ma Z, Hui B, Wang K, Ji G (2017) Long noncoding RNA CRNDE promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation via epigenetically silencing DUSP5/CDKN1A expression. Cell Death Dis 8:e2997. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.328
Sun XH, Fan WJ, An ZJ, Sun Y (2019) Inhibition of long non-coding RNA CRNDE increases chemosensitivity of medulloblastoma cells by targeting MiR-29c-3p. Oncol Res. https://doi.org/10.3727/096504019x15742472027401
Bai X, Wang W, Zhao P, Wen J, Guo X, Shen T, Shen J, Yang X (2019) LncRNA CRNDE acts as an oncogene in cervical cancer through sponging miR-183 to regulate CCNB1 expression. Carcinogenesis. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgz166
Wang Y, Wang Y, Li J, Zhang Y, Yin H, Han B (2015) CRNDE, a long-noncoding RNA, promotes glioma cell growth and invasion through mTOR signaling. Cancer Lett 367:122–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2015.03.027
Pop S, Enciu A-M, Necula LG, Tanase C (2018) Long non-coding RNAs in brain tumours: focus on recent epigenetic findings in glioma. J Cell Mol Med 22:4597–4610. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13781
Ginet V, Spiehlmann A, Rummel C, Rudinskiy N, Grishchuk Y, Luthi-Carter R, Clarke PGH, Truttmann AC, Puyal J (2014) Involvement of autophagy in hypoxic-excitotoxic neuronal death. Autophagy 10:846–860. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.28264
Koike M, Shibata M, Tadakoshi M, Gotoh K, Komatsu M, Waguri S, Kawahara N, Kuida K, Nagata S, Kominami E, Tanaka K, Uchiyama Y (2008) Inhibition of autophagy prevents hippocampal pyramidal neuron death after hypoxic-ischemic injury. Am J Pathol 172:454–469. https://doi.org/10.2353/ajpath.2008.070876
Lu Q, Harris VA, Kumar S, Mansour HM, Black SM (2015) Autophagy in neonatal hypoxia ischemic brain is associated with oxidative stress. Redox Biol 6:516–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2015.06.016
Xu LX, Tang XJ, Yang YY, Li M, Jin MF, Miao P, Ding X, Wang Y, Li YH, Sun B, Feng X (2017) Neuroprotective effects of autophagy inhibition on hippocampal glutamate receptor subunits after hypoxia-ischemia-induced brain damage in newborn rats. Neural Regen Res 12:417–424. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.202945
Xie C, Ginet V, Sun Y, Koike M, Zhou K, Li T, Li H, Li Q, Wang X, Uchiyama Y, Truttmann AC, Kroemer G, Puyal J, Blomgren K, Zhu C (2016) Neuroprotection by selective neuronal deletion of Atg7 in neonatal brain injury. Autophagy 12:410–423. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2015.1132134
Carloni S, Albertini MC, Galluzzi L, Buonocore G, Proietti F, Balduini W (2014) Increased autophagy reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia: role of protein synthesis and autophagic pathways. Exp Neurol 255:103–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.03.002
Cui D, Sun D, Wang X, Yi L, Kulikowicz E, Reyes M, Zhu J, Yang ZJ, Jiang W, Koehler RC (2017) Impaired autophagosome clearance contributes to neuronal death in a piglet model of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Cell Death Dis 8:e2919. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.318
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, CH., Lai, FF., Chen, S. et al. Silencing of long non-coding RNA CRNDE promotes autophagy and alleviates neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in rats. Mol Cell Biochem 472, 1–8 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03754-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03754-2