Abstract
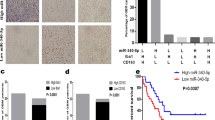
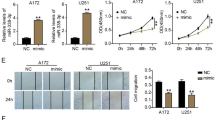
This study was aimed to explore the molecular mechanism of macrophage polarization and its effect on glioma progression. THP1 cells were cocultured in conditioned medium from U87 human glioblastoma cells to simulate the glioma microenvironment. The expression of miR-32 and PTEN in THP1 cells was detected by real-time PCR. A luciferase reporter assay was conducted to confirm the target relation between miR-32 and PTEN. Western blot assays and ELISA were performed to detect PTEN, M2 macrophage-specific markers, PI3K/AKT signaling proteins, and apoptosis-related proteins. U87 cell proliferation was evaluated by CCK-8 and colony forming assays, and the migration ability of the cells was evaluated by Transwell and wound healing assays. The U87 culture supernatant promoted the M2 phenotype of THP1 cells. miR-32 was upregulated and PTEN was downregulated in THP1 cells with the M2 phenotype in the glioma microenvironment. Luciferase assays confirmed that PTEN expression was suppressed by miR-32 through interaction with the 3′UTR of PTEN. Overexpression of miR-32 suppressed PTEN expression in THP1 cells. Overexpression of miR-32 or downregulation of PTEN promoted the expression of M2 macrophage-specific markers, thereby enhancing M2 macrophage polarization. Additionally, miR-32 inhibited THP1 cell apoptosis via suppressing the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Most importantly, the proliferation and migration capacities of U87 cells treated with the THP1 culture supernatant after miR-32 overexpression were enhanced, and these effects could be reversed by cotransfection with pcDNA3.1-PTEN. miR-32 negatively modulates PTEN, thereby promoting M2 macrophage transformation through PI3K/AKT signaling, enhancing glioma proliferation and migration abilities.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Xu J, Kromer C, Wolinsky Y, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan JS (2016) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2009-2013. Neuro Oncol 18:v1–v75. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/now207
Lapointe S, Perry A, Butowski NA (2018) Primary brain tumours in adults. Lancet 392:432–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30990-5
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK (2016) WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system, revised 4th edn. World Health Organization, Geneva
Guo M, Zhang X, Wang G, Sun J, Jiang Z, Khadarian K, Yu S, Zhao Y, Xie C, Zhang K, Zhu M, Shen H, Lin Z, Jiang C, Shen J, Zheng Y (2015) miR-603 promotes glioma cell growth via Wnt/beta-catenin pathway by inhibiting WIF1 and CTNNBIP1. Cancer Lett 360:76–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2015.02.003
Ren F, Fan M, Mei J, Wu Y, Liu C, Pu Q, You Z, Liu L (2014) Interferon-gamma and celecoxib inhibit lung-tumor growth through modulating M2/M1 macrophage ratio in the tumor microenvironment. Drug Des Devel Ther 8:1527–1538. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S66302
Lewis CE, Pollard JW (2006) Distinct role of macrophages in different tumor microenvironments. Cancer Res 66:605–612. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4005
Bi J, Zeng X, Zhao L, Wei Q, Yu L, Wang X, Yu Z, Cao Y, Shan F, Wei M (2016) miR-181a induces macrophage polarized to M2 phenotype and promotes M2 macrophage-mediated tumor cell metastasis by targeting KLF6 and C/EBPalpha. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 5:e368. https://doi.org/10.1038/mtna.2016.71
Wang Z, Brandt S, Medeiros A, Wang S, Wu H, Dent A, Serezani CH (2015) MicroRNA 21 is a homeostatic regulator of macrophage polarization and prevents prostaglandin E2-mediated M2 generation. PLoS ONE 10:e0115855. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0115855
Song H, Zhang Y, Liu N, Wan C, Zhang D, Zhao S, Kong Y, Yuan L (2016) miR-92b regulates glioma cells proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis via PTEN/Akt signaling pathway. J Physiol Biochem 72:201–211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-016-0470-z
Zhou K, Zhang T, Fan Y, Serick, Du G, Wu P, Geng D (2016) MicroRNA-106b promotes pituitary tumor cell proliferation and invasion through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by targeting PTEN. Tumour Biol 37:13469–13477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5155-2
Li KK, Xia T, Ma FM, Zhang R, Mao Y, Wang Y, Zhou L, Lau KM, Ng HK (2015) miR-106b is overexpressed in medulloblastomas and interacts directly with PTEN. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 41:145–164. https://doi.org/10.1111/nan.12169
Elhag R, Mazzio EA, Soliman KF (2015) The effect of silibinin in enhancing toxicity of temozolomide and etoposide in p53 and PTEN-mutated resistant glioma cell lines. Anticancer Res 35:1263–1269
Zhou W, Shi G, Zhang Q, Wu Q, Li B, Zhang Z (2014) MicroRNA-20b promotes cell growth of breast cancer cells partly via targeting phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN). Cell Biosci 4:62. https://doi.org/10.1186/2045-3701-4-62
Feng Y, Liu J, Kang Y, He Y, Liang B, Yang P, Yu Z (2014) miR-19a acts as an oncogenic microRNA and is up-regulated in bladder cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 33:67. https://doi.org/10.1186/PREACCEPT-9242556491295527
Cai G, Qiao S, Chen K (2015) Suppression of miR-221 inhibits glioma cells proliferation and invasion via targeting SEMA3B. Biol Res 48:37. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40659-015-0030-y
Su Y, He Q, Deng L, Wang J, Liu Q, Wang D, Huang Q, Li G (2014) MiR-200a impairs glioma cell growth, migration, and invasion by targeting SIM2-s. NeuroReport 25:12–17. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNR.0000000000000032
Mo YY (2012) MicroRNA regulatory networks and human disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 69:3529–3531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1123-1
Yin F, Zhang JN, Wang SW, Zhou CH, Zhao MM, Fan WH, Fan M, Liu S (2015) MiR-125a-3p regulates glioma apoptosis and invasion by regulating Nrg1. PLoS ONE 10:e0116759. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0116759
Yan C, Yu J, Liu Y, Kang W, Ma Z, Zhou L (2015) MiR-32 promotes gastric carcinoma tumorigenesis by targeting Kruppel-like factor 4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 467:913–920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.10.044
Wu W, Yang J, Feng X, Wang H, Ye S, Yang P, Tan W, Wei G, Zhou Y (2013) MicroRNA-32 (miR-32) regulates phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) expression and promotes growth, migration, and invasion in colorectal carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer 12:30. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-12-30
Jalava SE, Urbanucci A, Latonen L, Waltering KK, Sahu B, Janne OA, Seppala J, Lahdesmaki H, Tammela TL, Visakorpi T (2012) Androgen-regulated miR-32 targets BTG2 and is overexpressed in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Oncogene 31:4460–4471. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.624
Ma ZG, Yuan YP, Wu HM, Zhang X, Tang QZ (2018) Cardiac fibrosis: new insights into the pathogenesis. Int J Biol Sci 14:1645–1657. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.28103
Hambardzumyan D, Gutmann DH, Kettenmann H (2016) The role of microglia and macrophages in glioma maintenance and progression. Nat Neurosci 19:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4185
Lu-Emerson C, Snuderl M, Kirkpatrick ND, Goveia J, Davidson C, Huang Y, Riedemann L, Taylor J, Ivy P, Duda DG, Ancukiewicz M, Plotkin SR, Chi AS, Gerstner ER, Eichler AF, Dietrich J, Stemmer-Rachamimov AO, Batchelor TT, Jain RK (2013) Increase in tumor-associated macrophages after antiangiogenic therapy is associated with poor survival among patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol 15:1079–1087. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/not082
Prosniak M, Harshyne LA, Andrews DW, Kenyon LC, Bedelbaeva K, Apanasovich TV, Heber-Katz E, Curtis MT, Cotzia P, Hooper DC (2013) Glioma grade is associated with the accumulation and activity of cells bearing M2 monocyte markers. Clin Cancer Res 19:3776–3786. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1940
Ostuni R, Kratochvill F, Murray PJ, Natoli G (2015) Macrophages and cancer: from mechanisms to therapeutic implications. Trends Immunol 36:229–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2015.02.004
Shi Y, Ping YF, Zhou W, He ZC, Chen C, Bian BS, Zhang L, Chen L, Lan X, Zhang XC, Zhou K, Liu Q, Long H, Fu TW, Zhang XN, Cao MF, Huang Z, Fang X, Wang X, Feng H, Yao XH, Yu SC, Cui YH, Zhang X, Rich JN, Bao S, Bian XW (2017) Tumour-associated macrophages secrete pleiotrophin to promote PTPRZ1 signalling in glioblastoma stem cells for tumour growth. Nat Commun 8:15080. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15080
Zhu C, Kros JM, van der Weiden M, Zheng P, Cheng C, Mustafa DA (2017) Expression site of P2RY12 in residential microglial cells in astrocytomas correlates with M1 and M2 marker expression and tumor grade. Acta Neuropathol Commun 5:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-016-0405-5
Zhou W, Ke SQ, Huang Z, Flavahan W, Fang X, Paul J, Wu L, Sloan AE, McLendon RE, Li X, Rich JN, Bao S (2015) Periostin secreted by glioblastoma stem cells recruits M2 tumour-associated macrophages and promotes malignant growth. Nat Cell Biol 17:170–182. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3090
Pyonteck SM, Akkari L, Schuhmacher AJ, Bowman RL, Sevenich L, Quail DF, Olson OC, Quick ML, Huse JT, Teijeiro V, Setty M, Leslie CS, Oei Y, Pedraza A, Zhang J, Brennan CW, Sutton JC, Holland EC, Daniel D, Joyce JA (2013) CSF-1R inhibition alters macrophage polarization and blocks glioma progression. Nat Med 19:1264–1272. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3337
Li N, Qin JF, Han X, Jin FJ, Zhang JH, Lan L, Wang Y (2018) miR-21a negatively modulates tumor suppressor genes PTEN and miR-200c and further promotes the transformation of M2 macrophages. Immunol Cell Biol 96:68–80. https://doi.org/10.1111/imcb.1016
Li N, Qin J, Lan L, Zhang H, Liu F, Wu Z, Ni H, Wang Y (2015) PTEN inhibits macrophage polarization from M1 to M2 through CCL2 and VEGF-A reduction and NHERF-1 synergism. Cancer Biol Ther 16:297–306. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2014.1002353
Cheng Y, Tian Y, Xia J, Wu X, Yang Y, Li X, Huang C, Meng X, Ma T, Li J (2017) The role of PTEN in regulation of hepatic macrophages activation and function in progression and reversal of liver fibrosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 317:51–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2017.01.005
Wang G, Shi Y, Jiang X, Leak RK, Hu X, Wu Y, Pu H, Li WW, Tang B, Wang Y, Gao Y, Zheng P, Bennett MV, Chen J (2015) HDAC inhibition prevents white matter injury by modulating microglia/macrophage polarization through the GSK3beta/PTEN/Akt axis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:2853–2858. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1501441112
Zhou BH, Tan PP, Jia LS, Zhao WP, Wang JC, Wang HW (2018) PI3K/AKT signaling pathway involvement in fluoride-induced apoptosis in C2C12cells. Chemosphere 199:297–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.02.057
Ying J, Xu Q, Liu B, Zhang G, Chen L, Pan H (2015) The expression of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in gastric cancer and its role in gastric cancer prognosis. Onco Targets Ther 8:2427–2433. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S88592
Zhu Z, Sun H, Ma G, Wang Z, Li E, Liu Y, Liu Y (2012) Bufalin induces lung cancer cell apoptosis via the inhibition of PI3K/Akt pathway. Int J Mol Sci 13:2025–2035. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13022025
Li D, Qu X, Hou K, Zhang Y, Dong Q, Teng Y, Zhang J, Liu Y (2009) PI3K/Akt is involved in bufalin-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs 20:59–64. https://doi.org/10.1097/CAD.0b013e3283160fd6
Zhang LL, Zhang LF, Shi YB (2018) Down-regulated paxillin suppresses cell proliferation and invasion by inhibiting M2 macrophage polarization in colon cancer. Biol Chem 399:1285–1295. https://doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2018-0002
Jiang Q, Pan D, Yang Y, Hu Y, Fang L, Shang P, Xia Y, Li D (2018) Luteolin regulates macrophage polarization via the PI3K/Akt pathway to inhibit the apoptosis stimulated by angiotensin II. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 19:428–437. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389201019666180629143251
Tian Y, Piras BA, Kron IL, French BA, Yang Z (2015) Adenosine 2B receptor activation reduces myocardial reperfusion injury by promoting anti-inflammatory macrophages differentiation via PI3K/Akt pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2015:585297. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/585297
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, L., Li, X. MicroRNA-32 targeting PTEN enhances M2 macrophage polarization in the glioma microenvironment and further promotes the progression of glioma. Mol Cell Biochem 460, 67–79 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-019-03571-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-019-03571-2