Abstract
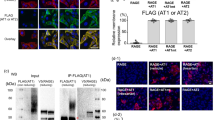
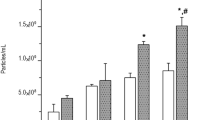
Biological effects of angiotensin II (AngII) such as regulation of AngII target genes may be triggered by interaction of AngII with intracellular AngII receptor types 1 and 2 (AT1 and AT2), defined as intracrine response. The aim of this study was to examine the presence of AT1 and AT2 receptors in nuclear membrane of human mesangial cells (HMCs) and evaluate the possible biological effects mediated by intracellular AT1 through an intracrine mechanism. Subcellular distribution of AT1 and AT2 was evaluated by immunofluorescence and by western blot in isolated nuclear extract. Endogenous intracellular synthesis of AngII was stimulated by high glucose (HG). Effects of HG were analyzed in the presence of candesartan, which prevents AngII internalization. Both receptors were found in nuclear membrane. Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled AngII added to isolated nuclei produced a fluorescence that was reduced in the presence of losartan or PD-123319 and quenched in the presence of both inhibitors simultaneously. HG induced overexpression of fibronectin and increased cell proliferation in the presence of candesartan, indicating an intracrine action of AngII induced by HG. Results showed the presence of nuclear receptors in HMCs that can be activated by AngII through an intracrine response independent of cytoplasmic membrane AngII receptors.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang J, Hara Y, Anrather J, Speth RC, Iadecola C, Pickel VM (2003) Angiotensin II subtype 1A (AT1A) receptors in the rat sensory vagal complex: subcellular localization and association with endogenous angiotensin. Neuroscience 122:21–36
Ellis B, Li XC, Miguel-Qin E, Gu V, Zhuo JL (2012) Evidence for a functional intracellular angiotensin system in the proximal tubule of the kidney. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 302:R494–R509. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00487.2011
Zhuo JL, Li XC (2011) New insights and perspectives on intrarenal renin-angiotensin system: focus on intracrine/intracellular angiotensin II. Peptides 32:1551–1565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2011.05.012
Weiland F, Verspohl EJ (2009) Local formation of angiotensin peptides with paracrine activity by adipocytes. J Pept Sci 15:767–776. https://doi.org/10.1002/psc.1174
De Mello WC (2015) Chemical communication between heart cells is disrupted by intracellular renin and angiotensin II: implications for heart development and disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 6:72. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2015.00072
Coble JP, Grobe JL, Johnson AK, Sigmund CD (2015) Mechanisms of brain renin angiotensin system-induced drinking and blood pressure: importance of the subfornical organ. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 308:R238–R249. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00486.2014
Wilson BA, Marshall AC, Alzayadneh EM, Chappell MC (2014) The ins and outs of angiotensin processing within the kidney. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 307:R487–R489. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00177.2014
Kumar R, Boim MA (2009) Diversity of pathways for intracellular angiotensin II synthesis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 18:33–39. https://doi.org/10.1097/MNH.0b013e32831a9e20
Vidotti DB, Casarini DE, Cristovam PC, Leite CA, Schor N, Boim MA (2004) High glucose concentration stimulates intracellular renin activity and angiotensin II generation in rat mesangial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 286:F1039–F1045. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00371.2003
Re R (2007) Intracellular renin-angiotensin system: the tip of the intracrine physiology iceberg. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:H905–H906. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00552.2007
Durvasula RV, Shankland SJ (2008) Activation of a local renin angiotensin system in podocytes by glucose. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 294:F830–F839. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00266.2007
Favre GA, Esnault VL, Van Obberghen E (2015) Modulation of glucose metabolism by the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 308:E435–E449. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00391.2014
Cook JL, Re RN (2012) Lessons from in vitro studies and a related intracellular angiotensin II transgenic mouse model. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 302:R482–R493. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00493.2011
Kumar R, Singh VP, Baker KM (2007) The intracellular renin-angiotensin system: a new paradigm. Trends Endocrinol Metab 18:208–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2007.05.001
Gonzalez AA, Prieto MC (2015) Roles of collecting duct renin and (pro)renin receptor in hypertension: mini review. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis 9:191–200. https://doi.org/10.1177/1753944715574817
Singh R, Singh AK, Alavi N, Leehey DJ (2003) Mechanism of increased angiotensin II levels in glomerular mesangial cells cultured in high glucose. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:873–880
Ho YF, Guenthner TM (1997) Isolation of liver nuclei that retain functional trans-membrane transport. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 38:163–168
Booz GW, Conrad KM, Hess AL, Singer HA, Baker KM (1992) Angiotensin-II-binding sites on hepatocyte nuclei. Endocrinology 130:3641–3649. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.130.6.1597161
Tadevosyan A, Maguy A, Villeneuve LR, Babin J, Bonnefoy A, Allen BG, Nattel S (2010) Nuclear-delimited angiotensin receptor-mediated signaling regulates cardiomyocyte gene expression. J Biol Chem 285:22338–22349. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.121749
Li XC, Zhuo JL (2008) Intracellular ANG II directly induces in vitro transcription of TGF-beta1, MCP-1, and NHE-3 mRNAs in isolated rat renal cortical nuclei via activation of nuclear AT1a receptors. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 294:C1034–C1045. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00432.2007
Pendergrass KD, Averill DB, Ferrario CM, Diz DI, Chappell MC (2006) Differential expression of nuclear AT1 receptors and angiotensin II within the kidney of the male congenic mRen2. Lewis rat. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290:F1497–F1506. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00317.2005
Bkaily G, Sleiman S, Stephan J, Asselin C, Choufani S, Kamal M, Jacques D, Gobeil F, D’Orléans-Juste P (2003) Angiotensin II AT1 receptor internalization, translocation and de novo synthesis modulate cytosolic and nuclear calcium in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 81:274–287
Pendergrass KD, Gwathmey TM, Michalek RD, Grayson JM, Chappell MC (2009) The angiotensin II-AT1 receptor stimulates reactive oxygen species within the cell nucleus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 384:149–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.04.126
Gwathmey TM, Shaltout HA, Pendergrass KD, Pirro NT, Figueroa JP, Rose JC, Diz DI, Chappell MC (2009) Nuclear angiotensin II type 2 (AT2) receptors are functionally linked to nitric oxide production. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 296:F1484–F1493. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.90766.2008
Gwathmey TM, Alzayadneh EM, Pendergrass KD, Chappell MC (2012) Novel roles of nuclear angiotensin receptors and signaling mechanisms. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 302:R518–R530. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00525.2011
Chappell MC (2016) Biochemical evaluation of the renin-angiotensin system: the good, bad, and absolute? Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 310:H137–H152. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00618.2015
Re RN, Cook JL (2011) Noncanonical intracrine action. J Am Soc Hypertens 5:435–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jash.2011.07.001
Zhuo JL, Li XC, Garvin JL, Navar LG, Carretero OA (2006) Intracellular ANG II induces cytosolic Ca2+ mobilization by stimulating intracellular AT1 receptors in proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290:F1382–F1390. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00269.2005
Singh VP, Le B, Bhat VB, Baker KM, Kumar R (2007) High-glucose-induced regulation of intracellular ANG II synthesis and nuclear redistribution in cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:H939–H948. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00391.2007
Acknowledgements
The authors are acknowledge the support to this work under Grants from Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível superior (CAPES), and Fundação Oswaldo Ramos, and are grateful to Laboratório Multiusuário 6 – Infar/Unifesp for their help in the analyses on Confocal Microscopy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Silva Novaes, A., Ribeiro, R.S., Pereira, L.G. et al. Intracrine action of angiotensin II in mesangial cells: subcellular distribution of angiotensin II receptor subtypes AT1 and AT2. Mol Cell Biochem 448, 265–274 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-018-3331-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-018-3331-y