Abstract
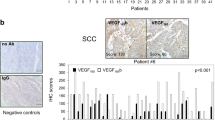
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family members play critical and complex roles in the regulation of cancer vascularization and metastasis. The exact molecular control of lung cancer metastasis by VEGF family members is not completely understood. Here, we showed that specimens from non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) contained significantly higher levels of placental growth factor (PlGF) than paired non-cancer tissue (p < 0.05, N = 25). Moreover, higher levels of PlGF were detected in NSCLC specimens from the patients who had distal metastases than those who had not. High-PlGF levels appeared to be associated with poor patient survival. In vitro, PlGF dose-dependently increased the ratio of pro-angiogenic VEGF isoform (VEGF165) versus anti-angiogenic VEGF isoform (VEGF165b), seemingly through induction of expression of splicing regulatory factor SRp40, resulting in the enhancement of the cancer cell metastatic potential. Higher levels of SRp40 were detected in NSCLC specimens, compared to paired non-cancer tissue (p < 0.05, N = 25). Finally, a strong correlation was detected between the levels of PlGF and SRp40 in NSCLC specimens (r = 0.83, p < 0.0001, N = 25). Together, these data suggest that PlGF may increase NSCLC metastasis through SRp40-mediated mRNA splicing of VEGF.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xue D, Yang Y, Liu Y, Wang P, Dai Y, Liu Q, Chen L, Shen J, Ju H, Li Y, Tan Z (2016) MicroRNA-206 attenuates the growth and angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer cells by blocking the 14-3-3zeta/STAT3/HIF-1alpha/VEGF signaling. Oncotarget 7:79805–79813. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.12972
Li Z, Guo C, Liu X, Zhou C, Zhu F, Wang X, Wang Q, Shi Y, Wang J, Zhao W, Zhang L (2016) TIPE2 suppresses angiogenesis and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) invasiveness via inhibiting Rac1 activation and VEGF expression. Oncotarget 7:62224–62239. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.11406
Li Y, Wang Y, Niu K, Chen X, Xia L, Lu D, Kong R, Chen Z, Duan Y, Sun J (2016) Clinical benefit from EGFR-TKI plus ginsenoside Rg3 in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR active mutation. Oncotarget 7:70535–70545. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.12059
Ferrara N (2009) Vascular endothelial growth factor. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:789–791. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.179663
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J (2003) The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 9:669–676. doi:10.1038/nm0603-669nm0603-669
Fischer C, Jonckx B, Mazzone M, Zacchigna S, Loges S, Pattarini L, Chorianopoulos E, Liesenborghs L, Koch M, De Mol M, Autiero M, Wyns S, Plaisance S, Moons L, van Rooijen N, Giacca M, Stassen JM, Dewerchin M, Collen D, Carmeliet P (2007) Anti-PlGF inhibits growth of VEGF(R)-inhibitor-resistant tumors without affecting healthy vessels. Cell 131:463–475. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.08.038
Autiero M, Waltenberger J, Communi D, Kranz A, Moons L, Lambrechts D, Kroll J, Plaisance S, De Mol M, Bono F, Kliche S, Fellbrich G, Ballmer-Hofer K, Maglione D, Mayr-Beyrle U, Dewerchin M, Dombrowski S, Stanimirovic D, Van Hummelen P, Dehio C, Hicklin DJ, Persico G, Herbert JM, Shibuya M, Collen D, Conway EM, Carmeliet P (2003) Role of PlGF in the intra- and intermolecular cross talk between the VEGF receptors Flt1 and Flk1. Nat Med 9:936–943. doi:10.1038/nm884nm884
Huo X, Li Y, Jiang Y, Sun X, Gu L, Guo W, Sun D (2015) Inhibition of ocular neovascularization by co-inhibition of VEGF-A and PLGF. Cell Physiol Biochem 35:1787–1796. doi:10.1159/000373990
Jiang H, Wu X, Wang H, Huang C, Zhang L (2015) Combined anti-PLGF and anti-endostatin treatments inhibit ocular hemangiomas. Cell Physiol Biochem 36:930–936. doi:10.1159/000430267
Ribatti D (2016) Tumor refractoriness to anti-VEGF therapy. Oncotarget 7:46668–46677. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.8694
Bates DO, MacMillan PP, Manjaly JG, Qiu Y, Hudson SJ, Bevan HS, Hunter AJ, Soothill PW, Read M, Donaldson LF, Harper SJ (2006) The endogenous anti-angiogenic family of splice variants of VEGF, VEGFxxxb, are down-regulated in pre-eclamptic placentae at term. Clin Sci (Lond) 110:575–585. doi:10.1042/CS20050292
Perrin RM, Konopatskaya O, Qiu Y, Harper S, Bates DO, Churchill AJ (2005) Diabetic retinopathy is associated with a switch in splicing from anti- to pro-angiogenic isoforms of vascular endothelial growth factor. Diabetologia 48:2422–2427. doi:10.1007/s00125-005-1951-8
Bates DO, Cui TG, Doughty JM, Winkler M, Sugiono M, Shields JD, Peat D, Gillatt D, Harper SJ (2002) VEGF165b, an inhibitory splice variant of vascular endothelial growth factor, is down-regulated in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 62:4123–4131
Diaz R, Pena C, Silva J, Lorenzo Y, Garcia V, Garcia JM, Sanchez A, Espinosa P, Yuste R, Bonilla F, Dominguez G (2008) p73 Isoforms affect VEGF, VEGF165b and PEDF expression in human colorectal tumors: VEGF165b downregulation as a marker of poor prognosis. Int J Cancer 123:1060–1067. doi:10.1002/ijc.23619
Rennel E, Waine E, Guan H, Schuler Y, Leenders W, Woolard J, Sugiono M, Gillatt D, Kleinerman E, Bates D, Harper S (2008) The endogenous anti-angiogenic VEGF isoform, VEGF165b inhibits human tumour growth in mice. Br J Cancer 98:1250–1257. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604309
Caceres JF, Kornblihtt AR (2002) Alternative splicing: multiple control mechanisms and involvement in human disease. Trends Genet 18:186–193
Nowak DG, Woolard J, Amin EM, Konopatskaya O, Saleem MA, Churchill AJ, Ladomery MR, Harper SJ, Bates DO (2008) Expression of pro- and anti-angiogenic isoforms of VEGF is differentially regulated by splicing and growth factors. J Cell Sci 121:3487–3495. doi:10.1242/jcs.016410
Giard DJ, Aaronson SA, Todaro GJ, Arnstein P, Kersey JH, Dosik H, Parks WP (1973) In vitro cultivation of human tumors: establishment of cell lines derived from a series of solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst 51:1417–1423
Albini A, Tosetti F, Li VW, Noonan DM, Li WW (2012) Cancer prevention by targeting angiogenesis. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 9:498–509. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2012.120
Welti J, Loges S, Dimmeler S, Carmeliet P (2013) Recent molecular discoveries in angiogenesis and antiangiogenic therapies in cancer. J Clin Invest 123:3190–3200. doi:10.1172/JCI70212
Yang Y, Sun M, Wang L, Jiao B (2013) HIFs, angiogenesis, and cancer. J Cell Biochem 114:967–974. doi:10.1002/jcb.24438
Takahashi A, Sasaki H, Kim SJ, Tobisu K, Kakizoe T, Tsukamoto T, Kumamoto Y, Sugimura T, Terada M (1994) Markedly increased amounts of messenger RNAs for vascular endothelial growth factor and placenta growth factor in renal cell carcinoma associated with angiogenesis. Cancer Res 54:4233–4237
Kim KJ, Cho CS, Kim WU (2012) Role of placenta growth factor in cancer and inflammation. Exp Mol Med 44:10–19. doi:10.3858/emm.2012.44.1.023
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Ethical approval
All experimental methods and protocols were approved by the Institutional Research Ethics Committee of First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Liu, T. Placental growth factor signaling regulates isoform splicing of vascular endothelial growth factor A in the control of lung cancer cell metastasis. Mol Cell Biochem 439, 163–169 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3145-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3145-3