Abstract
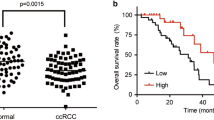
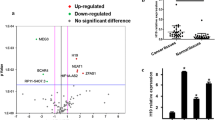
This study was to investigate the involvement of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) colon cancer-associated transcript-1 (CCAT1) in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and to further uncover its underlying mechanism. In this study, the expression of CCAT1 and Livin of RCC tissues or cells was determined using qRT-PCR (quantitative real-time PCR) and western blot, respectively. RNA pulldown and RIP (RNA-Binding Protein Immunoprecipitation) assays were performed to examine the sequence interaction between CCAT1 and Livin. The viability and apoptosis of RCC cells was assessed by MTT(3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) and TUNEL (TdT-mediated dUTP nick end labeling) assays, respectively. Mice of tumor animal models were established to observe the effect of CCAT1 on RCC tumor growth. The relative expression of CCAT1 in RCC tissues and cell lines was obviously higher than that of the control. CCAT1 knockdown could reduce cell viability and increase the apoptosis of RCC cells in vitro. Furthermore, Livin was significantly inhibited by CCAT1 silencing; RNA pulldown and RIP assays showed that CCAT1 was physically associated with Livin protein. Moreover, Livin overexpression not only significantly inhibited RCC cell apoptosis and increased cell viability, but completely reversed the si-CCAT1-mediated repression of cell viability. More importantly, CCAT1 silencing could inhibit the growth of RCC in vivo that was accompanied by the reduction of Livin in RCC tissues. CCAT1 inhibits RCC cell apoptosis and increases cell viability through up-regulation of Livin.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seliger B, Menig M, Lichtenfels R, Atkins D, Bukur J, Halder TM, Kersten M, Harder A, Ackermann A, Beck J (2003) Identification of markers for the selection of patients undergoing renal cell carcinoma-specific immunotherapy. Proteomics 3:979–990
Bracarda S (2009) Metastatic renal cell carcinoma: pathogenesis and the current medical landscape. Eur Urol Suppl 8:787–792
Ip JY, Nakagawa S (2012) Long non-coding RNAs in nuclear bodies. Dev Growth Differ 54:44–54. doi:10.1111/j.1440-169X.2011.01303.x
Lawson J, Singh R, Hultner M, Ariyur K, Martin L (2012) Long non-coding RNAs and cancer: a new frontier of translational research? Oncogene 31:4577–4587
Shao K, Shi T, Yang Y, Wang X, Da X, Zhou P (2016) Highly expressed lncRNA CRNDE promotes cell proliferation through Wnt/β-catenin signaling in renal cell carcinoma. Tumor Biol 37:15997−16004
Xiong J, Liu Y, Luo S, Jiang L, Zeng Y, Chen Z, Shi X, Lv B, Tang W (2017) High expression of the long non-coding RNA HEIRCC promotes Renal Cell Carcinoma metastasis by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 8:6555–6563. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.14149
Chen S, Ma P, Zhao Y, Li B, Jiang S, Xiong H, Wang Z, Wang H, Jin X, Liu C (2016) Biological function and mechanism of MALAT-1 in renal cell carcinoma proliferation and apoptosis: role of the MALAT-1-Livin protein interaction. J Physiol Sci. doi:10.1007/s12576-016-0486-8
Meng Z, Wei L, Huang Y, Shi J, Xun W (2016) Downregulation of the long noncoding RNA TUG1 inhibits the proliferation, migration, invasion and promotes apoptosis of renal cell carcinoma. J Mol Histol 47:421–428
Nissan A, Stojadinovic A, Mitrani-Rosenbaum S, Halle D, Grinbaum R, Roistacher M, Bochem A, Dayanc BE, Ritter G, Gomceli I, Bostanci EB, Akoglu M, Chen YT, Old LJ, Gure AO (2012) Colon cancer associated transcript-1: a novel RNA expressed in malignant and pre-malignant human tissues. Int J Cancer 130:1598–1606. doi:10.1002/ijc.26170
He X, Tan X, Wang X, Jin H, Liu L, Ma L, Yu H, Fan Z (2014) C-Myc-activated long noncoding RNA CCAT1 promotes colon cancer cell proliferation and invasion. Tumor Biol 35:12181–12188
Xin Y, Li Z, Shen J, Chan MT, Wu WK (2016) CCAT1: a pivotal oncogenic long non-coding RNA in human cancers. Cell Prolif 49:255–260
Salvesen GS, Duckett CS (2002) IAP proteins: blocking the road to death’s door. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:401–410. doi:10.1038/nrm830
Franklin MC, Kadkhodayan S, Ackerly H, Alexandru D, Distefano MD, Elliott LO, Flygare JA, Mausisa G, Okawa DC, Ong D (2003) Structure and function analysis of peptide antagonists of melanoma inhibitor of apoptosis (ML-IAP). Biochemistry 42:8223–8231
Altieri B, Sbiera S, Della Casa S, Weigand I, Wild V, Steinhauer S, Fadda G, Kocot A, Bekteshi M, Mambretti EM, Rosenwald A, Pontecorvi A, Fassnacht M, Ronchi CL (2017) Livin/BIRC7 expression as malignancy marker in adrenocortical tumors. Oncotarget 8:9323–9338. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.14067
Yin L, Liu S, Li C, Ding S, Bi D, Niu Z, Han L, Li W, Gao D, Liu Z (2016) CYLD downregulates Livin and synergistically improves gemcitabine chemosensitivity and decreases migratory/invasive potential in bladder cancer: the effect is autophagy-associated. Tumor Biol 37:1–12
Yang G, Cao X, Wang D, Wei S, Sun H, Bing H, Cui J, Liu B (2016) Overexpression of Livin promotes migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by induction of epithelial–mesenchymal transition via NF-κB activation. Acta Geosicientia Sin 25:579–582
Liu C, Wu X, Luo C, Hu Z, Yin Z, He Y, Du H, Zhang W, Jiang Q, Lin Y (2010) Antisense oligonucleotide targeting Livin induces apoptosis of human bladder cancer cell via a mechanism involving caspase 3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 29:63. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-29-63
Kempkensteffen C, Hinz S, Christoph F, Krause H, Koellermann J, Magheli A, Schrader M, Schostak M, Miller K, Weikert S (2007) Expression of the apoptosis inhibitor Livin in renal cell carcinomas: correlations with pathology and outcome. Tumour Biol 28:132–138
Liu B, Han M, Wen JK, Wang L (2007) Livin/ML-IAP as a new target for cancer treatment. Cancer Lett 250:168–176
Wang Z, Shuai L, Ding K, Ding S, Li C, Lu J, Gao D, Tong Z, Bi D (2016) Silencing Livin induces apoptotic and autophagic cell death, increasing chemotherapeutic sensitivity to cisplatin of renal carcinoma cells. Tumor Biol 37:15133–15143
Wagener N, Crnkovićmertens I, Vetter C, Machergöppinger S, Bedke J, Gröne EF, Zentgraf H, Pritsch M, Hoppeseyler K, Buse S (2007) Expression of inhibitor of apoptosis protein Livin in renal cell carcinoma and non-tumorous adult kidney. Br J Cancer 97:1271–1276
Crnkovićmertens I, Wagener N, Semzow J, Gröne EF, Haferkamp A, Hohenfellner M, Butz K, Hoppeseyler F (2007) Targeted inhibition of Livin resensitizes renal cancer cells towards apoptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci Cmls 64:1137–1144
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (NO. cstc2013jcyjA0437). Special thanks to Professor Liu Chuan for his technical guidance and fund support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Ma, P., Li, B. et al. LncRNA CCAT1 inhibits cell apoptosis of renal cell carcinoma through up-regulation of Livin protein. Mol Cell Biochem 434, 135–142 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3043-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3043-8