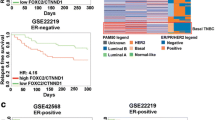
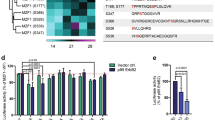
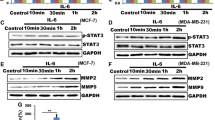
Abstract
Despite the current progress in cancer research and therapy, breast cancer remains the leading cause of mortality among half a million women worldwide. Migration and invasion of cancer cells are associated with prevalent tumor metastasis as well as high mortality. Extensive studies have powerfully established the role of prototypic second messenger cAMP and its two ubiquitously expressed intracellular cAMP receptors namely the classic protein kinaseA/cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) and the more recently discovered exchange protein directly activated by cAMP/cAMP-regulated guanine nucleotide exchange factor (EPAC/cAMP-GEF) in cell migration, cell cycle regulation, and cell death. Herein, we performed the analysis of the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) dataset to evaluate the essential role of cAMP molecular network in breast cancer. We report that EPAC1, PKA, and AKAP9 along with other molecular partners are amplified in breast cancer patients, indicating the importance of this signaling network. To evaluate the functional role of few of these proteins, we used pharmacological modulators and analyzed their effect on cell migration and cell death in breast cancer cells. Hence, we report that inhibition of EPAC1 activity using pharmacological modulators leads to inhibition of cell migration and induces cell death. Additionally, we also observed that the inhibition of EPAC1 resulted in disruption of its association with the microtubule cytoskeleton and delocalization of AKAP9 from the centrosome as analyzed by in vitro imaging. Finally, this study suggests for the first time the mechanistic insights of mode of action of a primary cAMP-dependent sensor, Exchange protein activated by cAMP 1 (EPAC1), via its interaction with A-kinase anchoring protein 9 (AKAP9). This study provides a new cell signaling cAMP–EPAC1–AKAP9 direction to the development of additional biotherapeutics for breast cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AKAP:
-
A-kinase anchoring protein
- PKA:
-
Protein kinase A
- EPAC:
-
Exchange protein activated by cAMP
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas
- ESI:
-
EPAC-specific inhibitor
References
Guan X (2015) Cancer metastases: challenges and opportunities. Acta Pharm Sin B 5:402–418. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2015.07.005
Dorsam RT, Gutkind JS (2007) G-protein-coupled receptors and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 7:79–94. doi:10.1038/nrc2069
Gidon A, Feinstein TN, Xiao K, Vilardaga JP (2016) Studying the regulation of endosomal cAMP production in GPCR signaling. Methods Cell Biol 132:109–126. doi:10.1016/bs.mcb.2015.10.007
Zhou C, Dai X, Chen Y, Shen Y, Lei S, Xiao T, Bartfai T, Ding J, Wang MW (2016) G protein-coupled receptor GPR160 is associated with apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of prostate cancer cells. Oncotarget 7:12823–12839. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.7313
Gloerich M, Bos JL (2010) Epac: defining a new mechanism for cAMP action. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 50:355–375. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.010909.105714
Gloerich M, Ponsioen B, Vliem MJ, Zhang Z, Zhao J, Kooistra MR, Price LS, Ritsma L, Zwartkruis FJ, Rehmann H, Jalink K, Bos JL (2010) Spatial regulation of cyclic AMP-Epac1 signaling in cell adhesion by ERM proteins. Mol Cell Biol 30:5421–5431. doi:10.1128/MCB.00463-10
Liu C, Takahashi M, Li Y, Dillon TJ, Kaech S, Stork PJ (2010) The interaction of Epac1 and Ran promotes Rap1 activation at the nuclear envelope. Mol Cell Biol 30:3956–3969. doi:10.1128/MCB.00242-10
Liu C, Takahashi M, Li Y, Song S, Dillon TJ, Shinde U, Stork PJ (2008) Ras is required for the cyclic AMP-dependent activation of Rap1 via Epac2. Mol Cell Biol 28:7109–7125. doi:10.1128/MCB.01060-08
Sehrawat S, Cullere X, Patel S, Italiano J Jr, Mayadas TN (2008) Role of Epac1, an exchange factor for Rap GTPases, in endothelial microtubule dynamics and barrier function. Mol Biol Cell 19:1261–1270. doi:10.1091/mbc.E06-10-0972
Cheng X, Ji Z, Tsalkova T, Mei F (2008) Epac and PKA: a tale of two intracellular cAMP receptors. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 40:651–662
Grandoch M, Rose A, ter Braak M, Jendrossek V, Rubben H, Fischer JW, Schmidt M, Weber AA (2009) Epac inhibits migration and proliferation of human prostate carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer 101:2038–2042. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605439
Rangarajan S, Enserink JM, Kuiperij HB, de Rooij J, Price LS, Schwede F, Bos JL (2003) Cyclic AMP induces integrin-mediated cell adhesion through Epac and Rap1 upon stimulation of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor. J Cell Biol 160:487–493. doi:10.1083/jcb.200209105
Lorenz R, Aleksic T, Wagner M, Adler G, Weber CK (2008) The cAMP/Epac1/Rap1 pathway in pancreatic carcinoma. Pancreas 37:102–103. doi:10.1097/MPA.0b013e318160748f
Onodera Y, Nam JM, Bissell MJ (2014) Increased sugar uptake promotes oncogenesis via EPAC/RAP1 and O-GlcNAc pathways. J Clin Invest 124:367–384. doi:10.1172/JCI63146
Honore S, Pasquier E, Braguer D (2005) Understanding microtubule dynamics for improved cancer therapy. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:3039–3056. doi:10.1007/s00018-005-5330-x
Pasquier E, Kavallaris M (2008) Microtubules: a dynamic target in cancer therapy. IUBMB Life 60:165–170. doi:10.1002/iub.25
Desai A, Mitchison TJ (1997) Microtubule polymerization dynamics. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 13:83–117. doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.13.1.83
Komarova YA, Vorobjev IA, Borisy GG (2002) Life cycle of MTs: persistent growth in the cell interior, asymmetric transition frequencies and effects of the cell boundary. J Cell Sci 115:3527–3539
Witczak O, Skalhegg BS, Keryer G, Bornens M, Tasken K, Jahnsen T, Orstavik S (1999) Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding an A-kinase anchoring protein located in the centrosome, AKAP450. EMBO J 18:1858–1868. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.7.1858
Rempel N (2001) Centrosomes as scaffolds: the role of pericentrin and protein kinase A-anchoring proteins. Einstein Q J Biol Med 18:54–58
Sehrawat S, Ernandez T, Cullere X, Takahashi M, Ono Y, Komarova Y, Mayadas TN (2011) AKAP9 regulation of microtubule dynamics promotes Epac1-induced endothelial barrier properties. Blood 117:708–718. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-02-268870
Frank B, Rigas SH, Bermejo JL, Wiestler M, Wagner K, Hemminki K, Reed MW, Sutter C, Wappenschmidt B, Balasubramanian SP, Meindl A, Kiechle M, Bugert P, Schmutzler RK, Bartram CR, Justenhoven C, Ko YD, Bruning T, Brauch H, Hamann U, Pharoah PP, Dunning AM, Pooley KA, Easton DF, Cox A, Burwinkel B (2008) The CASP8-652 6 N del promoter polymorphism and breast cancer risk: a multicenter study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 111:139–144. doi:10.1007/s10549-007-9752-z
Milne RL, Lorenzo-Bermejo J, Burwinkel B, Malats N, Arias JI, Zamora MP, Benitez J, Humphreys MK, Garcia-Closas M, Chanock SJ, Lissowska J, Sherman ME, Mannermaa A, Kataja V, Kosma VM, Nevanlinna H, Heikkinen T, Aittomaki K, Blomqvist C, Anton-Culver H, Ziogas A, Devilee P, van Asperen CJ, Tollenaar RA, Seynaeve C, Hall P, Czene K, Liu J, Irwanto AK, Kang D, Yoo KY, Noh DY, Couch FJ, Olson JE, Wang X, Fredericksen Z, Nordestgaard BG, Bojesen SE, Flyger H, Margolin S, Lindblom A, Fasching PA, Schulz-Wendtland R, Ekici AB, Beckmann MW, Wang-Gohrke S, Shen CY, Yu JC, Hsu HM, Wu PE, Giles GG, Severi G, Baglietto L, English DR, Cox A, Brock I, Elliott G, Reed MW, Beesley J, Chen X, Investigators K, Fletcher O, Gibson L, dos Santos Silva I, Peto J, Frank B, Heil J, Meindl A, Chang-Claude J, Hein R, Vrieling A, Flesch-Janys D, Southey MC, Smith L, Apicella C, Hopper JL, Dunning AM, Pooley KA, Pharoah PD, Hamann U, Pesch B, Ko YD, Easton DF, Chenevix-Trench G (2011) 7q21-rs6964587 and breast cancer risk: an extended case-control study by the Breast Cancer Association Consortium. J Med Genet 48:698–702. doi:10.1136/jmedgenet-2011-100303
Tsalkova T, Mei FC, Li S, Chepurny OG, Leech CA, Liu T, Holz GG, Woods VL Jr, Cheng X (2012) Isoform-specific antagonists of exchange proteins directly activated by cAMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:18613–18618. doi:10.1073/pnas.1210209109
Zhu Y, Chen H, Boulton S, Mei F, Ye N, Melacini G, Zhou J, Cheng X (2015) Biochemical and pharmacological characterizations of ESI-09 based EPAC inhibitors: defining the ESI-09 “therapeutic window”. Sci Rep 5:9344. doi:10.1038/srep09344
Almahariq M, Tsalkova T, Mei FC, Chen H, Zhou J, Sastry SK, Schwede F, Cheng X (2013) A novel EPAC-specific inhibitor suppresses pancreatic cancer cell migration and invasion. Mol Pharmacol 83:122–128. doi:10.1124/mol.112.080689
Song BW, Chang W, Hong BK, Kim IK, Cha MJ, Lim S, Choi EJ, Ham O, Lee SY, Lee CY, Park JH, Choi E, Song H, Jang Y, Hwang KC (2013) Protein kinase C activation stimulates mesenchymal stem cell adhesion through activation of focal adhesion kinase. Cell Transplant 22:797–809. doi:10.3727/096368912X656126
Fadok VA, Bratton DL, Guthrie L, Henson PM (2001) Differential effects of apoptotic versus lysed cells on macrophage production of cytokines: role of proteases. J Immunol 166:6847–6854
Koopman G, Reutelingsperger CP, Kuijten GA, Keehnen RM, Pals ST, van Oers MH (1994) Annexin V for flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on B cells undergoing apoptosis. Blood 84:1415–1420
Cullere X, Shaw SK, Andersson L, Hirahashi J, Luscinskas FW, Mayadas TN (2005) Regulation of vascular endothelial barrier function by Epac, a cAMP-activated exchange factor for Rap GTPase. Blood 105:1950–1955. doi:10.1182/blood-2004-05-1987
Fukuhara S, Sakurai A, Sano H, Yamagishi A, Somekawa S, Takakura N, Saito Y, Kangawa K, Mochizuki N (2005) Cyclic AMP potentiates vascular endothelial cadherin-mediated cell-cell contact to enhance endothelial barrier function through an Epac-Rap1 signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol 25:136–146. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.1.136-146.2005
Funaki C, Hodges RR, Dartt DA (2010) Identification of the Raf-1 signaling pathway used by cAMP to inhibit p42/p44 MAPK in rat lacrimal gland acini: role in potentiation of protein secretion. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51:6321–6328. doi:10.1167/iovs.10-5690
Wertheimer E, Krapf D, de la Vega-Beltran JL, Sanchez-Cardenas C, Navarrete F, Haddad D, Escoffier J, Salicioni AM, Levin LR, Buck J, Mager J, Darszon A, Visconti PE (2013) Compartmentalization of distinct cAMP signaling pathways in mammalian sperm. J Biol Chem 288:35307–35320. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.489476
Singhmar P, Huo X, Eijkelkamp N, Berciano SR, Baameur F, Mei FC, Zhu Y, Cheng X, Hawke D, Mayor F Jr, Murga C, Heijnen CJ, Kavelaars A (2016) Critical role for Epac1 in inflammatory pain controlled by GRK2-mediated phosphorylation of Epac1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:3036–3041. doi:10.1073/pnas.1516036113
Neve RM, Chin K, Fridlyand J, Yeh J, Baehner FL, Fevr T, Clark L, Bayani N, Coppe JP, Tong F, Speed T, Spellman PT, DeVries S, Lapuk A, Wang NJ, Kuo WL, Stilwell JL, Pinkel D, Albertson DG, Waldman FM, McCormick F, Dickson RB, Johnson MD, Lippman M, Ethier S, Gazdar A, Gray JW (2006) A collection of breast cancer cell lines for the study of functionally distinct cancer subtypes. Cancer Cell 10:515–527. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2006.10.008
Quail DF, Joyce JA (2013) Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med 19:1423–1437. doi:10.1038/nm.3394
Almahariq M, Mei FC, Wang H, Cao AT, Yao S, Soong L, Sun J, Cong Y, Chen J, Cheng X (2015) Exchange protein directly activated by cAMP modulates regulatory T-cell-mediated immunosuppression. Biochem J 465:295–303. doi:10.1042/BJ20140952
Acknowledgements
Seema Sehrawat is the recipient of BioCARe Award from Department of Biotechnology, Govt. of India and acknowledges the funding support. Shailja Singh acknowledges DBT PILOT project grant on cancer. Shiv Nadar Foundation is acknowledged for providing the Ph.D. fellowship to Mr. Naveen Kumar. Dr. Sonal Gupta is the recipient of University Grant Commission Postdoctoral fellowship For Women. We would like to thank Dr. Sunita Setlur, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA and Dr. Chandan Kumar-Sinha, Michigan Center for Translational Pathology, University of Michigan, and Ann Arbor, MI, USA for their advice on TCGA analysis. The TCGA analysis was performed using the breast cancer data available for the cbioportal. The results presented in this study are partly based upon data generated by the TCGA Research Network: http://cancergenome.nih.gov/. We also sincerely thank the financial support received from LRE JNU and ICMR CAR 2016 -17.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Naveen Kumar and Sonal Gupta—equal first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, N., Gupta, S., Dabral, S. et al. Role of exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (EPAC1) in breast cancer cell migration and apoptosis. Mol Cell Biochem 430, 115–125 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-2959-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-2959-3