Abstract
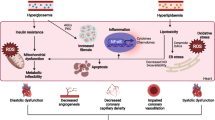
Blood and tissue levels of manganese (Mn) are lower in type 2 diabetic and atherosclerosis patients compared with healthy subjects. Adiponectin has anti-diabetic and anti-atherogenic properties. Impairment in Disulfide bond A-like protein (DsbA-L) is associated with low adiponectin levels and diabetes. This study investigates the hypothesis that the beneficial effects of Mn supplementation are mediated by adiponectin and DsbA-L. At 6 weeks of age, Male Zucker diabetic fatty rats (ZDF) were randomly divided into two groups: diabetic controls and Mn-supplemented diabetic rats. Each rat was supplemented with Mn (D+Mn, 16 mg/kg BW) or water (placebo, D+P) daily for 7 weeks by oral gavage. For cell culture studies, Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVEC) or 3T3L1 adipocytes were pretreated with Mn (0–10 µM MnCl2) for 24 h, followed by high glucose (HG, 25 mM) or normal glucose (5 mM) exposure for another 24 h. Mn supplementation resulted in higher adiponectin (p = 0.01), and lower ICAM-1 (p = 0.04) and lower creatinine (p = 0.04) blood levels compared to those in control ZDF rats. Mn-supplemented rats also caused reduced oxidative stress (ROS) and NADPH oxidase, and higher DsbA-L expression in the liver (p = 0.03) of ZDF rats compared to those in livers of control rats; however, Fe levels in liver were lower but not significant (p = 0.08). Similarly, treatment with high glucose (25 mM) caused a decrease in DsbA-L, which was prevented by Mn supplementation in HUVEC and adipocytes. Mechanistic studies with DsbA-L siRNA showed that the beneficial effects of Mn supplementation on ROS, NOX4, and ICAM-1 expression were abolished in DsbA-L knock-down HUVEC. These studies demonstrate that DsbA-L-linked adiponectin mediates the beneficial effects observed with Mn supplementation and provides evidence for a novel mechanism by which Mn supplementation can increase adiponectin and reduce the biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction in diabetes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sarwar MS, Ahmed S, Ullah MS, Kabir H, Rahman GM, Hasnat A, Islam MS (2013) Comparative study of serum zinc, copper, manganese, and iron in preeclamptic pregnant women. Biol Trace Elem Res 154:14–20
Koh ES, Kim SJ, Yoon HE, Chung JH, Chung S, Park CW, Chang YS, Shin SJ (2014) Association of blood manganese level with diabetes and renal dysfunction: a cross-sectional study of the Korean general population. BMC Endocr Disord 14:1
Baly DL, Schneiderman JS, Garcia-Welsh AL (1990) Effect of manganese deficiency on insulin binding, glucose transport and metabolism in rat adipocytes. J Nutr 120:1075–1079
Baly DL, Lönnerdal B, Keen CL (1985) Effects of high doses of manganese on carbohydrate homeostasis. Toxicol Lett 25:95–102
Bomb B, Kumawat D, Bomb P, Taly A, Bedi T, Bedi H (1988) Effect of manganese on regression of atherosclerosis in cholesterol fed rabbits. J Assoc Physicians India 36:149–150
Kumawat D, Bomb B, Bhatnagar H (1986) Effect of manganese on prevention of atherosclerosis in cholesterol fed rabbits. J Assoc Physicians India 34:704
Burlet E, Jain SK (2013) Manganese supplementation reduces high glucose-induced monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells and endothelial dysfunction in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. J Biol Chem 288:6409–6416
Walter RM, Uriu-Hare JY, Olin KL, Oster MH, Anawalt BD, Critchfield JW, Keen CL (1991) Copper, zinc, manganese, and magnesium status and complications of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 14:1050–1056
Kazi TG, Afridi HI, Kazi N, Jamali MK, Arain MB, Jalbani N, Kandhro GA (2008) Copper, chromium, manganese, iron, nickel, and zinc levels in biological samples of diabetes mellitus patients. Biol Trace Elem Res 122:1–18
Liu M, Liu F (2014) Regulation of adiponectin multimerization, signaling and function. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 28(1):25–31
Jiang Y, Owei I, Wan J, Ebenibo S, Dagogo-Jack S (2016) Adiponectin levels predict prediabetes risk: the pathobiology of prediabetes in a biracial cohort (POP-ABC) study. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care 4(1):e000194
Li F, Cheng K, Lam K, Vanhoutte P, Xu A (2011) Cross-talk between adipose tissue and vasculature: role of adiponectin. Acta physiol 203:167–180
Delaigle AlM, Jonas J-C, Bauche IB, Cornu O, Brichard SM (2004) Induction of adiponectin in skeletal muscle by inflammatory cytokines: in vivo and in vitro studies. Endocrinology 145:5589–5597
Piñeiro R, Iglesias MJ, Gallego R, Raghay K, Eiras S, Rubio J, Diéguez C, Gualillo O, González-Juanatey JR, Lago F (2005) Adiponectin is synthesized and secreted by human and murine cardiomyocytes. FEBS Lett 579:5163–5169.
Wolf AM, Wolf D, Avila MA, Moschen AR, Berasain C, Enrich B, Rumpold H, Tilg H (2006) Up-regulation of the anti-inflammatory adipokine adiponectin in acute liver failure in mice. J Hepatol 44:537–543
Komura N, Maeda N, Mori T, Kihara S, Nakatsuji H, Hirata A, Tochino Y, Funahashi T, Shimomura I (2013) Adiponectin protein exists in aortic endothelial cells. PloS ONE 8:e71271
Ebner A, Poitz DM, Alexiou K, Deussen A (2013) Secretion of adiponectin from mouse aorta and its role in cold storage-induced vascular dysfunction. Basic Res Cardiol 108:1–14
Ouchi N, Kihara S, Arita Y, Maeda K, Kuriyama H, Okamoto Y, Hotta K, Nishida M, Takahashi M, Nakamura T (1999) Novel modulator for endothelial adhesion molecules adipocyte-derived plasma protein adiponectin. Circulation 100:2473–2476
Ouchi N, Ohishi M, Kihara S, Funahashi T, Nakamura T, Nagaretani H, Kumada M, Ohashi K, Okamoto Y, Nishizawa H (2003) Association of hypoadiponectinemia with impaired vasoreactivity. Hypertension 42:231–234
Shimabukuro M, Higa N, Asahi T, Oshiro Y, Takasu N, Tagawa T, Ueda S, Shimomura I, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y (2003) Hypoadiponectinemia is closely linked to endothelial dysfunction in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:3236–3240
Son E-W, Lee S-R, Choi H-S, Koo H-J, Huh J-E, Kim M-H, Pyo S (2007) Effects of supplementation with higher levels of manganese and magnesium on immune function. Arch Pharm Res 30:743–749
Bae Y-J, Choi M-K, Kim M-H (2011) Manganese supplementation reduces the blood cholesterol levels in Ca-deficient ovariectomized rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 141:224–231
Metais C, Forcheron F, Abdallah P, Basset A, Del Carmine P, Bricca G, Beylot M (2008) Adiponectin receptors: expression in Zucker diabetic rats and effects of fenofibrate and metformin. Metabolism 57:946–953
Forcheron F, Basset A, Abdallah P, Del Carmine P, Gadot N, Beylot M (2009) Diabetic cardiomyopathy: effects of fenofibrate and metformin in an experimental model–the Zucker diabetic rat. Cardiovasc Diabetol 8:1
Holm A, Johansen P, Ahnfelt-Ronne I, Romer J (2004) Adipogenic and orexigenic effects of the ghrelin-receptor ligand tabimorelin are diminished in leptin-signalling-deficient ZDF rats. Eur J Endocrinol 150:893–904
Candiloros H, Muller S, Zeghari N, Donner M, Drouin P, Ziegler O (1995) Decreased erythrocyte membrane fluidity in poorly controlled IDDM: influence of ketone bodies. Diabetes Care 18(4):549–551
Malthankar GV, White BK, Bhushan A, Daniels CK, Rodnick KJ, Lai JC (2004) Differential lowering by manganese treatment of activities of glycolytic and tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle enzymes investigated in neuroblastoma and astrocytoma cells is associated with manganese-induced cell death. Neurochem Res 29:709–717
Isaac AO, Kawikova I, Bothwell AL, Daniels CK, Lai JC (2006) Manganese treatment modulates the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in astrocytoma and neuroblastoma cells. Neurochem Res 31:1305–1316
Manna P, Jain SK (2011) Hydrogen sulfide and L-cysteine increase PIP3 and glucose utilization by inhibiting PTEN and activating PI3K/AKT/PKCζ/λ in 3T3L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem 286:39848–39859
Kanikarla-Marie P, Jain SK (2014) l-Cysteine supplementation reduces high-glucose and ketone-induced adhesion of monocytes to endothelial cells by inhibiting ROS. Mol Cell Biochem 391:251–256
Jain SK, Kahlon G, Morehead L, Dhawan R, Lieblong B, Stapleton T, Caldito G, Hoeldtke R, Levine SN, Bass PF (2012) Effect of chromium dinicocysteinate supplementation on circulating levels of insulin, TNFα, oxidative stress, and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic subjects: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Mol Nutr Food Res 56:1333–1341
Satoh N, Naruse M, Usui T, Tagami T, Suganami T, Yamada K, Kuzuya H, Shimatsu A, Ogawa Y (2004) Leptin-to-adiponectin ratio as a potential atherogenic index in obese type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 27:2488–2490
Norata GD, Raselli S, Grigore L, Garlaschelli K, Dozio E, Magni P, Catapano AL (2007) Leptin: adiponectin ratio is an independent predictor of intima media thickness of the common carotid artery. Stroke 38:2844–2846
Oda N, Imamura S, Fujita T, Uchida Y, Inagaki K, Kakizawa H, Hayakawa N, Suzuki A, Takeda J, Horikawa Y (2008) The ratio of leptin to adiponectin can be used as an index of insulin resistance. Metabolism 57:268–273
Ntaios G, Gatselis NK, Makaritsis K, Dalekos GN (2013) Adipokines as mediators of endothelial function and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 227:216–221
Blankenberg S, Barbaux S, Tiret L (2003) Adhesion molecules and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 170:191–203
Sedeek M, Callera G, Montezano A, Gutsol A, Heitz F, Szyndralewiez C, Page P, Kennedy CR, Burns KD, Touyz RM (2010) Critical role of Nox4-based NADPH oxidase in glucose-induced oxidative stress in the kidney: implications in type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 299:F1348–F1358
Syed I, Kyathanahalli CN, Jayaram B, Govind S, Rhodes CJ, Kowluru RA, Kowluru A (2011) Increased Phagocyte-Like NADPH oxidase and ROS generation in Type 2 diabetic ZDF rat and human islets role of Rac1–JNK1/2 signaling pathway in mitochondrial dysregulation in the diabetic islet. Diabetes 60:2843–2852
Matsuda M, Shimomura I (2014) Roles of adiponectin and oxidative stress in obesity-associated metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 15(1):1–10. doi:10.1007/s11154-013-9271-7
Yuan F, Li Y-N, Liu Y-H, Yi B, Tian J-W, Liu F-Y (2012) Adiponectin inhibits the generation of reactive oxygen species induced by high glucose and promotes endothelial NO synthase formation in human mesangial cells. Mol Med Rep 6:449–453
Achari AE, Jain SK (2016) l-Cysteine supplementation increases adiponectin synthesis and secretion, and GLUT4 and glucose utilization by upregulating disulfide bond A-like protein expression mediated by MCP-1 inhibition in 3T3-L1 adipocytes exposed to high glucose. Mol Cell Biochem 414:105–113
Okamoto Y, Arita Y, Nishida M, Muraguchi M, Ouchi N, Takahashi M, Igura T, Inui Y, Kihara S, Nakamura T (2000) An adipocyte-derived plasma protein, adiponectin, adheres to injured vascular walls. Horm Metab Res 32:47–50
Arita Y, Kihara S, Ouchi N, Maeda K, Kuriyama H, Okamoto Y, Kumada M, Hotta K, Nishida M, Takahashi M (2002) Adipocyte-derived plasma protein adiponectin acts as a platelet-derived growth factor-BB–binding protein and regulates growth factor–induced common postreceptor signal in vascular smooth muscle cell. Circulation 105:2893–2898
Kumada M, Kihara S, Ouchi N, Kobayashi H, Okamoto Y, Ohashi K, Maeda K, Nagaretani H, Kishida K, Maeda N (2004) Adiponectin specifically increased tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 through interleukin-10 expression in human macrophages. Circulation 109:2046–2049
Hayashi M, Shibata R, Takahashi H, Ishii H, Aoyama T, Kasuga H, Yamada S, Ohashi K, Maruyama S, Matsuo S (2011) Association of adiponectin with carotid arteriosclerosis in predialysis chronic kidney disease. Am J Nephrol 34:249–255
Deng G, Long Y, Yu Y, Li M (2010) Adiponectin directly improves endothelial dysfunction in obese rats through the AMPK–eNOS Pathway. Int J Obes 34:165–171
Hui X, Lam KS, Vanhoutte PM, Xu A (2012) Adiponectin and cardiovascular health: an update. Br J Pharmacol 165:574–590
Rossander-Hulten L, Brune M, Sandstrom B, Lonnerdal B, Hallberg L (1991) Competitive inhibition of iron absorption by manganese and zinc in humans. Am J Clin Nutr 54:152–156
Davis CD, Wolf TL, Greger JL (1992) Varying levels of manganese and iron affect absorption and gut endogenous losses of manganese by rats. J Nutr 122:1300–1308
Fitsanakis VA, Zhang N, Garcia S, Aschner M (2010) Manganese (Mn) and iron (Fe): interdependency of transport and regulation. Neurotox Res 18:124–131
Gunshin H, Mackenzie B, Berger UV, Gunshin Y, Romero MF, Boron WF, Nussberger S, Gollan JL, Hediger MA (1997) Cloning and characterization of a mammalian proton-coupled metal-ion transporter. Nature 388:482–488
Daly MJ (2006) Modulating radiation resistance: insights based on defenses against reactive oxygen species in the radioresistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans. Clin Lab Med 26:491–504
Daly MJ (2009) A new perspective on radiation resistance based on Deinococcus radiodurans. Nat Rev Microbiol 7:237–245
Daly MJ, Gaidamakova EK, Matrosova VY, Vasilenko A, Zhai M, Venkateswaran A, Hess M, Omelchenko MV, Kostandarithes HM, Makarova KS, Wackett LP, Fredrickson JK, Ghosal D (2004) Accumulation of Mn(II) in Deinococcus radiodurans facilitates gamma-radiation resistance. Science 306:1025–1028
Acknowledgements
The authors are supported by Grants from NCCIH and the Office of Dietary Supplements of the National Institutes of Health RO1 AT007442, the Malcolm Feist Endowed Chair in Diabetes, and funded by a fellowship from the Malcolm Feist Cardiovascular Research Endowment, LSU Health Shreveport. The authors thank Ms Georgia Morgan for excellent editing of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burlet, E., Jain, S.K. Manganese supplementation increases adiponectin and lowers ICAM-1 and creatinine blood levels in Zucker type 2 diabetic rats, and downregulates ICAM-1 by upregulating adiponectin multimerization protein (DsbA-L) in endothelial cells. Mol Cell Biochem 429, 1–10 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2931-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2931-7