Abstract
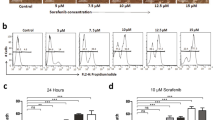
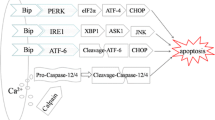
Recent reports considered that it was the disturbance of calcium homeostasis and the accumulation of misfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) that activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) apoptosis and promoted fibrosis resolution. However, the signal-transducing events that are activated by ER stress after HSCs activation were incompletely understood. In this study, we induced ER stress with thapsigargin (TG), and determined the activation of calpain and the cleavage of caspase by analyzing the protein levels and the correspondingly increased intracellular calcium levels and the induction of the proapoptotic transcription factor CHOP. Moreover, the phosphorylation of JNK and p38 MAPK were followed by the activation of the executioner caspases, caspase-3. As expected, preventing an increase in intracellular calcium levels using intracellular calcium chelators, EGTA, and BAPTA/AM, could substantially inhibit the phosphorylation of JNK and p38 MAPK, abolish the activation of calpains, namely caspase-12, caspase-9, and caspase-3, and provide significant protection for TG-treated activated HSCs. Interestingly, pretreatment with p38 MAPK inhibitor SB202190, JNK inhibitor SP600125, the pan-caspase inhibitor z-VAD-FMK, or calpain inhibitors calpeptin, significantly reduced the cell apoptosis and the cleavage of caspase-12 and caspase-3. However, pretreatment with z-VAD-FMK failed to reduce the activation of calpain. Additionally, pretreatment with SB202190 and SP600125 also decreased the expression of CHOP. Importantly, PDGF-induced collagen Col1α1 and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), markers for the perpetuation phase of HSCs activation, were inhibited in TG-treated activated HSCs. These findings showed that the Calpain/Caspase-12 activation induced by ER stress and the JNK/p38 MAPK phosphorylation induced by the increase of intracellular calcium concentration releasing from ER are the novel signaling pathway underlying the molecular mechanism of fibrosis recovery.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- α-SMA:
-
Alpha-smooth muscle actin
- CHOP:
-
C/EBP homologues protein
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase
- HF:
-
Hepatic fibrosis
- HSCs:
-
Hepatic stellate cells
- JNK:
-
C-jun N-terminal kinase
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- TG:
-
Thapsigargin
- UPR:
-
Unfolded protein response
References
De Minicis S, Rychlicki C, Agostinelli L, Saccomanno S, Candelaresi C, Trozzi L, Mingarelli E, Facinelli B, Magi G, Palmieri C, Marzioni M, Benedetti A, Svegliati-Baroni G (2013) Dysbiosis contributes to fibrogenesis in the course of chronic liver injury in mice. Hepatology 59(5):1738–1749. doi:10.1002/hep.26695
Jiang JX, Torok NJ (2013) Liver injury and the activation of the hepatic myofibroblasts. Curr Pathobiol Rep 1(3):215–223. doi:10.1007/s40139-013-0019-6
Svegliati-Baroni G, De Minicis S, Marzioni M (2008) Hepatic fibrogenesis in response to chronic liver injury: novel insights on the role of cell-to-cell interaction and transition. Liver Int 28(8):1052–1064. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2008.01825.x
Bian EB, Huang C, Wang H, Chen XX, Tao H, Zhang L, Lv XW, Li J (2013) The role of methyl-CpG binding protein 2 in liver fibrosis. Toxicology 309:9–14. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2013.04.008
Elsharkawy AM, Oakley F, Mann DA (2005) The role and regulation of hepatic stellate cell apoptosis in reversal of liver fibrosis. Apoptosis 10(5):927–939. doi:10.1007/s10495-005-1055-4
Kisseleva T, Brenner DA (2007) Role of hepatic stellate cells in fibrogenesis and the reversal of fibrosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 22(Suppl 1):S73–S78. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04658.x
Malhi H, Kaufman RJ (2011) Endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver disease. J Hepatol 54(4):795–809. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2010.11.005
Lenna S, Trojanowska M (2012) The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response in fibrosis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 24(6):663–668. doi:10.1097/BOR.0b013e3283588dbb
Friedman SL (2005) Mac the knife? Macrophages—the double-edged sword of hepatic fibrosis. J Clin Invest 115(1):29–32. doi:10.1172/JCI23928
Liu H, Li J, Huang Y, Huang C (2012) Inhibition of transient receptor potential melastain 7 channel increases HSCs apoptosis induced by TRAIL. Life Sci 90(15–16):612–618. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2012.02.012
Tang X, Yang J, Li J (2009) Sensitization of human hepatic stellate cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis by leflunomide. Biol Pharm Bull 32(6):963–967
Tang X, Yang J, Li J (2009) Accelerative effect of leflunomide on recovery from hepatic fibrosis involves TRAIL-mediated hepatic stellate cell apoptosis. Life Sci 84(15–16):552–557
Urra H, Dufey E, Lisbona F, Rojas-Rivera D, Hetz C (2013) When ER stress reaches a dead end. Biochim Biophys Acta 1833(12):3507–3517. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.07.024
Zhou AX, Tabas I (2013) The UPR in atherosclerosis. Semin Immunopathol 35(3):321–332. doi:10.1007/s00281-013-0372-x
Sammels E, Parys JB, Missiaen L, De Smedt H, Bultynck G (2010) Intracellular Ca2+ storage in health and disease: a dynamic equilibrium. Cell Calcium 47(4):297–314. doi:10.1016/j.ceca.2010.02.001
Logue SE, Cleary P, Saveljeva S, Samali A (2013) New directions in ER stress-induced cell death. Apoptosis 18(5):537–546. doi:10.1007/s10495-013-0818-6
de la Cadena SG, Hernandez-Fonseca K, Camacho-Arroyo I, Massieu L (2014) Glucose deprivation induces reticulum stress by the PERK pathway and caspase-7- and calpain-mediated caspase-12 activation. Apoptosis 19(3):414–427. doi:10.1007/s10495-013-0930-7
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu J, Yankner BA, Yuan J (2000) Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by amyloid-beta. Nature 403(6765):98–103. doi:10.1038/47513
Dourdin N, Bhatt AK, Dutt P, Greer PA, Arthur JS, Elce JS, Huttenlocher A (2001) Reduced cell migration and disruption of the actin cytoskeleton in calpain-deficient embryonic fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 276(51):48382–48388. doi:10.1074/jbc.M108893200
Raimbourg Q, Perez J, Vandermeersch S, Prignon A, Hanouna G, Haymann J-P, Baud L, Letavernier E (2013) The calpain/calpastatin system has opposing roles in growth and metastatic dissemination of melanoma. PLoS One 8(4):e60469
Morishima N, Nakanishi K, Takenouchi H, Shibata T, Yasuhiko Y (2002) An endoplasmic reticulum stress-specific caspase cascade in apoptosis. Cytochrome c-independent activation of caspase-9 by caspase-12. J Biol Chem 277(37):34287–34294. doi:10.1074/jbc.M204973200
Zhang H, Li H, Liu X, Bi J (2013) Effect of caspase-9 inhibition on endoplasmic reticulum stress induced cortical neuronal injury in rats. Int J Clin Exp Med 6(7):546–551
Brenner C, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Kroemer G (2013) Decoding cell death signals in liver inflammation. J Hepatol 59(3):583–594. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2013.03.033
Parsons CJ, Takashima M, Rippe RA (2007) Molecular mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 22(Suppl 1):S79–S84. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04659.x
Xie JL, Li J, Huang C, Huang Y, Zhang SP, Lin Z, Ji JQ (2012) The expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress in recovery of CCl4 induced liver fibrosis in rat. Acta Univ Med Anhui 47(9):1028–1032
Darling NJ, Cook SJ (2014) The role of MAPK signalling pathways in the response to endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biochim Biophys Acta. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.01.009
Lu T-H, Tseng T-J, Su C-C, Tang F-C, Yen C-C, Liu Y-Y, Yang C-Y, Wu C-C, Chen K-L, Hung D-Z (2014) Arsenic induces reactive oxygen species-caused neuronal cell apoptosis through JNK/ERK-mediated mitochondria-dependent and GRP 78/CHOP-regulated pathways. Toxicol Lett 224(1):130–140
Wang JQ, Chen X, Zhang C, Tao L, Zhang ZH, Liu XQ, Xu YB, Wang H, Li J, Xu DX (2013) Phenylbutyric acid protects against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrogenesis in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 266(2):307–316. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2012.11.007
Lim M, Devi L, Rozenfeld R (2011) Cannabidiol causes activated hepatic stellate cell death through a mechanism of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Dis 2(6):e170
Paredes RM, Bollo M, Holstein D, Lechleiter JD (2013) Luminal Ca2+ depletion during the unfolded protein response in Xenopus oocytes: cause and consequence. Cell Calcium 53(4):286–296. doi:10.1016/j.ceca.2013.01.002
Failli P, Ruocco C, De Franco R, Caligiuri A, Gentilini A, Giotti A, Gentilini P, Pinzani M (1995) The mitogenic effect of platelet-derived growth factor in human hepatic stellate cells requires calcium influx. Am J Physiol 269(5 Pt 1):C1133–C1139
Hashmi AZ, Hakim W, Kruglov EA, Watanabe A, Watkins W, Dranoff JA, Mehal WZ (2007) Adenosine inhibits cytosolic calcium signals and chemotaxis in hepatic stellate cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 292(1):G395–G401. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00208.2006
Hernández-Gea V, Hilscher M, Rozenfeld R, Lim MP, Nieto N, Werner S, Devi LA, Friedman SL (2013) Endoplasmic reticulum stress induces fibrogenic activity in hepatic stellate cells through autophagy. J Hepatol 59(1):98–104
De Minicis S, Candelaresi C, Agostinelli L, Taffetani S, Saccomanno S, Rychlicki C, Trozzi L, Marzioni M, Benedetti A, Svegliati-Baroni G (2012) Endoplasmic Reticulum stress induces hepatic stellate cell apoptosis and contributes to fibrosis resolution. Liver Int 32(10):1574–1584. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2012.02860.x
Nelson WB, Smuder AJ, Hudson MB, Talbert EE, Powers SK (2012) Cross-talk between the calpain and caspase-3 proteolytic systems in the diaphragm during prolonged mechanical ventilation. Crit Care Med 40(6):1857–1863. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e318246bb5d
Storr SJ, Lee KW, Woolston CM, Safuan S, Green AR, Macmillan RD, Benhasouna A, Parr T, Ellis IO, Martin SG (2012) Calpain system protein expression in basal-like and triple-negative invasive breast cancer. Ann Oncol 23(9):2289–2296. doi:10.1093/annonc/mds176
Fang L, Zhan S, Huang C, Cheng X, Lv X, Si H, Li J (2013) TRPM7 channel regulates PDGF-BB-induced proliferation of hepatic stellate cells via PI3K and ERK pathways. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 272(3):713–725. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2013.08.009
Si HF, Lv X, Guo A, Jiang H, Li J (2008) Suppressive effect of leflunomide on rat hepatic stellate cell proliferation involves on PDGF-BB-elicited activation of three mitogen-activated protein kinases. Cytokine 42(1):24–31. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2008.01.017
Tamaki N, Hatano E, Taura K, Tada M, Kodama Y, Nitta T, Iwaisako K, Seo S, Nakajima A, Ikai I, Uemoto S (2008) CHOP deficiency attenuates cholestasis-induced liver fibrosis by reduction of hepatocyte injury. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 294(2):G498–G505. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00482.2007
Cai DT, Jin H, Xiong QX, Liu WG, Gao ZG, Gu GX, Qiu YH (2013) ER stress and ASK1-JNK activation contribute to oridonin-induced apoptosis and growth inhibition in cultured human hepatoblastoma HuH-6 cells. Mol Cell Biochem 379(1–2):161–169. doi:10.1007/s11010-013-1638-2
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation Project (No. 81102493, 81273526, 81072686) and the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (No. 20103420120001).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Y Huang and Xiaohui Li are co-first authors; they contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Li, X., Wang, Y. et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced hepatic stellate cell apoptosis through calcium-mediated JNK/P38 MAPK and Calpain/Caspase-12 pathways. Mol Cell Biochem 394, 1–12 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2073-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2073-8