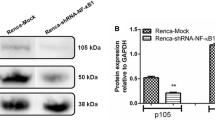
Abstract
Phospholipase Cε (PLCε), a downstream effector of small GTPase superfamily, has been identified to play a crucial role in tumorigenesis. Previously, our studies have showed that PLCε promotes proliferation of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) cells. However, the molecular mechanisms by which PLCε enhances the survival phenotype of RCC cells are still not fully instructed. In the present study, we first demonstrated that PLCε was highly expressed and had a close correlation with Ki67 protein expression in RCC tissue samples. Further, we found that downregulation of PLCε expression repressed growth and induced apoptosis in RCC cells. In addition, we reported a mechanism by which knockdown of PLCε gene potently suppressed the nuclear factor kappa (NF-κB) signaling pathway through action on inhibitor of κB kinase. Moreover, silencing PLCε gene decreased vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression, which was a downstream growth factor of NF-κB signaling pathway. Finally, downregulation of VEGF was severely enhanced by treatment cells with NF-κB specific inhibitor BAY11-7028 in PLCε knockdown cells. Taken together, these findings suggest that PLCε promotes RCC cell growth via NF-κB-mediated upregulation of VEGF.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Drucker BJ (2005) Renal cell carcinoma: current status and future prospects. Cancer Treat Rev 31(7):536–545
Ahmedin Jemal DVM, Rebecca Siegel MPH, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ (2009) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 59(4):225–249. doi:10.3322/caac.20006
Song C, Hu CD, Masago M, Kariyai K, Yamawaki-Kataoka Y, Shibatohge M, Wu D, Satoh T, Kataoka T (2001) Regulation of a novel human phospholipase C, PLCepsilon, through membrane targeting by Ras. J Biol Chem 276(4):2752–2757
Wing MR, Bourdon DM, Harden TK (2003) PLC-epsilon: a shared effector protein in Ras-, Rho-, and G alpha beta gamma-mediated signaling. Mol Interv 3(5):273–280
Rhee SG (2001) Regulation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C*. Annu Rev Biochem 70(1):281–312. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.70.1.281
Bai Y, Edamatsu H, Maeda S, Saito H, Suzuki N, Satoh T, Kataoka T (2004) Crucial role of phospholipase Cε in chemical carcinogen-induced skin tumor development. Cancer Res 64(24):8808–8810
Burguignon LY, Gilad E, Brightman A, Diedrich F, Singleton P (2006) Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction with leukemia-associated RhoGEF and epidermal growth factor receptor promotes Rho/Ras co-activation, phospholipase Cϵ-Ca2+ signaling, and cytoskeleton modification in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 281(20):14026–14040
Wang LD, Zhou FY, Li XM et al (2010) Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects identifies susceptibility loci at PLCE1 and C20orf54. Nat Genet 42(9):759–763. doi:10.1038/ng.648
Guo YC, Luo CL, Cai XZ, WU XH (2008) Expression and clinical significance of phospholipase C-epsilon gene in transitional cell carcinoma of bladder. Chin J Clin Lab Sci 26(1):41–52
Ling Y, Chunli L, Xiaohou W, Qiaoling Z (2011) Involvement of the PLCε/PKCα pathway in human BIU-87 bladder cancer cell proliferation. Cell Biol Int 35(10):1031–1036. doi:10.1042/CBI20090101
Cheng H, Luo C, Wu X, Zhang Y, He Y, Wu Q, Xia Y, Zhang J (2011) shRNA targeting PLCε inhibits bladder cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Urology 78(2):474. doi:10.1016/j.urology e7–474
Ou L, Guo Y, Luo C, Wu X, Zhao Y, Cai X (2010) RNA interference suppressing PLCE1 gene expression decreases invasive power of human bladder cancer T24 cell line. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 200(2):110–119. doi:10.1016/j.cancergencyto
Gilmore TD (2006) Introduction to NF-κB: players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene 25(51):6680–6684
Dolcet X, Llobet D, Pallares J, Matias-Guiu X (2005) NF-kB in development and progression of human cancer. Virchows Arch 446(5):475–482
Karin M (2006) Nuclear factor-κB in cancer development and progression. Nature 441(7092):431–436
Richmond Ann (2002) NF-κB, chemokine gene transcription and tumour growth. Nat Rev Immunol 2(9):664–674. doi:10.1038/nri887
Rayet B, Gelinas C (1999) Aberrant rel/nfkb genes and activity in human cancer. Oncogene 18(49):6938–6947
He G, Yu GY, Temkin V, Ogata H, Kuntzen C, Sakurai T, Sieghart W, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Leffert HL, Karin M (2010) Hepatocyte IKKβ/NF-κB inhibits tumor promotion and progression by preventing oxidative stress-driven STAT3 activation. Cancer Cell 17(3):286–297. doi:10.1016/j.ccr
Umar S, Sarkar S, Cowey S, Singh P (2008) Activation of NF-κB is required for mediating proliferative and antiapoptotic effects of progastrin on proximal colonic crypts of mice, in vivo. Oncogene 27(42):5599–5611
Oya M, Takayanagi A, Horiguchi A, Mizuno R, Ohtsubo M, Marumo K, Shimizu N, Murai M (2003) Increased nuclear factor-κB activation is related to the tumor development of renal cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 24(3):377–384
Ferrara N, Kerbel RS (2005) Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature 438(7070):967–974. doi:10.1038/nature04483
Hicklin DJ, Ellis LM (2005) Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol 23(5):1011–1027
Berse B, Brown LF, Van de Water L, Dvorak HF, Senger DR (1992) Vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) gene is expressed differentially in normal tissues, macrophages, and tumors. Mol Biol Cell 3(2):211–220
Verheul HM, Hoekman K, Luykx-de Bakker S, Eekman CA, Folman CC, Broxterman HJ, Pinedo HM (1997) Platelet: transporter of vascular endothelial growth factor. Clin Cancer Res 3(12 Pt 1):2187–2190
Ferrara N (2005) VEGF as a therapeutic target in cancer. Oncology 69(Suppl. 3):11–16. doi:10.1159/000088479
Benjamin LE, Golijanin D, Itin A, Pode D, Keshet E (1999) Selective ablation of immature blood vessels in established human tumors follows vascular endothelial growth factor withdrawal. J Clin Invest 103(2):159–165
Zhang X, Yamashita M, Uetsuki H, Kakehi Y (2002) Angiogenesis in renal cell carcinoma: evaluation of microvessel density, vascular endothelial growth factor and matrix metalloproteinases. Int J Urol 9(9):509–514
Yildiz E, Gokce G, Kilicarslan H, Ayan S, Goze OF, Gultekin EY (2004) Prognostic value of the expression of Ki-67, CD44 and vascular endothelial growth factor, and microvessel invasion, in renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int 93(7):1087–1093
Jacobsen J, Grankvist K, Rasmuson T, Bergh A, Landberg G, Ljungberg B (2004) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor protein in human renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int 93(3):297–302
Xu B, He Y, Wu X, Luo C, Liu A, Zhang J (2012) Exploration of the correlations between interferon-γ in patient serum and HEPACAM in bladder transitional cell carcinoma, and the interferon-γ mechanism inhibiting BIU-87 proliferation. J Urol 188(4):1346–1353. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2012.06.005
Wang Q, Luo C, Wu X, Du H, Song X, Fan Y (2013) HepaCAM and p-mTOR are closely correlated in transitional cell carcinoma of bladder and expression of hepaCAM inhibits proliferation via an AMPK/mTOR-dependent pathway in human bladder cancer cells. J Urol. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2013.05.013
Yun S, Hong WP, Choi JH, Yi KS, Chae SK, Ryu SH, Suh PG (2008) Phospholipase C-epsilon augments epidermal growth factor-dependent cell growth by inhibiting epidermal growth factor receptor down-regulation. J Biol Chem 283(1):341–349
Arsura M, Mercurio F, Oliver AL, Thorgeirsson SS, Sonenshein GE (2000) Role of the IkappaB kinase complex in oncogenic Ras- and Raf-mediated transformation of rat liver epithelial cells. Mol Cell Biol 20(15):5381–5391
Li H, Ye X, Mahanivong C, Bian D, Chun J, Huang S (2005) Signaling mechanisms responsible for lysophosphatidic acid-induced urokinase plasminogen activator expression in ovarian cancer cells. J Biol Chem 280(11):10564–10571
Fan S, Meng Q, Laterra JJ, Rosen EM (2007) Ras effector pathways modulate scatter factor-stimulated NF-kappaB signaling and protection against DNA damage. Oncogene 26(33):4774–4796
Arai Y, Nonomura N, Nakai Y, Nishimura K, Oka D, Shiba M, Nakayama M, Takayama H, Mizutani Y, Miki T, Okuyama A (2008) The growth-inhibitory effects of dexamethasone on renal cell carcinoma in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Invest 26(1):35–40
Oka D, Nishimura K, Shiba M, Nakai Y, Arai Y, Nakayama M, Takayama H, Inoue H, Okuyama A, Nonomura N (2007) Sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide suppresses tumor growth in a xenograft model of renal cell carcinoma by inhibiting the activation of NF-kappaB. Int J Cancer 120(12):2576–2581
Paradis V, Ben Lagha N, Zeimoura L, Blanchet P, Eschwege P, Ba N, Benoît G, Jardin A, Bedossa P (2000) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in renal cell carcinomas. Virchows Arch 436(4):351–356
Li M, Edamatsu H, Kitazawa R, Kitazawa S, Kataoka T (2009) Phospholipase Cepsilon promotes intestinal tumorigenesis of Apc(Min/+) mice through augmentation of inflammation and angiogenesis. Carcinogenesis 30(8):1424–1432
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of P. R. China (Grant No. 81072086).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, Hf., Ou, Lp., Song, Xd. et al. Nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway is involved in phospholipase Cε-regulated proliferation in human renal cell carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biochem 389, 265–275 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1948-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1948-4