Abstract
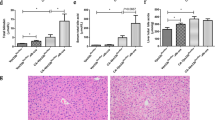
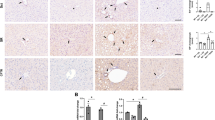
The bile salt export pump (BSEP/Bsep; gene symbol ABCB11/Abcb11) translocates bile salts across the hepatocyte canalicular membrane into bile in humans and mice. In humans, mutations in the ABCB11 gene cause a severe childhood liver disease known as progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 2. Targeted inactivation of mouse Bsep produces milder persistent cholestasis due to detoxification of bile acids through hydroxylation and alternative transport pathways. The purpose of the present study was to determine whether functional expression of hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP) and microsomal epoxide hydrolase (mEH) is altered by Bsep inactivation in mice and whether bile acids regulate CYP and mEH expression in Bsep −/− mice. CYP expression was determined by measuring protein levels of Cyp2b, Cyp2c and Cyp3a enzymes and CYP-mediated activities including lithocholic acid hydroxylation, testosterone hydroxylation and alkoxyresorufin O-dealkylation in hepatic microsomes prepared from female and male Bsep −/− mice fed a normal or cholic acid (CA)-enriched diet. The results indicated that hepatic lithocholic acid hydroxylation was catalyzed by Cyp3a/Cyp3a11 enzymes in Bsep −/− mice and that 3-ketocholanoic acid and murideoxycholic acid were major metabolites. CA feeding of Bsep −/− mice increased hepatic Cyp3a11 protein levels and Cyp3a11-mediated testosterone 2β-, 6β-, and 15β-hydroxylation activities, increased Cyp2b10 protein levels and Cyp2b10-mediated benzyloxyresorufin O-debenzylation activity, and elevated Cyp2c29 and mEH protein levels. We propose that bile acids upregulate expression of hepatic Cyp3a11, Cyp2b10, Cyp2c29 and mEH in Bsep −/− mice and that Cyp3a11 and multidrug resistance-1 P-glycoproteins (Mdr1a/1b) are vital components of two distinct pathways utilized by mouse hepatocytes to expel bile acids.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hrycay EG, Bandiera SM (2008) Cytochrome P450 enzymes. In: Gad SC (ed) Preclinical development handbook: ADME and biopharmaceutical properties. Wiley, Hoboken, pp 627–696
Hrycay EG, Bandiera SM (2009) Expression, function and regulation of mouse cytochrome P450 enzymes: comparison with human cytochrome P450 enzymes. Curr Drug Metab 10:1151–1183 (Addendum in Curr Drug Metab 2010; 11:560)
Hrycay EG, Bandiera SM (2012) The monooxygenase, peroxidase, and peroxygenase properties of cytochrome P450. Arch Biochem Biophys 522:71–89
Hofmann AF (1999) The continuing importance of bile acids in liver and intestinal disease. Arch Intern Med 159:2647–2658
Hofmann AF (2002) Cholestatic liver disease: pathophysiology and therapeutic options. Liver 22(Suppl 2):14–19
Hofmann AF, Hagey LR (2008) Bile acids: chemistry, pathochemistry, biology, pathobiology, and therapeutics. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:2461–2483
Ling V, Wang R, Sheps JA (2011) Polyhydroxylated bile acids for treatment of biliary disorders. Patent Application Number: 20110263546
Wang R, Salem M, Yousef IM, Tuchweber B, Lam P, Childs SJ, Helgason CD, Ackerley C, Phillips MJ, Ling V (2001) Targeted inactivation of sister of P-glycoprotein gene (spgp) in mice results in nonprogressive but persistent intrahepatic cholestasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:2011–2016
Kosters A, Karpen SJ (2008) Bile acid transporters in health and disease. Xenobiotica 38:1043–1071
Sinal CJ, Tohkin M, Miyata M, Ward JM, Lambert G, Gonzalez FJ (2000) Targeted disruption of the nuclear receptor FXR/BAR impairs bile acid and lipid homeostasis. Cell 102:731–744
Plass JRM, Mol O, Heegsma J, Geuken M, Faber KN, Jansen PLM, Müller M (2002) Farnesoid X receptor and bile salts are involved in transcriptional regulation of the gene encoding the human bile salt export pump. Hepatology 35:589–596
Zollner G, Fickert P, Fuchsbichler A, Silbert D, Wagner M, Arbeiter S, Gonzalez FJ, Marschall HU, Zatloukal K, Denk H, Trauner M (2003) Role of nuclear bile acid receptor, FXR, in adaptive ABC transporter regulation by cholic and ursodeoxycholic acid in mouse liver, kidney and intestine. J Hepatol 39:480–488
Childs S, Yeh RL, Hui D, Ling V (1998) Taxol resistance mediated by transfection of the liver-specific sister gene of P-glycoprotein. Cancer Res 58:4160–4167
Lam P, Wang R, Ling V (2005) Bile acid transport in sister of P-glycoprotein (ABCB11) knockout mice. Biochemistry 44:12598–12605
Wang R, Chen HL, Liu L, Sheps JA, Phillips MJ, Ling V (2009) Compensatory role of P-glycoproteins in knockout mice lacking the bile salt export pump. Hepatology 50:948–956
Strautnieks SS, Bull LN, Knisely AS, Kocoshis SA, Dahl N, Arnell H, Sokal E, Dahan K, Childs S, Ling V, Tanner MS, Kagalwalla AF, Németh A, Pawllowska J, Baker A, Mieli-Vergani G, Freimer NB, Gardiner RM, Thompson RJ (1998) A gene encoding a liver-specific ABC transporter is mutated in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Nat Genet 20:233–238
Wang R, Lam P, Liu L, Forrest D, Yousef IM, Mignault D, Phillips MJ, Ling V (2003) Severe cholestasis induced by cholic acid feeding in knockout mice of sister of P-glycoprotein. Hepatology 38:1489–1499
Davit-Spraul A, Gonzales E, Baussan C, Jacquemin E (2009) Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Orphanet J Rare Dis 4:1–12
Perwaiz S, Forrest D, Mignault D, Tuchweber B, Phillips MJ, Wang R, Ling V, Yousef IM (2003) Appearance of atypical 3α,6β7β12α-tetrahydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid in spgp knockout mice. J Lipid Res 44:494–502
Megaraj V, Lida T, Jungsuwadee P, Hofmann AF, Vore M (2010) Hepatobiliary disposition of 3α,6α,7α,12α-tetrahydroxy-cholanoyl taurine: a substrate for multiple canalicular transporters. Drug Metab Dispos 38:1723–1730
Miyata M, Kudo G, Lee YH, Yang TJ, Gelboin HV, Fernandez-Salguero P, Kimura P, Gonzalez FJ (1999) Targeted disruption of the microsomal epoxide hydrolase gene: microsomal epoxide hydrolase is required for the carcinogenic activity of 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene. J Biol Chem 274:23963–23968
Fretland AJ, Omiecinski CJ (2000) Epoxide hydrolases: biochemistry and molecular biology. Chem Biol Interact 129:41–59
Morisseau C, Newman JW, Wheelock CE, Hill T III, Morin D, Buckpitt AR, Hammock BD (2008) Development of metabolically stable inhibitors of mammalian microsomal epoxide hydrolase. Chem Res Toxicol 21:951–957
von Dippe P, Amoui M, Stellwagon RH, Levy D (1996) The functional expression of sodium-dependent bile acid transport in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells transfected with the cDNA for microsomal epoxide hydrolase. J Biol Chem 271:18176–18180
Ananthanarayanan M, Bucuvalas JC, Shneider BL, Sipple CJ, Suchy FJ (1991) An ontogenically regulated 48-kDa protein is a component of the Na+-bile acid cotransporter of rat liver. Am J Physiol-Gastrointest Liver Physiol 261:G810–G817
von Dippe P, Amoui M, Alves C, Levy D (1993) Na+-dependent bile acid transport by hepatocytes is mediated by a protein similar to microsomal epoxide hydrolase. Am J Physiol- Gastrointest Liver Physiol 264:G528–G534
Zhu QS, von Dippe P, Xing W, Levy D (1999) Membrane topology and cell surface targeting of microsomal epoxide hydrolase: evidence for multiple topological orientations. J Biol Chem 274:27898–27904
Zhu QS, Xing W, Qian B, von Dippe P, Shneider BJ, Fox VL, Levy D (2003) Inhibition of human m-epoxide hydrolase gene expression in a case of hypercholanemia. Biochim Biophys Acta 1638:208–216
Kullak-Ublick GA, Stieger B, Hagenbuch B, Meier PJ (2000) Hepatic transport of bile salts. Sem Liver Dis 20:273–292
Stieger B (2011) The role of the sodium-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) and of the bile salt export pump (BSEP) in physiology and pathophysiology of bile formation. Handb Exp Pharmacol 201:205–259
von Dippe P, Zhu QS, Levy D (2003) Cell surface expression and bile acid transport function of one topological form of m-epoxide hydrolase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 309:804–809
Alves C, von Dippe P, Amoui M, Levy D (1993) Bile acid transport into hepatocyte smooth endoplasmic reticulum vesicles is mediated by microsomal epoxide hydrolase, a membrane protein exhibiting two distinct topological orientations. J Biol Chem 268:20148–20155
Arrese M, Pizarro M, Solís N, Accatino L (1997) Adaptive regulation of hepatic bile salt transport: role of bile salt hydrophobicity and microtubule-dependent vesicular pathway. J Hepatol 26:694–702
Crawford JM, Berken CA, Gollan JL (1988) Role of the hepatocyte microtubular system in the excretion of bile salts and biliary lipid: implications for intracellular vesicular transport. J Lipid Res 29:144–156
Erlinger S (1996) Do intracellular organelles have any role in transport of bile acids by hepatocytes? J Hepatol 24(Suppl 1):88–93
Araya Z, Wikvall K (1999) 6α-Hydroxylation of taurochenodeoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid by CYP3A4 in human liver microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1438:47–54
Bodin K, Lindbom U, Diczfalusy U (2005) Novel pathways of bile acid metabolism involving CYP3A4. Biochim Biophys Acta 1687:84–93
Deo AK, Bandiera SM (2008) Biotransformation of lithocholic acid by rat hepatic microsomes: metabolite analysis by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Drug Metab Dispos 36:442–451
Deo AK, Bandiera SM (2009) 3-Ketocholanoic acid is the major in vitro human hepatic microsomal metabolite of lithocholic acid. Drug Metab Dispos 37:1938–1947
Xie W, Radominska-Pandya A, Shi Y, Simon CM, Nelson MC, Ong ES, Waxman DJ, Evans RM (2001) An essential role for nuclear receptors SXR/PXR in detoxification of cholestatic bile acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:3375–3380
Deo AK, Bandiera SM (2008) Identification of human hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in the biotransformation of cholic and chenodeoxycholic acid. Drug Metab Dispos 36:1983–1991
Wong A, Bandiera SM (1996) Inductive effect of Telazol® on hepatic expression of cytochrome P450 2B in rats. Biochem Pharmacol 52:735–742
Kania-Korwel I, Hrycay EG, Bandiera SM, Lehmler HJ (2008) 2,2′3,3′6,6′-Hexachlorobiphenyl (PCB 136) atropisomers interact enantioselectively with hepatic microsomal cytochrome P450 enzymes. Chem Res Toxicol 21:1295–1303
Omura T, Sato R (1964) The carbon monoxide-binding pigment of liver microsomes. I. Evidence for its hemoprotein nature. J Biol Chem 239:2370–2378
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Anderson MD, Bandiera SM, Chang TKH, Bellward GD (1998) Effect of androgen administration during puberty on hepatic CYP2C11, CYP3A, and CYP2A1 expression in adult female rats. Drug Metab Dispos 26:1031–1038
Burke MD, Thompson S, Weaver RJ, Wolf CR, Mayer RT (1994) Cytochrome P450 specificities of alkoxyresorufin O-dealkylation in human and rat liver. Biochem Pharmacol 48:923–936
Hrycay EG, Bandiera SM (2003) Spectral interactions of tetrachlorobiphenyls with hepatic microsomal cytochrome P450 enzymes. Chem Biol Interact 146:285–296
Ryan DE, Thomas PE, Levin W (1980) Hepatic microsomal cytochrome P-450 from rats treated with isosafrole. J Biol Chem 255:7941–7955
Meyer RP, Hagemeyer CE, Knoth R, Kurz G, Volk B (2001) Oxidative hydrolysis of scoparone by cytochrome P450 CYP2C29 reveals a novel metabolite. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 285:32–39
Jarukamjorn K, Sakuma T, Miyaura JI, Nemoto N (1999) Different regulation of the expression of mouse hepatic cytochrome P450 2B enzymes by glucocorticoid. Arch Biochem Biophys 369:89–99
Schuetz EG, Schmid W, Schutz G, Brimer C, Yasuda K, Kamataki T, Bornheim L, Myles K, Cole TJ (2000) The glucocorticoid receptor is essential for induction of cytochrome P-4502B by steroids but not for drug or steroid induction of Cyp3A or P-450 reductase in mouse liver. Drug Metab Dispos 28:268–278
Schuetz EG, Umbenhauer DR, Yasuda K, Brimer C, Nguyen L, Relling MV, Schuetz JD, Schinkel AH (2000) Altered expression of hepatic cytochromes P-450 in mice deficient in one or more mdr1 genes. Mol Pharmacol 57:188–197
Yamada H, Gohyama N, Honda SI, Hara T, Harada N, Oguri K (2002) Estrogen-dependent regulation of the expression of hepatic Cyp2b and 3a isoforms: assessment using aromatase-deficient mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 180:1–10
Bornheim LM, Correia MA (1990) Selective inactivation of mouse liver cytochrome P-450IIIA by cannabidiol. Mol Pharmacol 38:319–326
Bornheim LM, Correia MA (1989) Purification and characterization of a mouse liver cytochrome P-450 induced by cannabidiol. Mol Pharmacol 36:377–383
Nerurkar PV, Park SS, Thomas PE, Nims RW, Lubet RA (1993) Methoxyresorufin and benzyloxyresorufin: substrates preferentially metabolized by cytochromes P4501A2 and 2B, respectively, in the rat and mouse. Biochem Pharmacol 46:933–943
Guo GL, Lambert G, Negishi M, Ward JM, Brewer HB Jr, Kliewer SA, Gonzalez FJ, Sinal CJ (2003) Complementary roles of farnesoid X receptor, pregnane X receptor, and constitutive androstane receptor in protection against bile acid toxicity. J Biol Chem 278:45062–45071
Staudinger JL, Goodwin B, Jones SA, Hawkins-Brown D, MacKenzie KI, LaTour A, Liu Y, Klaassen CD, Brown KK, Reinhard J, Willson TM, Koller BH, Kliewer SA (2001) The nuclear receptor PXR is a lithocholic acid sensor that protects against liver toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:3369–3374
Zhang J, Huang W, Qatanani M, Evans RM, Moore DD (2004) The constitutive androstane receptor and pregnane X receptor function coordinately to prevent bile acid-induced hepatotoxicity. J Biol Chem 279:49517–49522
Schuetz EG, Strom S, Yasuda K, Lecureur V, Assem M, Brimer C, Lamba J, Kim RB, Ramachandran V, Komoroski BJ, Venkataramanan R, Cai H, Sinal CJ, Gonzalez FJ, Schuetz JD (2001) Disrupted bile acid homeostasis reveals an unexpected interaction among nuclear hormone receptors, transporters, and cytochrome P450. J Biol Chem 276:39411–39418
Goodwin B, Gauthier KC, Umetani M, Watson MA, Lochansky MI, Collins JL, Leitersdorf E, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA, Repa JJ (2003) Identification of bile acid precursors as endogenous ligands for the nuclear xenobiotic pregnane X receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:223–228
Gnerre C, Schuster GU, Roth A, Handschin C, Johansson L, Looser R, Parini P, Podvinec M, Robertsson K, Gustafsson JJ, Meyer UA (2005) LXR deficiency and cholesterol feeding affect the expression and phenobarbital-mediated induction of cytochromes P450 in mouse liver. J Lipid Res 46:1633–1642
Setchell KD, Dumaswala R, Colombo C, Ronchi M (1988) Hepatic bile acid metabolism during early development revealed from the analysis of human fetal gallbladder bile. J Biol Chem 263:16637–16644
Bremmelgaard A, Sjovall J (1980) Hydroxylation of cholic, chenodeoxycholic, and deoxycholic acids in patients with intrahepatic cholestasis. J Lipid Res 21:1072–1081
Nakagawa M, Setchell KD (1990) Bile acid metabolism in early life: studies of amniotic fluid. J Lipid Res 31:1089–1098
Yousef IM, Bouchard G, Tuchweber B, Plaa GL (1997) Monohydroxy bile acid induced cholestasis: role of biotransformation. Drug Metab Rev 29:167–181
Wang H, Negishi M (2003) Transcriptional regulation of cytochrome P450 2B genes by nuclear receptors. Curr Drug Metab 4:515–525
Teng S, Piquette-Miller M (2007) Hepatoprotective role of PXR activation and MRP3 in cholic acid-induced cholestasis. Br J Pharmacol 151:367–376
Harada N, Negishi M (1984) Mouse liver testosterone 15α-hydroxylase (cytochrome P-45015α). Purification, regioselectivity, stereospecificity, and sex-dependent expression. J Biol Chem 259:1265–1271
Sakuma T, Takai M, Endo Y, Kuroiwa M, Ôhara A, Jarukamjorn K, Honma R, Nemoto N (2000) A novel female-specific member of the CYP3A gene subfamily in the mouse liver. Arch Biochem Biophys 377:153–162
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (Grant Number MOP-81174 to S. B. and Grant Number MOP-42560 to V. L.) for supporting this work. We also thank Drs. I. Kania-Korwel and H. J. Lehmler (University of Iowa) for supplying hepatic microsomes prepared from female wild-type mice. We appreciate the skilled assistance of Ms. Grace Leung in the preparation of several figures and the valued assistance of Mr. Chris Low in the treatment of mice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hrycay, E., Forrest, D., Liu, L. et al. Hepatic bile acid metabolism and expression of cytochrome P450 and related enzymes are altered in Bsep −/− mice. Mol Cell Biochem 389, 119–132 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1933-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1933-y