Abstract
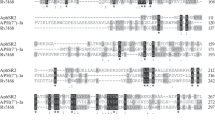
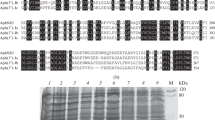
As part of an overall project to characterize the streptomycin phosphotransferase enzyme APH(6)-Id, which confers bacterial resistance to streptomycin, we cloned, expressed, purified, and characterized the enzyme. When expressed in Escherichia coli, the recombinant enzyme increased by up to 70-fold the minimum inhibitory concentration needed to inhibit cell growth. Size-exclusion chromatography gave a molecular mass of 31.4 ± 1.3 kDa for the enzyme, showing that it functions as a monomer. Activity was assayed using three methods: (1) an HPLC-based method that measures the consumption of streptomycin over time; (2) a spectrophotometric method that utilizes a coupled assay; and (3) a radioenzymatic method that detects production of 32P-labeled streptomycin phosphate. Altogether, the three methods demonstrated that streptomycin was consumed in the APH(6)-Id-catalyzed reaction, ATP was hydrolyzed, and streptomycin phosphate was produced in a substrate-dependent manner, demonstrating that APH(6)-Id is a streptomycin phosphotransferase. Steady-state kinetic analysis gave the following results: K m(streptomycin) of 0.38 ± 0.13 mM, K m(ATP) of 1.03 ± 0.1 mM, V max of 3.2 ± 1.1 μmol/min/mg, and k cat of 1.7 ± 0.6 s−1. Our study demonstrates that APH(6)-Id is a bona fide streptomycin phosphotransferase, functions as a monomer, and confers resistance to streptomycin.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jones D, Metzger HJ, Schatz A, Waksman SA (1944) Control of gram-negative bacteria in experimental animals by streptomycin. Science 100:103–105
Carter AP, Clemons WM, Broderson DE, Morgan-Warren RJ, Wimberly BT, Ramakrishnan V (2000) Functional insights from the structure of the 30S ribosomal subunit and its interactions with antibiotics. Nature 407:340–348
Davis BD (1987) Mechanism of bactericidal action of aminoglycosides. Microbiol Rev 51:341–350
Wright GD (1999) Aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes. Curr Opin Microbiol 2:499–503
Piepersberg W (1996) Streptomycin and related aminoglycosides. In: Vining LC, Stuttard C (eds) Genetics and biochemistry of antibiotic production. Butterworth Heinemann, Halifax, pp 531–570
Distler J, Mansouri K, Mayer G, Stockmann M, Piepersberg W (1992) Streptomycin biosynthesis and its regulation in Streptomycetes. Gene 115:105–111
Lim C-K, Smith MCM, Petty J, Baumberg S, Wootton JC (1989) Streptomyces griseus streptomycin phosphotransferase: expression of its gene in Escherichia coli and sequence homology with other antibiotic phosphotransferases and with eukaryotic protein kinases. J Gen Microbiol 135:3289–3302
Sugiyama M, Sakamoto M, Mochizuki H, Nimi O, Nomi R (1983) Purification and characterization of streptomycin 6-kinase, an enzyme implicated in self-protection of a streptomycin-producing micro-organism. J Gen Microbiol 129:1683–1687
Heinzel P, Werbitzky O, Distler J, Piepersbert W (1988) A second streptomycin resistance gene from Streptomyces griseus codes for streptomycin-3″-phosphotransferase. Relationships between antibiotic and protein kinases. Arch Microbiol 150:184–192
Shaw KJ, Rather PN, Hare RS, Miller GH (1993) Molecular genetics of aminoglycoside resistance genes and familial relationships of the aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes. Microbiol Rev 57:138–163
Mazodier P, Cossart P, Giraud E, Gasser F (1985) Completion of the nucleotide sequence of the central region of Tn5 confirms the presence of three resistance genes. Nucleic Acids Res 13:195–205
Scholz P, Haring V, Wittmann-Liebold B, Ashman D, Bagdasarian M, Scherzinger E (1989) Complete nucleotide sequence and gene organization of the broad-host-range plasmid RSF1010. Gene 75:271–288
Sundin GW, Bender CL (1993) Ecological and genetic analysis of copper and streptomycin resistance in Pseudomonas syringae pv. Syringae. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:1018–1024
Chiou C-S, Jones AL (1993) Nucleotide sequence analysis of a transposon (Tn5393) carrying streptomycin resistance genes in Erwinia amylovora and other gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol 175:732–740
Chiou C-S, Jones AL (1995) Expression and identification of the strA–strB gene pair from streptomycin-resistant Erwinia amylovora. Gene 152:47–51
Sundin GW, Bender CL (1996) Dissemination of the strA–strB streptomycin-resistance genes among commensal and pathogenic bacteria from humans, animals, and plants. Mol Ecol 5:133–143
Sundin GW (2000) Examination of base pair variants of the strA–strB streptomycin resistance genes from bacterial pathogens of humans, animals and plants. J Antimicrob Chemother 46:848–849
Pezella C, Ricci A, DiGiannatale E, Luzzi I, Carattoli A (2004) Tetracycline and streptomycin resistance genes, transposons, and plasmids in Salmonella enterica isolates from animals in Italy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48:903–908
Shaw PC, Liang AC, Kam KC, Ling JM (1996) Presence of strA–strB gene within a streptomycin-resistance operon in a clinical isolate of Shigella flexneri. Pathology 28:356–358
Collins AC III, Ashenafi M, Saunders AA, Byrnes WM (2007) Cloning and expression of streptomycin-inactivating enzymes APH(6)-Ia and APH(6)-Id. Cell Mol Biol 53:74–79
National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, NCCLS (1990) Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically. Approved Standard M7-A2, 2nd edn. NCCLS, Villanova
National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (1990) Performance standards for antimicrobial disk susceptibility tests. Approved Standard M2-A4, 4th edn. NCCLS, Villanova
Michael SS, Duch M, Paludan K, Jorgensen P, Finn SP (1992) Measurement of hygromycin B phosphotransferase activity in crude mammalian cell extracts by a simple dot-blot assay. Gene 112:257–260
Luedtke NW, Schepartz A (2005) Lanthanide-mediated phosphoester hydrolysis and phosphate elimination from phosphopeptides. Chem Commun 43:5426–5428
Martindale W (1982) The extra pharmacopoeia, 28th edn. Pharmaceutical Press, London
Collins III AC (2007b) Cloning, sequencing and expression of the gene for streptomycin-inactivating enzyme APH(6)-Ia from Streptomyces griseus. Dissertation, Howard University
Perlin MH, McCarty SC, Greer JP (1988) Coupled spectrofluorometric assay for aminoglycoside phosphotransferases. Anal Biochem 171:145–149
Fromm HJ, Zewe V (1962) Kinetic studies of yeast hexokinase. J Biol Chem 237:3027–3032
Siregar JJ, Miroshnikov K, Mobashery S (1995) Purification, characterization, and investigation of the mechanism of aminoglycoside 3′-phosphotransferase type Ia. Biochemistry 34:12681–12688
van Overbeek LS, Wellington EMH, Egan S, Smalla K, Heuer H, Collard J-M, Guillaume G, Karagouni AD, Nikolakopoulou TL, van Elsas JD (2002) Prevalence of streptomycin-resistance genes in bacterial populations in European habitats. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 42:277–288
Ramón-García S, Otal I, Martín C, Gómez-Lus R, Aínsa JA (2006) Novel streptomycin resistance gene from Mycobacterium fortuitum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50:3920–3922
McKay GA, Wright GD (1995) Kinetic mechanism of aminoglycoside phosphotransferase type IIIa: evidence for a Theorell–Chance mechanism. J Biol Chem 270:24686–24692
Thompson PR, Hughes DW, Cianciotto NP, Wright GD (1998) Spectinomycin kinase from Legionella pneumophila: characterization of substrate specificity and identification of catalytically important residues. J Biol Chem 273:14788–14795
Tolba S, Egan S, Kallifidas D, Wellington EHM (2002) Distribution of streptomycin resistance and biosynthesis genes in streptomycetes recovered from different soil sites. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 42:269–276
Wiener P, Egan S, Wellington EMH (1998) Evidence for transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in soil populations of streptomycetes. Mol Ecol 7:120501216
Egan S, Wiener P, Kallifidas D, Wellington EMH (1998) Transfer of streptomycin biosynthesis gene clusters within Streptomycetes isolated from soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:5061–5063
Anderson AS, Clark DJ, Gibbons PH, Sigmund JM (2002) The detection of diverse aminoglycoside phosphotransferases within natural populations of actinomycetes. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 29:60–69
Benveniste R, Davies J (1973) Aminoglycoside antibiotic-inactivating enzymes in actinomycetes similar to those present in clinical isolates of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70:2276–2280
Davies J, Wright GD (1997) Bacterial resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics. Trends Microbiol 5:234–240
Todar KG (2012) Todar’s online textbook of bacteriology. http://textbookofbacteriology.net/index.html. Accessed 3 May 2012
McKay GA, Thompson PR, Wright GD (1994) Broad spectrum aminoglycoside phosphotransferase type III from Enterococcus: overexpression, purification, and substrate specificity. Biochemistry 33:6936–6944
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support from the U. S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) RCMI program (Grant number 8G12MD007597) and MBRS-SCORE program (Grants number 3S06GM0816-33S1, SC3GM083752, and SC1GM08232). We especially thank Ms. Myrna Stupart of the Department of Microbiology at Howard University for help with the antibiotic susceptibility protocols and for providing E. coli control strain MM294.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashenafi, M., Ammosova, T., Nekhai, S. et al. Purification and characterization of aminoglycoside phosphotransferase APH(6)-Id, a streptomycin-inactivating enzyme. Mol Cell Biochem 387, 207–216 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1886-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1886-1