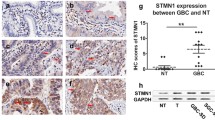
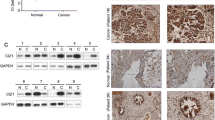
Abstract
Gallbladder cancer (GBC) is one of the most lethal neoplasm and is the fifth most common malignancy of gastrointestinal tract. The prognosis of gallbladder cancer is extremely terrible partially due to metastasis. Thus, understanding the molecular pathways controlling metastasis of this lethal disease may provide new targets for targeted therapeutic approach. In this study, we investigated the function of nemo-like kinase (NLK) in GBC growth and migration. Lentivirus-mediated siRNA was employed to alleviate the expression level of NLK in GBC cell lines (GBC-SD and SGC-996). Real-time PCR and western-blot analysis demonstrated that both mRNA and protein levels of NLK in GBC-SD and SGC-996 cells were decreased after infection with NLK-siRNA-expressing lentivirus (Lv-shNLK). The proliferation and in vitro tumorigenesis (colony formation) ability as well as migration of GBC-SD and SGC-996 cells with low NLK expression decreased significantly. Our results suggested that NLK is a key regulator involved in proliferation and migration of GBC, and it could be used as a potential therapeutic target for GBC.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
05 October 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-021-04229-8
References
Gourgiotis S, Kocher HM, Solaini L, Yarollahi A, Tsiambas E, Salemis NS (2008) Gallbladder cancer. Am J Surg 196(2):252–264. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2007.11.011
Zhu AX, Hong TS, Hezel AF, Kooby DA (2010) Current management of gallbladder carcinoma. Oncologist 15(2):168–181. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2009-0302
Brott BK, Pinsky BA, Erikson RL (1998) Nlk is a murine protein kinase related to Erk/MAP kinases and localized in the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(3):963–968
Mirkovic I, Charish K, Gorski SM, McKnight K, Verheyen EM (2002) Drosophila nemo is an essential gene involved in the regulation of programmed cell death. Mech Dev 119(1):9–20
Ishitani T, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Nagai S, Nishita M, Meneghini M, Barker N, Waterman M, Bowerman B, Clevers H, Shibuya H, Matsumoto K (1999) The TAK1-NLK-MAPK-related pathway antagonizes signalling between beta-catenin and transcription factor TCF. Nature 399(6738):798–802. doi:10.1038/21674
Yamada M, Ohnishi J, Ohkawara B, Iemura S, Satoh K, Hyodo-Miura J, Kawachi K, Natsume T, Shibuya H (2006) NARF, an nemo-like kinase (NLK)-associated ring finger protein regulates the ubiquitylation and degradation of T cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor (TCF/LEF). J Biol Chem 281(30):20749–20760. doi:10.1074/jbc.M602089200
Ohkawara B, Shirakabe K, Hyodo-Miura J, Matsuo R, Ueno N, Matsumoto K, Shibuya H (2004) Role of the TAK1-NLK-STAT3 pathway in TGF-beta-mediated mesoderm induction. Genes Dev 18(4):381–386. doi:10.1101/gad.1166904
Satoh K, Ohnishi J, Sato A, Takeyama M, Iemura S, Natsume T, Shibuya H (2007) Nemo-like kinase-myocyte enhancer factor 2A signaling regulates anterior formation in Xenopus development. Mol Cell Biol 27(21):7623–7630. doi:10.1128/MCB.01481-07
Biggs WH 3rd, Meisenhelder J, Hunter T, Cavenee WK, Arden KC (1999) Protein kinase B/Akt-mediated phosphorylation promotes nuclear exclusion of the winged helix transcription factor FKHR1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(13):7421–7426
Miyata Y, Nishida E (1999) Distantly related cousins of MAP kinase: biochemical properties and possible physiological functions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 266(2):291–295. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.1705
Kortenjann M, Nehls M, Smith AJ, Carsetti R, Schuler J, Kohler G, Boehm T (2001) Abnormal bone marrow stroma in mice deficient for nemo-like kinase, Nlk. Eur J Immunol 31(12):3580–3587. doi:10.1002/1521-4141(200112)31:12<3580:AID-IMMU3580>3.0.CO;2-N
Yasuda J, Tsuchiya A, Yamada T, Sakamoto M, Sekiya T, Hirohashi S (2003) Nemo-like kinase induces apoptosis in DLD-1 human colon cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 308(2):227–233
Jung KH, Kim JK, Noh JH, Eun JW, Bae HJ, Xie HJ, Ahn YM, Park WS, Lee JY, Nam SW (2010) Targeted disruption of Nemo-like kinase inhibits tumor cell growth by simultaneous suppression of cyclin D1 and CDK2 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Biochem 110(3):687–696. doi:10.1002/jcb.22579
Ding Y, Huang Y, Song N, Gao X, Yuan S, Wang X, Cai H, Fu Y, Luo Y (2010) NFAT1 mediates placental growth factor-induced myelomonocytic cell recruitment via the induction of TNF-alpha. J Immunol 184(5):2593–2601. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0902378
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11010_2012_1365_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Figure S1. Expression of NLK gene in GBC cell lines, GBC-SD and SGC-996. A. Analysis of NLK mRNA in both GBC cell lines by using quantitative real-time PCR assay. B. Analysis of NLK protein in both GBC cell lines by using western blot assay. (TIFF 227 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, Z., Li, M., Wu, W. et al. NLK is a key regulator of proliferation and migration in gallbladder carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biochem 369, 27–33 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1365-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1365-0