Abstract
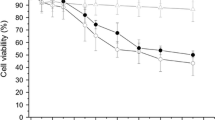
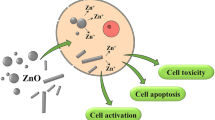
There is an ongoing concern regarding the biocompatibility of nanoparticles with sizes less than 100 nm as compared to larger particles of the same nominal substance. In this study, we investigated the toxic properties of magnetite stabilized with polyacrylate sodium. The magnetite was characterized by X-ray powder diffraction analysis, and the mean particle diameter was calculated using the Scherrer formula and was found to be 9.3 nm. In this study, we treated lung epithelial cells with different concentrations of magnetite and investigated their effects on oxidative stress and cell proliferation. Our data showed an inhibition of cell proliferation in magnetite-treated cells with a significant dose-dependent activation and induction of reactive oxygen species. Also, we observed a depletion of antioxidants, glutathione, and superoxide dismutase, respectively, as compared with control cells. In addition, apoptotic-related protease/enzyme such as caspase-3 and -8 activities, were increased in a dose-dependent manner with corresponding increased levels of DNA fragmentation in magnetite-treated cells compared to than control cells. Together, the present study reveals that magnetite exposure induces oxidative stress and depletes antioxidant levels in the cells to stimulate apoptotic pathway for cell death.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oberdorster G, Oberdorster E, Oberdorster J (2005) Nanotoxicology: an emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ Health Perspect 113:823–839
Salata OV (2004) Applications of nanoparticles in biology and medicine. J Nanobiotechnol 2:3
Inoue K, Takano H, Yanagisawa R et al (2005) Effects of airway exposure to nanoparticles on lung inflammation induced by bacterial endotoxin in mice. Environ Health Perspect 114:1325–1330
Olbrich C, Scholer N, Tabatt K, kayser O, Muller RH (2004) Cytotoxicity studies of Dynasan 114 solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) on RAW 264.7 macrophages impact of phagocytosis on viability and cytokine production. J Pharm Pharmacol 56:883–891
Shvedova AA, Kisin ER, Mercer R, Murray AR, Johnson VJ et al (2005) Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 289:L698–L708
Berry CC, Wells S, Charles S, Curtis ASG (2003) Dextran and albumin derivatised iron oxide nanoparticles: influence on fibroblasts in vitro. Biomaterials 24:4551–4557
Lacava LM, Lacava ZGM, Da Silva MF, Silva O, Chaves SB, Azevedo RB (2001) Magnetic resonance of a dextrancoated magnetic fluid intravenously administered in mice. Biophys J 80:2483–2486
Gupta AK, Curtis AS (2004) Surface modified superparamagnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery: interaction studies with human fibroblasts in culture. J Mater Sci Mater Med 15(4):493–496
Shubayev VI, Pisanic TR, Jin S (2009) Magnetic nanoparticles for theragnostics. Adv Drug Delivery Rev 61:467–477
Cornelis K, Hurlburt CS (1977) Manual of mineralogy. Wiley, New York
Kwei GH, von Dreele RB, Williams A, Goldstone JA, Lawson AC II, Warburton WK (1990) Structure and valence from complementary anomalous X-ray and neutron powder diffraction. J Molecul Struct 223:383–406
Perez JM, Simeone FJ, Saeki Y, Josephson L, Weissleder R (2003) Viral induced self-assembly of magnetic nanoparticles allows the detection of viral particles in biological media. J Am Chem Soc 125:10192–10193
Song Q, Zhang ZJ (2004) Shape control and associated magnetic properties of spinel cobalt ferrite nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 126:6164–6168
Li W, Ma N, Ong LL et al (2008) Enhanced thoracic gene delivery by magnetic nanobead-mediated vector. J Gene Med 10:897–909
Kim JS, Yoon TJ, Yu KN, Kim BG, Park SJ, Kim HW (2006) Toxicity and tissue distribution of magnetic nanoparticles in mice. Toxicol Sci 89:338–347
Hafeli UO, Pauer GJ (1999) In vitro and in vivo toxicity of magnetic microspheres. J Magn Magn Mater 194:76–82
Garcia MP, Parca RM, Chaves SB, Silva LP, Santos AD, Lacava ZGM (2005) Morphological analysis of mouse lungs after treatment with magnetite-based magnetic fluid stabilized with DMSA. J Magn Magn Mater 293:277–282
Ravichandran P, Periyakaruppan A, Sadanandan B, Ramesh V, Hall JC, Jejelowo O, Ramesh GT (2009) Induction of apoptosis in rat lung epithelial cells by multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 23:333–334
Manna SK, Sarkar S, Barr J, Wise K, Barrera EV, Jejelowo O, Rice-Ficht AC, Ramesh GT (2005) Single-walled carbon nanotube induces oxidative stress and activates nuclear transcription factor-kappaB in human keratinocytes. Nano Lett 5:1676–1684
Gopikrishnan R, Zhang K, Ravichandran P, Biradar S, Ramesh V, Goornavar V, Jeffers RB, Pradhan A, Hall JC, Baluchamy S, Ramesh GT (2011) Epitaxial growth of the zinc oxide nanorods, their characterization and in vitro biocompatibility studies. J Mater Sci Mater Med. doi 10.1007/s10856-011-4405-5
Sharma CS, Sarkar S, Periyakaruppan A, Barr J, Wise K, Thomas R, Wilson BL, Ramesh GT (2007) Single-walled carbon nanotubes induces oxidative stress in rat lung epithelial cells. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 7:2466–2472
Periakaruppan A, Kumar F, Sarkar S, Sharma CS, Ramesh GT (2007) Uranium induces oxidative stress in lung epithelial cells. Arch Toxicol 81:389–395
Baluchamy S, Ravichandran P, Periakaruppan A, Ramesh V, Hall J, Zhang Y, Gridle S, Wu H, Ramesh GT (2010) Induction of cell death through alteration of oxidants and antioxidants in lung epithelial cells exposed to high energy protons. J Biol Chem 285:24769–24774
Periyakaruppan A, Sarkar S, Ravichandran P, Sadanandan B, Sharma CS, Ramesh V, Hall JC, Thomas R, Wilson BL, Ramesh GT (2009) Uranium induces apoptosis in lung epithelial cells. Arch Toxicol 83:595–600
Ravichandran P, Baluchamy S, Sadanandan B, Gopikrishnan R, Biradar S, Ramesh V, Hall JC, Ramesh GT (2010) Multiwalled carbon nanotubes activate NF-кB and AP-1 signaling pathways to induce apoptosis in rat lung epithelial cells. Apoptosis 15:1507–1516
Itoh H, Sugimoto T (2003) Systematic control of size, shape, structure, and magnetic properties of uniform magnetite and maghemite particles. J Colloid Interface Sci 265:283–295
Voit W, Kim DK, Zapka W, Muhammed M, Rao KV (2001) Magnetic behavior of coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in ferrofluids. Mater Res Soc 676:781–786
Huang M, Khor E, Lim LY (2004) Uptake and cytotoxicity of chitosan molecules and nanoparticles: effects of molecular weight and degree of deacetylation. Pharm Res 21:344–353
Warheit DB (2004) Nanoparticles: Health impacts? Mater Today 7:32–35
Nel A, Xia T, Li N (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311:622–627
Berry CC, Wells S, Charles S, Aitchison G, Curtis AS (2004) Cell response to dextran and albumin derivatised iron oxide nanoparticles post internalization. Biomaterials 25:5405–5413
Apopa PL, Qian Y, Shao R, Guo NL, Schwegler-Berry D, Pacurari M, Porter D, Shi X, Vallyathan V, Castranova V, Flynn DC (2009) Iron oxide nanoparticles induce human microvascular endothelial cell permeability through reactive oxygen species production and microtubule remodeling. Part Fibre Toxicol 6:1
Manna SK, Rangasamy T, Wise K, Sarkar S, Shishodia S, Biswal S, Ramesh GT (2006) Long term environmental tobacco smoke activates nuclear transcription factor-kappa B, activator protein-1, and stress responsive kinases in mouse brain. Biochem Pharmacol 71:1602–1609
Rice-Evans C, Burdon R (1993) Free radical-lipid interactions and their pathological consequences. Prog Lipid Res 32:71–110
Riley PA (1994) Free radicals in biology: oxidative stress and the effects of ionizing radiation. Int J Radiat Biol 65:27–33
Podia M, Grundmann-Kollmann M (2001) Low molecular weight antioxidants and their role in skin ageing. Clin Exp Dermatol 26:578–582
Sardesai VM (1995) Role of antioxidants in health maintenance. Nutr Clin Pract 10:19–25
Zhao Y, Kiningham KK, Lin SM, St Clair DK (2001) Over expression of MnSOD protects murine fibrosarcoma cells (FSa-II) from apoptosis and promotes a differentiation program upon treatment with 5-Azacytidine: involvement of MAPK and NFκB Pathways. Antioxid Redox Signal 3:375–386
Dominguez-Rodriguez IR, Gomez-Contreras PC, Hernandez-Flores G, Lerma-Diaz JM, Carranco A, Cervantes-Munguia R, Orbach-Arbouys S, Bravo-Cuella A (2001) In vivo inhibition by antioxidants of adriamycin-induced apoptosis in murine peritoneal macrophages. Anti Cancer Res 21:1869–1872
Shi YG (2002) Mechanisms of caspase activation and inhibition during apoptosis. Mol Cell 9:459–470
Nicholson DW, Ali A, Thornberry NA, Vaillancourt JP, Ding CK, Gallant M, Gareau Y, Griffin PR, Labelle M, Lazebnik YA, Munday NA, Raju SM, Smulson ME, Yamin TT, Yu VL, Miller DK (1995) Identification and inhibition of the ICE/CED-3 protease necessary for mammalian apoptosis. Nature 376:37–43
Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ (2004) Cell death: critical control points. Cell 116(2):205–219
Patlolla A, Patlolla B, Tchounwou P (2010) Evaluation of cell viability, DNA damage, and cell death in normal human dermal fibroblast cells induced by functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Mol Cell Biochem 338:225–232
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by NIH funding NIH 1P20MD001822-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1596-8.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramesh, V., Ravichandran, P., Copeland, C.L. et al. Magnetite induces oxidative stress and apoptosis in lung epithelial cells. Mol Cell Biochem 363, 225–234 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1174-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1174-x