Abstract
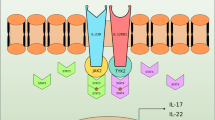
Cytokine-mediated immunity plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of various autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Increasing evidence has revealed the importance of IL-23, which closely resembles IL-12 structurally and immunologically, in linking innate and adaptive immunity. IL-23, a newly identified heterodimeric pro-inflammatory cytokine, is composed of a p40 subunit in common with IL-12 and a unique p19 subunit. Recent evidence suggests that IL-23, rather than IL-12, is the crucial factor in the pathogenesis of various immune-mediated disorders. In addition, recent studies have explored the role of IL-23 in patients with RA. An elevated expression of IL-23 has been demonstrated in the synovial fibroblasts and plasma of patients with RA. Moreover, an association between IL-23 and IL-23R polymorphisms with susceptibility to RA has been reported. Therefore, the targeting of IL-23 or the IL-23 receptor has been proposed as a potential therapeutic approach for RA. In this review we will discuss the biological features of IL-23, and summarize recent advances in our understanding of the role of IL-23 in the pathogenesis and treatment of RA.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li X, Yuan FL, Lu WG, Zhao YQ, Li CW, Li JP, Xu RS (2010) The role of interleukin-17 in mediating joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 397:131–135
Partsch G, Steiner G, Leeb BF, Dunky A, Broll H, Smolen JS (1997) Highly increased levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and other proinflammatory cytokines in psoriatic arthritis synovial fluid. J Rheumatol 24:518–523
Steiner G, Tohidast-Akrad M, Witzmann G, Vesely M, Studnicka-Benke A, Gal A, Kunaver M, Zenz P, Smolen JS (1999) Cytokine production by synovial T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 38:202–213
Firestein GS, Alvaro-Gracia JM, Maki R (1990) Quantitative analysis of cytokine gene expression in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol 144:3347–3353
Popa C, van Tits LJ, Barrera P, Lemmers HL, van den Hoogen FH, van Riel PL, Radstake TR, Netea MG, Roest M, Stalenhoef AF (2009) Anti-inflammatory therapy with tumour necrosis factor alpha inhibitors improves high-density lipoprotein cholesterol antioxidative capacity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Ann Rheum Dis 68:868–872
Suzuki H, Ayabe T, Kamimura J, Kashiwagi H (1991) Anti-IL-1 alpha autoantibodies in patients with rheumatic diseases and in healthy subjects. Clin Exp Immunol 85:407–412
Patel AM, Moreland LW (2010) Interleukin-6 inhibition for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a review of tocilizumab therapy. Drug Des Devel Ther 4:263–278
Nuki G, Bresnihan B, Bear MB, McCabe D (2002) Long-term safety and maintenance of clinical improvement following treatment with anakinra (recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: extension phase of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 46:2838–2846
Wolfe F, Michaud K (2004) Lymphoma in rheumatoid arthritis: the effect of methotrexate and anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in 18, 572 patients. Arthritis Rheum 50:1740–1751
Ooi JD, Phoon RK, Holdsworth SR, Kitching AR (2009) IL-23, not IL-12, directs autoimmunity to the Goodpasture antigen. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:980–989
Brentano F, Ospelt C, Stanczyk J, Gay RE, Gay S, Kyburz D (2009) Abundant expression of the interleukin (IL)23 subunit p19, but low levels of bioactive IL23 in the rheumatoid synovium: differential expression and Toll-like receptor-(TLR) dependent regulation of the IL23 subunits, p19 and p40, in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 68:143–150
Di Meglio P, Di Cesare A, Laggner U, Chu CC, Napolitano L, Villanova F, Tosi I, Capon F, Trembath RC, Peris K, Nestle FO (2011) The IL23R R381Q gene variant protects against immune-mediated diseases by impairing IL-23-induced Th17 effector response in humans. PLoS One 6:e17160
Cargill M, Schrodi SJ, Chang M, Garcia VE, Brandon R, Callis KP, Matsunami N, Ardlie KG, Civello D, Catanese JJ, Leong DU, Panko JM, McAllister LB, Hansen CB, Papenfuss J, Prescott SM, White TJ, Leppert MF, Krueger GG, Begovich AB (2007) A large-scale genetic association study confirms IL12B and leads to the identification of IL23R as psoriasis-risk genes. Am J Hum Genet 80:273–290
Duerr RH, Taylor KD, Brant SR, Rioux JD, Silverberg MS, Daly MJ, Steinhart AH, Abraham C, Regueiro M, Griffiths A, Dassopoulos T, Bitton A, Yang H, Targan S, Datta LW, Kistner EO, Schumm LP, Lee AT, Gregersen PK, Barmada MM, Rotter JI, Nicolae DL, Cho JH (2006) A genome-wide association study identifies IL23R as an inflammatory bowel disease gene. Science 314:1461–1463
Izcue A, Hue S, Buonocore S, Arancibia-Carcamo CV, Ahern PP, Iwakura Y, Maloy KJ, Powrie F (2008) Interleukin-23 restrains regulatory T cell activity to drive T cell-dependent colitis. Immunity 28:559–570
Aggarwal S, Ghilardi N, Xie MH, de Sauvage FJ, Gurney AL (2003) Interleukin-23 promotes a distinct CD4 T cell activation state characterized by the production of interleukin-17. J Biol Chem 278:1910–1914
Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein WM, Mattson J, Basham B, Sedgwick JD, McClanahan T, Kastelein RA, Cua DJ (2005) IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med 201:233–240
Bettelli E, Korn T, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK (2008) Induction and effector functions of T(H)17 cells. Nature 453:1051–1057
Wendling D (2008) Interleukin 23: a key cytokine in chronic inflammatory disease. Joint Bone Spine 75:517–519
Kageyama Y, Kobayashi H, Kato N (2009) Infliximab treatment reduces the serum levels of interleukin-23 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol 19:657–662
Goriely S, Goldman M (2008) Interleukin-12 family members and the balance between rejection and tolerance. Curr Opin Organ Transplant 13:4–9
Oppmann B, Lesley R, Blom B, Timans JC, Xu Y, Hunte B, Vega F, Yu N, Wang J, Singh K, Zonin F, Vaisberg E, Churakova T, Liu M, Gorman D, Wagner J, Zurawski S, Liu Y, Abrams JS, Moore KW, Rennick D, de Waal-Malefyt R, Hannum C, Bazan JF, Kastelein RA (2000) Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity 13:715–725
Lupardus PJ, Garcia KC (2008) The structure of interleukin-23 reveals the molecular basis of p40 subunit sharing with interleukin-12. J Mol Biol 382:931–941
Yoshida A, Koide Y, Uchijima M, Yoshida TO (1994) IFN-gamma induces IL-12 mRNA expression by a murine macrophage cell line, J774. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 198:857–861
Langrish CL, McKenzie BS, Wilson NJ, de Waal Malefyt R, Kastelein RA, Cua DJ (2004) IL-12 and IL-23: master regulators of innate and adaptive immunity. Immunol Rev 202:96–105
Bettelli E, Kuchroo VK (2005) IL-12- and IL-23-induced T helper cell subsets: birds of the same feather flock together. J Exp Med 201:169–171
Harrington LE, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, Turner H, Murphy TL, Murphy KM, Weaver CT (2005) Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat Immunol 6:1123–1132
McKenzie BS, Kastelein RA, Cua DJ (2006) Understanding the IL-23-IL-17 immune pathway. Trends Immunol 27:17–23
Iwakura Y, Ishigame H (2006) The IL-23/IL-17 axis in inflammation. J Clin Invest 116:1218–1222
Beadling C, Slifka MK (2006) Regulation of innate and adaptive immune responses by the related cytokines IL-12, IL-23, and IL-27. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 54:15–24
Kastelein RA, Hunter CA, Cua DJ (2007) Discovery and biology of IL-23 and IL-27: related but functionally distinct regulators of inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol 25:221–242
van de Vosse E, Lichtenauer-Kaligis EG, van Dissel JT, Ottenhoff TH (2003) Genetic variations in the interleukin-12/interleukin-23 receptor (beta1) chain, and implications for IL-12 and IL-23 receptor structure and function. Immunogenetics 54:817–829
Parham C, Chirica M, Timans J, Vaisberg E, Travis M, Cheung J, Pflanz S, Zhang R, Singh KP, Vega F, To W, Wagner J, O’Farrell AM, McClanahan T, Zurawski S, Hannum C, Gorman D, Rennick DM, Kastelein RA, de Waal Malefyt R, Moore KW (2002) A receptor for the heterodimeric cytokine IL-23 is composed of IL-12Rbeta1 and a novel cytokine receptor subunit, IL-23R. J Immunol 168:5699–5708
Fitch E, Harper E, Skorcheva I, Kurtz SE, Blauvelt A (2007) Pathophysiology of psoriasis: recent advances on IL-23 and Th17 cytokines. Curr Rheumatol Rep 9:461–467
Zhang Z, Andoh A, Yasui H, Inatomi O, Hata K, Tsujikawa T, Kitoh K, Takayanagi A, Shimizu N, Fujiyama Y (2005) Interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha upregulate interleukin-23 subunit p19 gene expression in human colonic subepithelial myofibroblasts. Int J Mol Med 15:79–83
Liu FL, Chen CH, Chu SJ, Chen JH, Lai JH, Sytwu HK, Chang DM (2007) Interleukin (IL)-23 p19 expression induced by IL-1beta in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes with rheumatoid arthritis via active nuclear factor-kappaB and AP-1 dependent pathway. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46:1266–1273
Sheibanie AF, Khayrullina T, Safadi FF, Ganea D (2007) Prostaglandin E2 exacerbates collagen-induced arthritis in mice through the inflammatory interleukin-23/interleukin-17 axis. Arthritis Rheum 56:2608–2619
Lankford CS, Frucht DM (2003) A unique role for IL-23 in promoting cellular immunity. J Leukoc Biol 73:49–56
Harrington LE, Mangan PR, Weaver CT (2006) Expanding the effector CD4 T-cell repertoire: the Th17 lineage. Curr Opin Immunol 18:349–356
Yang XO, Panopoulos AD, Nurieva R, Chang SH, Wang D, Watowich SS, Dong C (2007) STAT3 regulates cytokine-mediated generation of inflammatory helper T cells. J Biol Chem 282:9358–9363
Paradowska-Gorycka A, Grzybowska-Kowalczyk A, Wojtecka-Lukasik E, Maslinski S (2010) IL-23 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Immunol 71:134–145
Tan ZY, Bealgey KW, Fang Y, Gong YM, Bao S (2009) Interleukin-23: immunological roles and clinical implications. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:733–735
Sato K, Suematsu A, Okamoto K, Yamaguchi A, Morishita Y, Kadono Y, Tanaka S, Kodama T, Akira S, Iwakura Y, Cua DJ, Takayanagi H (2006) Th17 functions as an osteoclastogenic helper T cell subset that links T cell activation and bone destruction. J Exp Med 203:2673–2682
Wiekowski MT, Leach MW, Evans EW, Sullivan L, Chen SC, Vassileva G, Bazan JF, Gorman DM, Kastelein RA, Narula S, Lira SA (2001) Ubiquitous transgenic expression of the IL-23 subunit p19 induces multiorgan inflammation, runting, infertility, and premature death. J Immunol 166:7563–7570
Belladonna ML, Renauld JC, Bianchi R, Vacca C, Fallarino F, Orabona C, Fioretti MC, Grohmann U, Puccetti P (2002) IL-23 and IL-12 have overlapping, but distinct, effects on murine dendritic cells. J Immunol 168:5448–5454
Murphy CA, Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein W, McClanahan T, Kastelein RA, Sedgwick JD, Cua DJ (2003) Divergent pro- and antiinflammatory roles for IL-23 and IL-12 in joint autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med 198:1951–1957
Kim HR, Cho ML, Kim KW, Juhn JY, Hwang SY, Yoon CH, Park SH, Lee SH, Kim HY (2007) Up-regulation of IL-23p19 expression in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts by IL-17 through PI3-kinase-, NF-kappaB- and p38 MAPK-dependent signalling pathways. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46:57–64
Kim HR, Kim HS, Park MK, Cho ML, Lee SH, Kim HY (2007) The clinical role of IL-23p19 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol 36:259–264
Ju JH, Cho ML, Moon YM, Oh HJ, Park JS, Jhun JY, Min SY, Cho YG, Park KS, Yoon CH, Min JK, Park SH, Sung YC, Kim HY (2008) IL-23 induces receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand expression on CD4+ T cells and promotes osteoclastogenesis in an autoimmune arthritis model. J Immunol 181:1507–1518
Rasmussen TK, Andersen T, Hvid M, Hetland ML, Horslev-Petersen K, Stengaard-Pedersen K, Holm CK, Deleuran B (2010) Increased interleukin 21 (IL-21) and IL-23 are associated with increased disease activity and with radiographic status in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 37:2014–2020
Melis L, Vandooren B, Kruithof E, Jacques P, De Vos M, Mielants H, Verbruggen G, De Keyser F, Elewaut D (2010) Systemic levels of IL-23 are strongly associated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis but not spondylarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 69:618–623
Farago B, Magyari L, Safrany E, Csongei V, Jaromi L, Horvatovich K, Sipeky C, Maasz A, Radics J, Gyetvai A, Szekanecz Z, Czirjak L, Melegh B (2008) Functional variants of interleukin-23 receptor gene confer risk for rheumatoid arthritis but not for systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 67:248–250
Orozco G, Rueda B, Robledo G, Garcia A, Martin J (2007) Investigation of the IL23R gene in a Spanish rheumatoid arthritis cohort. Hum Immunol 68:681–684
Park JH, Kim YJ, Park BL, Bae JS, Shin HD, Bae SC (2009) Lack of association between interleukin 23 receptor gene polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility. Rheumatol Int 29:781–786
Yago T, Nanke Y, Kawamoto M, Furuya T, Kobashigawa T, Kamatani N, Kotake S (2007) IL-23 induces human osteoclastogenesis via IL-17 in vitro, and anti-IL-23 antibody attenuates collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Arthritis Res Ther 9:R96
Kageyama Y, Ichikawa T, Nagafusa T, Torikai E, Shimazu M, Nagano A (2007) Etanercept reduces the serum levels of interleukin-23 and macrophage inflammatory protein-3 alpha in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 28:137–143
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the China National Science Foundation Grants No. 30873080.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rong, C., Hu, W., Wu, Fr. et al. Interleukin-23 as a potential therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Cell Biochem 361, 243–248 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1109-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1109-6