Abstract
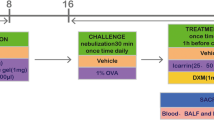
Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) is known to produce nitric oxide (NO), which is a main contributor to asthmatic airway inflammation. Recent studies have shown that phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) is ubiquitously expressed in airway epithelial cells and its inhibition could relieve airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness. This study aimed to explore the interaction of PI3K and NO signaling in allergic asthma. We investigated the effects of PI3K inhibitor wortmannin on iNOS expression in bronchiole epithelial cells and NO, IL-4 and IFN-γ levels in lung tissues of asthmatic rat model, which was prepared by 10% OVA solution sensitization and 1% OVA aerosol challenge. Our results showed that the ratio of eosinophils to total cells in BALF, PI3K activity, NO and IL-4 levels in lung tissues was increased after OVA sensitization and challenge, but then was attenuated by the administration of wortmannin. In contrast, IFN-γ level in lung tissues was decreased after OVA sensitization and challenge and increased after the administration of wortmannin. The expression of iNOS protein in bronchiole epithelial cells, iNOS mRNA level and iNOS activity in lung tissues was markedly upregulated after OVA sensitization and challenge, but the upregulation was significantly antagonized by wortmannin. Taken together, these data provide evidence that PI3K functions upstream to modulate iNOS/NO signaling, which then promotes the development of airway inflammation in asthmatic animal model. PI3K inhibitor wortmannin could lead to reduced iNOS expression and NO production, therefore inhibiting airway inflammatory responses.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coccia EM, Stellacci E, Marziali G et al (2000) IFN-gamma and IL-4 differently regulate inducible NO synthase gene expression through IRF-1 modulation. Int Immunol 12:977–985
Prado CM, Leick-Maldonado EA, Yano L et al (2006) Effects of nitric oxide synthases in chronic allergic airway inflammation and remodeling. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 35:457–465
Kharitonov SA, Yates D, Robbins RA et al (1994) Increased nitric oxide in exhaled air of asthmatic patients. Lancet 343:133–135
Steudel W, Kirmse M, Weimann J et al (2000) Exhaled nitric oxide production by nitric oxide synthase-deficient mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 162:1262–1267
Eynott PR, Paavolainen N, Groneberg DA et al (2003) Role of nitric oxide in chronic allergen-induced airway cell proliferation and inflammation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 304:22–29
Vanhaesebroeck B, Ali K, Bilancio A et al (2005) Signalling by PI3K isoforms: insights from gene-targeted mice. Trends Biochem Sci 30:194–204
Chantry D, Vojtek A, Kashishian A et al (1997) p110delta, a novel phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase catalytic subunit that associates with p85 and is expressed predominantly in leukocytes. J Biol Chem 272:19236–19241
Krymskaya VP, Ammit AJ, Hoffman RK et al (2001) Activation of class IA PI3K stimulates DNA synthesis in human airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 280:L1009–L1018
Ito K, Caramori G, Adcock IM (2007) Therapeutic potential of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors in inflammatory respiratory disease. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 321:1–8
Takeda M, Ito W, Tanabe M et al (2010) The pathophysiological roles of PI3Ks and therapeutic potential of selective inhibitors in allergic inflammation. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 152:90–95
Thomas M, Owen C (2008) Inhibition of PI-3 kinase for treating respiratory disease: good idea or bad idea? Curr Opin Pharmacol 8:267–274
Duan W, Aguinaldo Datiles AM, Leung BP et al (2005) An anti-inflammatory role for a phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor LY294002 in a mouse asthma model. Int Immunopharmacol 5:495–502
Ezeamuzie CI, Sukumaran J, Philips E (2001) Effect of wortmannin on human eosinophil responses in vitro and on bronchial inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in rats in vivo. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164:1633–1639
Lee KS, Lee HK, Hayflick JS et al (2006) Inhibition of phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta attenuates allergic airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness in murine asthma model. FASEB J 20:455–465
Xiong Y, Karupiah G, Hogan SP et al (1999) Inhibition of allergic airway inflammation in mice lacking nitric oxide synthase 2. J Immunol 162:445–452
De Sanctis GT, MacLean JA, Hamada K et al (1999) Contribution of nitric oxide synthases 1, 2, and 3 to airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in a murine model of asthma. J Exp Med 189:1621–1630
Donnelly LE, Barnes PJ (2002) Expression and regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase from human primary airway epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 26:144–151
Jiang J, Malavia N, Suresh V et al (2009) Nitric oxide gas phase release in human small airway epithelial cells. Respir Res 10:24–31
Takemoto K, Ogino K, Shibamori M et al (2007) Transiently, paralleled upregulation of arginase and nitric oxide synthase and the effect of both enzymes on the pathology of asthma. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 293:L1419–L1426
Schedel M, Pinto LA, Schaub B et al (2008) IRF-1 gene variations influence IgE regulation and atopy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 177:613–621
Dai R, Phillips RA, Karpuzoglu E et al (2009) Estrogen regulates transcription factors STAT-1 and NF-kappaB to promote inducible nitric oxide synthase and inflammatory responses. J Immunol 183:6998–7005
Bratt JM, Franzi LM, Linderholm AL et al (2009) Arginase enzymes in isolated airways from normal and nitric oxide synthase 2-knockout mice exposed to ovalbumin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 234:273–280
Feder LS, Stelts D, Chapman RW et al (1997) Role of nitric oxide on eosinophilic lung inflammation in allergic mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 17:436–442
Kang YJ, Lee YS, Lee GW et al (1999) Inhibition of activation of nuclear factor kappaB is responsible for inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression by higenamine, an active component of aconite root. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 291:314–320
Khanduja KL, Kaushik G, Khanduja S et al (2011) Corticosteroids affect nitric oxide generation, total free radicals production, and nitric oxide synthase activity in monocytes of asthmatic patients. Mol Cell Biochem 346:31–37
Kwak YG, Song CH, Yi HK et al (2003) Involvement of PTEN in airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in bronchial asthma. J Clin Invest 111:1083–1092
Myou S, Leff AR, Myo S et al (2003) Blockade of inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in immune-sensitized mice by dominant-negative phosphoinositide 3-kinase-TAT. J Exp Med 198:1573–1582
Tigani B, Hannon JP, Mazzoni L et al (2000) Effects of wortmannin on bronchoconstrictor responses to adenosine in actively sensitised Brown Norway rats. Eur J Pharmacol 406:469–476
Marwick JA, Chung KF, Adcock IM (2010) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase isoforms as targets in respiratory disease. Ther Adv Respir Dis 4:19–34
Hattori Y, Hattori S, Kasai K (2003) Lipopolysaccharide activates Akt in vascular smooth muscle cells resulting in induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase through nuclear factor-kappa B activation. Eur J Pharmacol 481:153–158
Pinho V, Souza DG, Barsante MM et al (2005) Phosphoinositide-3 kinases critically regulate the recruitment and survival of eosinophils in vivo: importance for the resolution of allergic inflammation. J Leukoc Biol 77:800–810
Kao SJ, Lei HC, Kuo CT et al (2005) Lipoteichoic acid induces nuclear factor-kappaB activation and nitric oxide synthase expression via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, Akt, and p38 MAPK in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Immunology 115:366–374
Sakai K, Suzuki H, Oda H et al (2006) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase in nitric oxide synthesis in macrophage: critical dimerization of inducible nitric-oxide synthase. J Biol Chem 281:17736–17742
Kuroda E, Antignano F, Ho VW et al (2011) SHIP represses Th2 skewing by inhibiting IL-4 production from basophils. J Immunol 186:323–332
Kristof AS, Fielhaber J, Triantafillopoulos A et al (2006) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent suppression of the human inducible nitric-oxide synthase promoter is mediated by FKHRL1. J Biol Chem 281:23958–23968
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by a grant from the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Y2080466).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, X., Hu, X., Xu, H. et al. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor suppresses inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in bronchiole epithelial cells in asthmatic rats. Mol Cell Biochem 359, 293–299 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1023-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1023-y